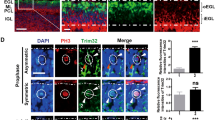
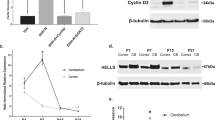
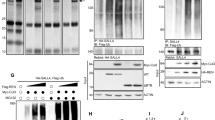
Abstract
Postnatal proliferation of cerebellar granule neuron precursors (CGNPs), proposed cells of origin for the SHH-associated subgroup of medulloblastoma, is driven by Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) in the developing cerebellum. Shh induces the oncogene Yes-associated protein (YAP), which drives IGF2 expression in CGNPs and mouse Shh-associated medulloblastomas. To determine how IGF2 expression is regulated downstream of YAP, we carried out an unbiased screen for transcriptional regulators bound to IGF2 promoters. We report that Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1), an onco-protein regulating transcription and translation, binds to IGF2 promoter P3. We observed that YB-1 is upregulated across human medulloblastoma subclasses as well as in other varieties of pediatric brain tumors. Utilizing the cerebellar progenitor model for the Shh subgroup of medulloblastoma in mice, we show for the first time that YB-1 is induced by Shh in CGNPs. Its expression is YAP-dependent and it is required for IGF2 expression in CGNPs. Finally, both gain-of function and loss-of-function experiments reveal that YB-1 activity is required for sustaining CGNP and medulloblastoma cell (MBC) proliferation. Collectively, our findings describe a novel role for YB-1 in driving proliferation in the developing cerebellum and MBCs and they identify the SHH:YAP:YB1:IGF2 axis as a powerful target for therapeutic intervention in medulloblastomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Packer RJ, Cogen P, Vezina G, Rorke LB . Medulloblastoma: clinical and biologic aspects. Neuro Oncol 1999; 1: 232–250.
Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A, Greulich H et al. Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1424–1430.
Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG, Mack S et al. Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1408–1414.
Pomeroy SL, Cho YJ . Molecular fingerprints of medulloblastoma and their application to clinical practice. Future Oncol 2011; 7: 327–329.
Eberhart CG . Even cancers want commitment: lineage identity and medulloblastoma formation. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 105–107.
Dahmane N, Ruiz i Altaba A . Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development 1999; 126: 3089–3100.
Wallace VA . Purkinje-cell-derived Sonic hedgehog regulates granule neuron precursor cell proliferation in the developing mouse cerebellum. Curr Biol 1999; 9: 445–448.
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP . Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic Hedgehog. Neuron 1999; 22: 103–114.
Bhatia B, Northcott PA, Hambardzumyan D, Govindarajan B, Brat DJ, Arbiser JL et al. Tuberous sclerosis complex suppression in cerebellar development and medulloblastoma: separate regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin activity and p27 Kip1 localization. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7224–7234.
Fernandez LA, Northcott PA, Dalton J, Fraga C, Ellison D, Angers S et al. YAP1 is amplified and up-regulated in hedgehog-associated medulloblastomas and mediates Sonic hedgehog-driven neural precursor proliferation. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 2729–2741.
Parathath SR, Mainwaring LA, Fernandez LA, Campbell DO, Kenney AM . Insulin receptor substrate 1 is an effector of sonic hedgehog mitogenic signaling in cerebellar neural precursors. Development 2008; 135: 3291–3300.
Fernandez LA, Squatrito M, Northcott P, Awan A, Holland EC, Taylor MD et al. Oncogenic YAP promotes radioresistance and genomic instability in medulloblastoma through IGF2-mediated Akt activation. Oncogene 2012; 31: 1923–1937.
Mainwaring LA, Kenney AM . Divergent functions for eIF4E and S6 kinase by sonic hedgehog mitogenic signaling in the developing cerebellum. Oncogene 2011; 30: 1784–1797.
Kenney AM, Widlund HR, Rowitch DH . Hedgehog and PI-3 kinase signaling converge on Nmyc1 to promote cell cycle progression in cerebellar neuronal precursors. Development 2004; 131: 217–228.
Hatton BA, Villavicencio EH, Tsuchiya KD, Pritchard JI, Ditzler S, Pullar B et al. The Smo/Smo model: hedgehog-induced medulloblastoma with 90% incidence and leptomeningeal spread. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 1768–1776.
