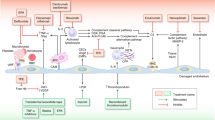
Abstract
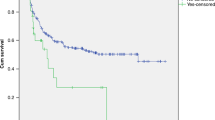
Terminal complement blockade by humanised monoclonal antibody eculizumab has been used to treat transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) in recent years. This retrospective international study conducted by the Paediatric Diseases (PDWP) and Inborn Error Working Party (IEWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) describes outcome and response of 82 paediatric patients from 29 centres who developed TA-TMA and were treated with eculizumab between January 2014 and May 2019. The median time from hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) to TA-TMA manifestation was 92 days (range: 7–606) and from TA-TMA diagnosis to the start of eculizumab treatment 6 days (range: 0–135). Most patients received eculizumab weekly (72%, n = 55) with a standard weight (kg)-based dose (78%, n = 64). Six months from beginning of eculizumab therapy, the cumulative incidence of TA-TMA resolution was 36.6% (95% CI: 26.2–47) and the overall survival (OS) was 47.1% (95% CI: 35.9–57.5). All 43 patients with unresolved TA-TMA died. The cause of death was HSCT-related in 41 patients. This study also documents poor outcome of patients without aGvHD and their frequent concomitant viral infections. Considering recent publications, intensified eculizumab dosing and complement monitoring could potentially improve upon outcomes observed in this study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No research-supporting data are shared in a public repository.
References
Jodele S, Fukuda T, Vinks A, Mizuno K, Laskin BL, Goebel J, et al. Eculizumab therapy in children with severe hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2014;20:518–25.
Jodele S. Complement in pathophysiology and treatment of transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathies. Semin Hematol. 2018;55:159–66.
Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Jodele S. Small vessels, big trouble in the kidneys and beyond: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood. 2011;118:1452–62.
Jodele S. Variable eculizumab clearance requires pharmacodynamic monitoring to optimize therapy for thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:307–15.
Dhakal P, Giri S, Pathak R, Bhatt VR. Eculizumab in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Clin Appl Thromb. 2017;23:175–80.
Jodele S, Zhang K, Zou F, Laskin B, Dandoy CE, Myers KC, et al. The genetic fingerprint of susceptibility for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood. 2016;127:989–96.
Gavriilaki E, Touloumenidou T, Sakellari I, Batsis I, Mallouri D, Psomopoulos F, et al. Pretransplant genetic susceptibility: clinical relevance in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:638–46.
Cho BS, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, et al. Validation of recently proposed consensus criteria for thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2010;90:918–26.
Kraft S, Bollinger N, Bodenmann B, Heim D, Bucher C, Lengerke C, et al. High mortality in hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy with and without concomitant acute graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:540–8.
Elfeky R, Lucchini G, Lum S-H, Ottaviano G, Builes N, Nademi Z, et al. New insights into risk factors for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in pediatric HSCT. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2418–29.
Schoettler M, Lehmann LE, Margossian S, Lee M, Kean LS, Kao PC, et al. Risk factors for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy and mortality in a pediatric cohort. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2536–47.
Gavriilaki E, Sakellari I, Karafoulidou I, Pasteli N, Batsis I, Mallouri D, et al. Intestinal thrombotic microangiopathy: a distinct entity in the spectrum of graft-versus-host disease. Int J Hematol. 2019;110:529–32.
Dvorak CC, Higham C, Shimano KA. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in pediatric hematopoietic cell transplant recipients: a practical approach to diagnosis and management. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:133.
Rosenthal J. Hematopoietic cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Blood Med. 2016;7:181–6.
Jodele S, Medvedovic M, Luebbering N, Chen J, Dandoy CE, Laskin BL, et al. Interferon-complement loop in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood Adv. 2020;4:1166–77.
Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Lane A, Laskin BL, Teusink-Cross A, Myers KC, et al. Complement blockade for TA-TMA: Lessons learned from a large pediatric cohort treated with eculizumab. Blood. 2020;135:1049–57.
De Fontbrune FS, Galambrun C, Sirvent A, Huynh A, Faguer S, Nguyen S, et al. Use of eculizumab in patients with allogeneic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study from the SFGM-TC. Transplantation. 2015;99:1953–9.
Vasu S, Wu H, Satoskar A, Puto M, Roddy J, Blum W, et al. Eculizumab therapy in adults with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Nat Publ Gr. 2016;51:1241–4.
Bohl SR, Kuchenbauer F, von Harsdorf S, Kloevekorn N, Schönsteiner SS, Rouhi A, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a comparison of eculizumab therapy and conventional therapy. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017;23:2172–7.
Rudoni J, Jan A, Hosing C, Aung F, Yeh J. Eculizumab for transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in adult allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Eur J Haematol. 2018;101:389–98.
Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Myers KC, El-Bietar J, Nelson A, Wallace G, et al. New approaches in the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment of pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Transfus Apher Sci. 2016;54:181–90.
Uderzo C, Sonata J. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) and consensus based diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations: which TA-TMA patients to treat and when? J Bone Marrow Res. 2014;02:157–63.
Ho VT, Cutler C, Carter S, Martin P, Adams R, Horowitz M. et al. Blood and marrow transplant clinical trials network toxicity committee consensus summary: thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;575:571–5.
