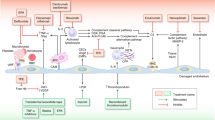
Abstract
Transplant associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) is life-threatening complication post allogeneic stem cell transplant (ASCT). Risk factors and prognosis of TA-TMA are not well defined. We retrospectively studied consecutive ASCT patients with AML, ALL, and CML from January 2008 to March 2019 to study the incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of TMA. Definitive and probable TA-TMA was defined using Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT-CTN) and Cho criteria, respectively. Risk factors explored were age, gender, diagnosis, type of transplant, use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) pre transplant, conditioning regimen, and acute GVHD. Standard statistical methods were used. Total 241 patients, 179 (74.2 %) males, median age of 29 years were studied. Diagnoses were AML in 104, ALL in 85 (Ph+ve 23) and CML 52. Total 26 (10.7%) patients (22 males) developed TA-TMA at median of day+102. On multivariate analysis, pre-HSCT TKI (OR 2.7, p = 0.028), haplo-HSCT (OR 3.16, p = 0.018) and presence of acute GVHD (OR 4.17, p = 0.003) were significant risk factors. With a median follow up of 60 months, median OS with and without TA-TMA was 18 and 97 months respectively (p = 0.021). The association of pre-HSCT with TKI with TA-TMA merits further exploration in prospective studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khosla J, Yeh AC, Spitzer TR, Dey BR. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: current paradigm and novel therapies. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2018;53:129–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2017.207.
Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Jodele S. Small vessels, big trouble in the kidneys and beyond: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood. 2011;118:1452–62. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-02-321315.
Uderzo C, Bonanomi S, Busca A, Renoldi M, Ferrari P, Iacobelli M, et al. Risk factors and severe outcome in thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2006;82:638–44.
Ho VT, Cutler C, Carter S, Martin P, Adams R, Horowitz M, et al. Blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network toxicity committee consensus summary: thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:571–5.
Ruutu T, Barosi G, Benjamin RJ, Clark RE, George JN, Gratwohl A, et al. Diagnostic criteria for hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated microangiopathy: results of a consensus process by an International Working Group. Haematologica. 2007;92:95–100.
Cho BS, Min CK, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Lee S. et al. Clinical impact of thrombotic microangiopathy on the outcome of patients with acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008;41:813–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705976.
Cho BS, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ. et al. Validation of recently proposed consensus criteria for thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation . 2010;90:918–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181f24e8d.
Thachil J. Nitric oxide in transplantation-related thrombotic microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2009;43:513–4.
Ricklin D, Cines DB. TMA: beware of complements. Blood. 2013;122:1997–9.
Dhakal P, Bhatt VR. Is complement blockade an acceptable therapeutic strategy for hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy? Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:352–6.
Jodele S, Laskin B, Fukuda T, Vinks A, Mizuno K, Goebel J, et al. Eculizumab treatment improves survival in patients with high-risk hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015;21:S225–S226.
Pasvolsky O, Leader A, Iakobishvili Z, Wasserstrum Y, Kornowski R, Raanani P. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor associated vascular toxicity in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cardio Oncol. 2015;1:5 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40959-015-0008-5.
Guignabert C, Phan C, Seferian A, Huertas A, Tu L, Thuillet R. et al. Dasatinib induces lung vascular toxicity and predisposes to pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3207–18. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI86249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Punatar, S., Kalantri, S.A., Chichra, A. et al. Pre-transplant use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and transplant associated thrombotic microangiopathy - a single centre analysis of incidence, risk factors and outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 1558–1562 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01213-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01213-0
This article is cited by
-
Sorafenib
Reactions Weekly (2021)