Hu JF, Vu TH, Hoffman AR . Differential biallelic activation of three insulin-like growth factor II promoters in the mouse central nervous system. Mol Endocrinol 1995; 9: 628–636.
Lasham A, Print CG, Woolley AG, Dunn SE, Braithwaite AW . YB-1: oncoprotein, prognostic marker and therapeutic target? Biochem J 2013; 449: 11–23.
Shibao K, Takano H, Nakayama Y, Okazaki K, Nagata N, Izumi H et al. Enhanced coexpression of YB-1 and DNA topoisomerase II alpha genes in human colorectal carcinomas. Int J Cancer 1999; 83: 732–737.
Gimenez-Bonafe P, Fedoruk MN, Whitmore TG, Akbari M, Ralph JL, Ettinger S et al. YB-1 is upregulated during prostate cancer tumor progression and increases P-glycoprotein activity. Prostate 2004; 59: 337–349.
Oda Y, Sakamoto A, Shinohara N, Ohga T, Uchiumi T, Kohno K et al. Nuclear expression of YB-1 protein correlates with P-glycoprotein expression in human osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res 1998; 4: 2273–2277.
Kamura T, Yahata H, Amada S, Ogawa S, Sonoda T, Kobayashi H et al. Is nuclear expression of Y box-binding protein-1 a new prognostic factor in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma? Cancer 1999; 85: 2450–2454.
Yahata H, Kobayashi H, Kamura T, Amada S, Hirakawa T, Kohno K et al. Increased nuclear localization of transcription factor YB-1 in acquired cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2002; 128: 621–626.
Gu C, Oyama T, Osaki T, Kohno K, Yasumoto K . Expression of Y box-binding protein-1 correlates with DNA topoisomerase IIalpha and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in lung cancer. Anticancer Res 2001; 21: 2357–2362.
Shibahara K, Sugio K, Osaki T, Uchiumi T, Maehara Y, Kohno K et al. Nuclear expression of the Y-box binding protein, YB-1, as a novel marker of disease progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 3151–3155.
Oda Y, Ohishi Y, Saito T, Hinoshita E, Uchiumi T, Kinukawa N et al. Nuclear expression of Y-box-binding protein-1 correlates with P-glycoprotein and topoisomerase II alpha expression, and with poor prognosis in synovial sarcoma. J Pathol 2003; 199: 251–258.
Bargou RC, Jurchott K, Wagener C, Bergmann S, Metzner S, Bommert K et al. Nuclear localization and increased levels of transcription factor YB-1 in primary human breast cancers are associated with intrinsic MDR1 gene expression. Nat Med 1997; 3: 447–450.
Janz M, Harbeck N, Dettmar P, Berger U, Schmidt A, Jurchott K et al. Y-box factor YB-1 predicts drug resistance and patient outcome in breast cancer independent of clinically relevant tumor biologic factors HER2, uPA and PAI-1. Int J Cancer 2002; 97: 278–282.
Rubinstein DB, Stortchevoi A, Boosalis M, Ashfaq R, Guillaume T . Overexpression of DNA-binding protein B gene product in breast cancer as detected by in vitro-generated combinatorial human immunoglobulin libraries. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 4985–4991.
Huang J, Tan PH, Li KB, Matsumoto K, Tsujimoto M, Bay BH . Y-box binding protein, YB-1, as a marker of tumor aggressiveness and response to adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 2005; 26: 607–613.
Wu J, Lee C, Yokom D, Jiang H, Cheang MC, Yorida E et al. Disruption of the Y-box binding protein-1 results in suppression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and HER-2. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 4872–4879.
Faury D, Nantel A, Dunn SE, Guiot MC, Haque T, Hauser P et al. Molecular profiling identifies prognostic subgroups of pediatric glioblastoma and shows increased YB-1 expression in tumors. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1196–1208.
Pham NV, Nguyen MT, Hu JF, Vu TH, Hoffman AR . Dissociation of IGF2 and H19 imprinting in human brain. Brain Res 1998; 810: 1–8.
Hartmann W, Koch A, Brune H, Waha A, Schuller U, Dani I et al. Insulin-like growth factor II is involved in the proliferation control of medulloblastoma and its cerebellar precursor cells. Am J Pathol 2005; 166: 1153–1162.