Ruutu T, Barosi G, Benjamin RJ, Clark RE, George JN, Gratwohl A, et al. Transplant-associated microangiopathy: results of a consensus process by an International Working Group. Haematologica. 2007;92:95–100.
Carreras E, Dufour C, Mohty M, Kroger N. The EBMT Handbook. In: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies. Springer Nature; 2019. p. 99–104.
Benjamini Yoav, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate - a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
Jodele S, Davies SM, Lane A, Khoury J, Dandoy C, Goebel J, et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults. Blood 2014;124:645–53.
Rabinowe SN, Soiffer RJ, Tarbell NJ, Neuberg D, Freedman AS, Seifter J, et al. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome following bone marrow transplantation in adults for hematologic malignancies. Blood. 1991;77:1837–44. PMID: 2015407. Blood. 1991;77:1837–44
George JN, Li X, McMinn JR, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, Selby GB. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome following allogeneic HPC transplantation: a diagnostic dilemma. Transfusion. 2004;44:294–304.
Li A, Wu Q, Davis C, Kirtane KS, Pham PD, Sorror ML, et al. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy is a multifactorial disease unresponsive to immunosuppressant withdrawal. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:570–6.
De Latour RP, Xhaard A, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Coppo P, Fischer AM, Helley D, et al. Successful use of eculizumab in a patient with post-transplant thrombotic microangiopathy. Br J Haematol; 2013;161:279–80.
Jodele S, Licht C, Goebel J, Dixon BP, Zhang K, Sivakumaran TA, et al. Abnormalities in the alternative pathway of complement in children with hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood. 2013;122:2003–7.
Jodele S, Fukuda T, Mizuno K, Vinks AA, Laskin BL, Goebel J, et al. Variable eculizumab clearance requires pharmacodynamic monitoring to optimize therapy for thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:307–15.
Röth A, Nishimura JI, Nagy Z, Gaàl-Weisinger J, Panse J, Yoon SS, et al. The complement C5 inhibitor crovalimab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2020;135:912–20.
Risitano AM, Röth A, Soret J, Frieri C, de Fontbrune FS, Marano L, et al. Addition of iptacopan, an oral factor B inhibitor, to eculizumab in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and active haemolysis: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8:e344–54.
Hillmen P, Szer J, Weitz I, Röth A, Höchsmann B, Panse J, et al. Pegcetacoplan versus eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1028–37.
Harder MJ, Kuhn N, Schrezenmeier H, von Zabern I, Weinstock C, Simmet T. et al. Incomplete inhibition eculizumab: mechanistic Evid residual C5 Act strong complement activation. Blood. 2017;129:970–80.
Uderzo C, Bonanomi S, Busca A, Renoldi M, Ferrari P, Iacobelli M, et al. Risk factors and severe outcome in thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2006;82:638–44.
Cho BS, Min CK, Eom KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Lee S, et al. Clinical impact of thrombotic microangiopathy on the outcome of patients with acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008;41:813–20.
Zeisbrich M, Becker N, Benner A, Radujkovic A, Schmitt K, Beimler J, et al. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy is an endothelial complication associated with refractoriness of acute GvHD. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:1399–405.
Takatsuka H, Wakae T, Mori A, Okada M, Fujimori Y, Takemoto Y, et al. Endothelial damage caused by cytomegalovirus and human herpesvirus-6. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2003;31:475–9.
Haines HL, Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Yin HJ, Lawrence J, et al. Blood, and not urine, BK viral load predicts renal outcome in children with hemorrhagic cystitis following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2011;17:1512–9.
Yeates L, Slatter M, Bonanomi S, Lim W, Ong S, Dalissier A, et al. Use of defibrotide to treat transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy-a retrospective study of the paediatric diseases and inborn errors working parties of EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:S412.
Martínez-Muñoz ME, Forés R, Lario A, Bautista G, Bueno JL, de Miguel C, et al. Use of defibrotide to treat adult patients with transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:142–5.
Harrell FEJ, Lee KL, Califf RM, Pryor DB, Rosati RA. Regression modelling strategies for improved prognostic prediction. Stat Med. 1984;3:143–52.
Acknowledgements
We thank William Boreland for the language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of the work: PS, RE, J-EG, ZP, AL, SC, Data collection: PS, RE, CSH, AD, TCQ, DBS, SHL, MF, TC, HP, MIB-C, JH, MG-V, AY, FF, MW, NvdW, RP, GK, CS, BJ, SLA, YB, MV, PR, KP, SC, KK, MB, JB, KM, BN, Data analysis and interpretation: J-EG, AD, PS, SC, Drafting the article: PS, RE, J-EG, Critical revision of the article: PS, RE, J-EG, CSH, TCQ, HP, MW, CS, BJ, SC, JB, ZP, BN, AL, SC, Final approval of the version to be published: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
TCQ, DO, MS presents educational programs for the diagnosis of thrombotic microangiopathy and paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria on the speaker’s bureau for Alexion Pharmaceuticals. He has no other financial competing interests. DBS provided advisory services for Alexion Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Svec, P., Elfeky, R., Galimard, JE. et al. Use of eculizumab in children with allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation associated thrombotic microangiopathy - a multicentre retrospective PDWP and IEWP EBMT study. Bone Marrow Transplant 58, 129–141 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01852-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01852-x