Abstract
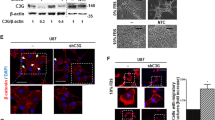
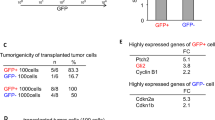
Four-and-a-half LIM protein2 (FHL2) is a member of the LIM-only protein family, which plays a critical role in tumorigenesis. We previously reported that FHL2 is upregulated and plays an oncogenic role in glioblastoma (GBM), the most common and aggressive brain tumor. GBM is also marked by amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene and its mutations, of which EGFRvIII is the most common and functionally significant. Here we report that FHL2 physically interacts with the wild-type EGFR and its mutated EGFRvIII form in GBM cells. Expression of FHL2 caused increased EGFR and EGFRvIII protein levels and this was due to an increase in protein stability rather than an increase in EGFR mRNA expression. In contrast, FHL2 knockdown using RNA interference reduced EGFR and EGFRvIII protein expression and the phosphorylation levels of EGFR and AKT. Consistent with these features, EGFR expression was significantly lower in mouse FHL2-null astrocytes, where reintroduction of FHL2 was able to restore EGFR levels. Using established GBM cell lines and patient-derived neurosphere lines, FHL2 silencing markedly induced cell apoptosis in EGFRvIII-positive cells. Targeting FHL2 significantly prevented EGFRvIII-positive GBM tumor growth in vivo. FHL2 expression also positively correlated with EGFR expression in GBM samples from patients. Taken together, our results demonstrate that FHL2 interacts with EGFR and EGFRvIII to increase their levels and this promotes glioma growth, representing a novel mechanism that may be therapeutically targetable.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96.
Genini M, Schwalbe P, Scholl FA, Remppis A, Mattei MG, Schafer BW. Subtractive cloning and characterization of DRAL, a novel LIM-domain protein down-regulated in rhabdomyosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 1997;16:433–42.
Gabriel B, Fischer DC, Orlowska-Volk M, zurHausen A, Schüle R, Müller JM, et al. Expression of the transcriptional coregulator FHL2 in human breast cancer: a clinic pathologic study. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2006;13:69–75.
Wang J, Yang Y, Xia HH, Gu Q, Lin MC, Jiang B, et al. Suppression of FHL2 expression induces cell differentiation and inhibits gastric and colon carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1066–76.
Hua G, He C, Lv X, Fan L, Wang C, Remmenga SW, et al. The four and a half LIM domains 2 (FHL2) regulates ovarian granulosa cell tumor progression via controlling AKT1 transcription. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2297.
Jin H, Lee K, Kim YH, Oh HK, Maeng YI, Kim TH, et al. Scaffold protein FHL2 facilitates MDM2-mediated degradation of IER3 to regulate proliferation of cervical cancer cells. Oncogene. 2016;35:5106–18.
Nouët Y, Dahan J, Labalette C, Levillayer F, Julien B, Jouvion G, et al. The four and a half LIM-only protein 2 regulates liver homeostasis and contributes to carcinogenesis. J Hepatol. 2012;57:1029–36.
Dahan J, Nouët Y, Jouvion G, Levillayer F, Adib-Conquy M, Cassard-Doulcier AM, et al. LIM-only protein FHL2 activates NF-κB signaling in the control of liver regeneration and hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:3299–308.
Genini M, Schwalbe P, Scholl FA, Remppis A, Mattei MG, Schäfer BW. Subtractive cloning and characterization of DRAL, a novel LIM-domain protein down-regulated in rhabdomyosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 1997;16:433–42.
Verset L, Feys L, Trépant AL, De Wever O, Demetter P. FHL2: a scaffold protein of carcinogenesis, tumour-stroma interactions and treatment response. Histol Histopathol. 2016;31:469–78.
Li M, Wang J, Ng SS, Chan CY, Chen AC, Xia HP, et al. The four-and-a-half-LIM protein 2 (FHL2) is overexpressed in gliomas and associated with oncogenic activities. Glia. 2008;56:1328–38.
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, et al. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:98–110.
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, et al. Malignant astrocyticglioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2683–710.
Del Vecchio CA, Li G, Wong AJ. Targeting EGF receptor variant III: tumor-specific peptide vaccination for malignant gliomas. Expert Rev Vaccin. 2012;11:133–44.
Thorne AH, Zanca C, Furnari F. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting and challenges in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18:914–8.
Thelemann A, Petti F, Griffin G, Iwata K, Hunt T, Settinari T, et al. Phosphotyrosine signaling networks in epidermal growth factor receptor overexpressing squamous carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Proteom. 2005;4:356–76.
Labalette C, Nouët Y, Levillayer F, Armengol C, Renard CA, Soubigou G, et al. LIM-only protein FHL2 mediates ras-induced transformation through cyclin D1 and p53 pathways. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3761.
Purow BW, Sundaresan TK, Burdick MJ, Kefas BA, Comeau LD, Hawkinson MP, et al. Notch-1 regulates transcription of the epidermal growth factor receptor through p53. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:918–25.
Fielitz J, van Rooij E, Spencer JA, Shelton JM, Latif S, van der Nagel R, et al. Loss of muscle-specific RING-finger 3 predisposes the heart to cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:4377–82.
Padfield E, Ellis HP, Kurian KM. Current therapeutic advances targeting EGFR and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 2015;5:5.
Lin SY, Makino K, Xia W, Matin A, Wen Y, Kwong KY, et al. Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:802–8.
Latha K, Li M, Chumbalkar V, Gururaj A, Hwang Y, Dakeng S, et al. Nuclear EGFRvIII-STAT5b complex contributes to glioblastoma cell survival by direct activation of the Bcl-XL promoter. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:509–20.