Chowdhury RP, Gupta S, Chatterji D . Identification and characterization of the dps promoter of Mycobacterium smegmatis: promoter recognition by stress-specific extracytoplasmic function sigma factors sigmaH and sigmaF. J Bacteriol 2007; 189: 8973–8981.
Zhang C, Basta T, Jensen ED, Klymkowsky MW . The beta-catenin/VegT-regulated early zygotic gene Xnr5 is a direct target of SOX3 regulation. Development 2003; 130: 5609–5624.
Gall JG, Bellini M, Wu Z, Murphy C . Assembly of the nuclear transcription and processing machinery: Cajal bodies (coiled bodies) and transcriptosomes. Mol Biol Cell 1999; 10: 4385–4402.
Rotwein P, Hall LJ . Evolution of insulin-like growth factor II: characterization of the mouse IGF-II gene and identification of two pseudo-exons. DNA Cell Biol 1990; 9: 725–735.
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN et al. Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 2002; 297: 1559–1561.
Northcott PA, Shih DJ, Peacock J, Garzia L, Morrissy AS, Zichner T et al. Subgroup-specific structural variation across 1000 medulloblastoma genomes. Nature 2012; 488: 49–56.
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME . Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001; 11: 297–305.
Kenney AM, Rowitch DH . Sonic hedgehog promotes G(1) cyclin expression and sustained cell cycle progression in mammalian neuronal precursors. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 9055–9067.
Corrales JD, Rocco GL, Blaess S, Guo Q, Joyner AL . Spatial pattern of sonic hedgehog signaling through Gli genes during cerebellum development. Development 2004; 131: 5581–5590.
Bai CB, Auerbach W, Lee JS, Stephen D, Joyner AL . Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development 2002; 129: 4753–4761.
Kenney AM, Cole MD, Rowitch DH . Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development 2003; 130: 15–28.
En-Nia A, Yilmaz E, Klinge U, Lovett DH, Stefanidis I, Mertens PR . Transcription factor YB-1 mediates DNA polymerase alpha gene expression. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 7702–7711.
Uchiumi T, Fotovati A, Sasaguri T, Shibahara K, Shimada T, Fukuda T et al. YB-1 is important for an early stage embryonic development: neural tube formation and cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 40440–40449.
Miwa A, Higuchi T, Kobayashi S . Expression and polysome association of YB-1 in various tissues at different stages in the lifespan of mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006; 1760: 1675–1681.
Eliseeva IA, Kim ER, Guryanov SG, Ovchinnikov LP, Lyabin DN . Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) and its functions. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2011; 76: 1402–1433.
Finkbeiner MR, Astanehe A, To K, Fotovati A, Davies AH, Zhao Y et al. Profiling YB-1 target genes uncovers a new mechanism for MET receptor regulation in normal and malignant human mammary cells. Oncogene 2009; 28: 1421–1431.
Tiberi L, Bonnefont J, van den Ameele J, Le Bon SD, Herpoel A, Bilheu A et al. A BCL6/BCOR/SIRT1 complex triggers neurogenesis and suppresses medulloblastoma by repressing Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Cancer Cell 2014; 26: 797–812.
Callahan CA, Ofstad T, Horng L, Wang JK, Zhen HH, Coulombe PA et al. MIM/BEG4, a Sonic hedgehog-responsive gene that potentiates Gli-dependent transcription. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 2724–2729.
Lee J, Platt KA, Censullo P, Ruiz i Altaba A . Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development. Development 1997; 124: 2537–2552.
Fernandez LA, Squatrito M, Northcott P, Awan A, Holland EC, Taylor MD et al. Oncogenic YAP promotes radioresistance and genomic instability in medulloblastoma through IGF2-mediated Akt activation. Oncogene 2011; 31: 1923–1937.
Reginensi A, Scott RP, Gregorieff A, Bagherie-Lachidan M, Chung C, Lim DS et al. Yap- and Cdc42-dependent nephrogenesis and morphogenesis during mouse kidney development. PLoS Genet 2013; 9: e1003380.
Wu J, Stratford AL, Astanehe A, Dunn SE . YB-1 is a transcription/translation factor that orchestrates the oncogenome by hardwiring signal transduction to gene expression. Transl Oncogenomics 2007; 2: 49–65.
Grant CE, Deeley RG . Cloning and characterization of chicken YB-1: regulation of expression in the liver. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13: 4186–4196.