Hsu SC, Miller SA, Wang Y, Hung MC. Nuclear EGFR is required for cisplatin resistance and DNA repair. Am J Transl Res. 2009;1:249–58.
Liu Z, Han L, Dong Y, Tan Y, Li Y, Zhao M, Xie H, Ju H, Wang H, Zhao Y, Zheng Q, Wang Q, Su J, Fang C, Fu S, Jiang T, Liu J, Li X, Kang C, Ren H. EGFRvIII/integrin β3 interaction in hypoxic and vitronectinenriching microenvironment promote GBM progression and metastasis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:4680–94.
Vouri M, Croucher DR, Kennedy SP, An Q, Pilkington GJ, Hafizi S. Axl-EGFR receptor tyrosine kinase hetero-interaction provides EGFR with access to pro-invasive signalling in cancer cells. Oncogenesis. 2016;5:e266.
Li L, Puliyappadamba VT, Chakraborty S, Rehman A, Vemireddy V, Saha D, et al. EGFR wild type antagonizes EGFRvIII-mediated activation of Met in glioblastoma. Oncogene. 2015;34:129–34.
Jahani-Asl A, Yin H, Soleimani VD, Haque T, Luchman HA, Chang NC, et al. Control of glioblastoma tumorigenesis by feed-forward cytokine signaling. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19:798–806.
Cvrljevic AN, Akhavan D, Wu M, Martinello P, Furnari FB, Johnston AJ, et al. Activation of Src induces mitochondrial localisation of de2-7EGFR (EGFRvIII) in glioma cells: implications for glucose metabolism. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:2938–50.
Zhu H, Cao XY, Ali-Osman F, Keir S. Lo HWEGFR and EGFRvIII interact with PUMA to inhibit mitochondrial translocalization of PUMA and PUMA-mediated apoptosis independent of EGFR kinase activity. Cancer Lett. 2010;294:101–10.
Stutz MA, Shattuck DL, Laederich MB, Carraway KL 3rd, Sweeney C. LRIG1 negatively regulates the oncogenic EGF receptor mutant EGFRvIII. Oncogene. 2008;27:5741–52.
Davies GC, Ryan PE, Rahman L, Zajac-Kaye M, Lipkowitz S. EGFRvIII undergoes activation-dependent downregulation mediated by the Cbl proteins. Oncogene. 2006;25:6497–509.
Hiratani I, Yamamoto N, Mochizuki T, Ohmori SY, Taira M. Selective degradation of excess Ldb1 by Rnf12/RLIM confers proper Ldb1 expression levels and Xlim-1/Ldb1 stoichiometry in Xenopus organizer functions. Development. 2003;130:4161–75.
Sangadala S, Boden SD, Viggeswarapu M, Liu Y, Titus L. LIM mineralization protein-1 potentiates bone morphogenetic protein responsiveness via a novel interaction with Smurf1 resulting in decreased ubiquitination of Smads. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17212–9.
Fomchenko EI, Holland EC. Mouse models of brain tumors and their applications in preclinical trials. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5288–97.
Holland EC, Celestino J, Dai C, Schaefer L, Sawaya RE, et al. Combined activation of Ras and Akt in neural progenitors induces glioblastoma formation in mice. Nat Genet. 2000;25:55–7.
Read RD, Cavenee WK, Furnari FB, Thomas JB. A drosophila model for EGFR-Ras and PI3K-dependent human glioma. PLoS Genet. 2009 Feb;5:e1000374.
Labalette C, Nouët Y, Levillayer F, Armengol C, Renard CA, Soubigou G, et al. The LIM-only protein FHL2 mediates ras-induced transformation through cyclin D1 and p53 pathways. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3761.
Lan Q, Wang A, Cheng Y, Mukasa A, Ma J, Hong L, et al. Guanylate binding protein-1 mediates EGFRvIII and promotes glioblastoma growth in vivo but not in vitro. Oncotarget. 2016;7:9680–91.
Chu PH, Bardwell WM, Gu Y, Ross J Jr, Chen J. FHL2 (SLIM3) is not essential for cardiac development and function. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:7460–2.
Schildge S., Bohrer C., Beck K., Schachtrup C., Isolation and culture of mouse cortical astrocytes. J Vis Exp. 2013;71:pii: 50079
Paul C, Lacroix M, Iankova I, Julien E, Schäfer BW, Labalette C, et al. The LIM-only protein FHL2 is a negative regulator of E4F1. Oncogene. 2006;25:5475–84.
Nishi H, Nishi KH, Johnson AC. Early Growth Response-1 gene mediates up-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression during hypoxia. Cancer Res. 2002;62:827–34.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572480 and 81172401, to M.L.) and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University Youth pre-Research Fund (SDFEYQN1607, to L.S.). We thank Drs. Yu Wei and Ju Chen for the generous gifts of FHL2 null MEF cells and FHL2 knockout newborn mice. M.L. was also partially supported by Jiangsu distinguished Medical Professorship award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Yu, S., Xu, H. et al. FHL2 interacts with EGFR to promote glioblastoma growth. Oncogene 37, 1386–1398 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0068-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0068-0
This article is cited by
-
FHL2 deficiency impairs follicular development and fertility by attenuating EGF/EGFR/YAP signaling in ovarian granulosa cells
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
TAB182 aggravates progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by enhancing β-catenin nuclear translocation through FHL2 dependent manner
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Poly(p-phenylenevinylene) nanoparticles modified with antiEGFRvIII for specific glioblastoma therapy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Fusion genes in gynecologic tumors: the occurrence, molecular mechanism and prospect for therapy
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Prediction of regulatory targets of alternative isoforms of the epidermal growth factor receptor in a glioblastoma cell line
BMC Bioinformatics (2019)