Sabath DE, Podolin PL, Comber PG, Prystowsky MB . cDNA cloning and characterization of interleukin 2-induced genes in a cloned T helper lymphocyte. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 12671–12678.
Ito K, Tsutsumi K, Kuzumaki T, Gomez PF, Otsu K, Ishikawa K . A novel growth-inducible gene that encodes a protein with a conserved cold-shock domain. Nucleic Acids Res 1994; 22: 2036–2041.
Stenina OI, Poptic EJ, DiCorleto PE . Thrombin activates a Y box-binding protein (DNA-binding protein B) in endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: 579–587.
Lossi L, Alasia S, Salio C, Merighi A . Cell death and proliferation in acute slices and organotypic cultures of mammalian CNS. Prog Neurobiol 2009; 88: 221–245.
Lee JE, Pintar J, Efstratiadis A . Pattern of the insulin-like growth factor II gene expression during early mouse embryogenesis. Development 1990; 110: 151–159.
Jurchott K, Bergmann S, Stein U, Walther W, Janz M, Manni I et al. YB-1 as a cell cycle-regulated transcription factor facilitating cyclin A and cyclin B1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 27988–27996.
Mertens PR, Harendza S, Pollock AS, Lovett DH . Glomerular mesangial cell-specific transactivation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 transcription is mediated by YB-1. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 22905–22912.
Uchiumi T, Kohno K, Tanimura H, Matsuo K, Sato S, Uchida Y et al. Enhanced expression of the human multidrug resistance 1 gene in response to UV light irradiation. Cell Growth Differ 1993; 4: 147–157.
Lasham A, Lindridge E, Rudert F, Onrust R, Watson J . Regulation of the human fas promoter by YB-1, Puralpha and AP-1 transcription factors. Gene 2000; 252: 1–13.
Lasham A, Moloney S, Hale T, Homer C, Zhang YF, Murison JG et al. The Y-box-binding protein, YB1, is a potential negative regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 35516–35523.
Homer C, Knight DA, Hananeia L, Sheard P, Risk J, Lasham A et al. Y-box factor YB1 controls p53 apoptotic function. Oncogene 2005; 24: 8314–8325.
Reiss K . Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor—a potential therapeutic target in medulloblastomas. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2002; 6: 539–544.
Hahn H, Wojnowski L, Specht K, Kappler R, Calzada-Wack J, Potter D et al. Patched target Igf2 is indispensable for the formation of medulloblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 28341–28344.
Mill P, Mo R, Hu MC, Dagnino L, Rosenblum ND, Hui CC . Shh controls epithelial proliferation via independent pathways that converge on N-Myc. Dev Cell 2005; 9: 293–303.
Dolfini D, Mantovani R . Targeting the Y/CCAAT box in cancer: YB-1 (YBX1) or NF-Y? Cell Death Differ 2013; 20: 676–685.
Corcoran RB, Bachar Raveh T, Barakat MT, Lee EY, Scott MP . Insulin-like growth factor 2 is required for progression to advanced medulloblastoma in patched1 heterozygous mice. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 8788–8795.
Jung K, Wu F, Wang P, Ye X, Abdulkarim BS, Lai R . YB-1 regulates Sox2 to coordinately sustain stemness and tumorigenic properties in a phenotypically distinct subset of breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014; 14: 328.
Kool M, Koster J, Bunt J, Hasselt NE, Lakeman A, van Sluis P et al. Integrated genomics identifies five medulloblastoma subtypes with distinct genetic profiles, pathway signatures and clinicopathological features. PLoS One 2008; 3: e3088.
Shih DJ, Northcott PA, Remke M, Korshunov A, Ramaswamy V, Kool M et al. Cytogenetic prognostication within medulloblastoma subgroups. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 886–896.
Suresh K . An overview of randomization techniques: an unbiased assessment of outcome in clinical research. J Hum Reprod Sci 2011; 4: 8–11.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the resources available from the Winship Cancer Institute (WCI)- Pathology Core Lab for paraffin embedding of tissues. We acknowledge the assistance provided by Neil Anthony (Integrated Imaging Core, Emory University) during image acquisition and analysis. We thank Tobey Macdonald, Matthew Schniederjan and Megan Hamling from Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta (CHOA) for providing human medulloblastoma tissue sections. We also thank Daniel Brat and Carol Tucker-Burden for assistance in slice culture experiments. We greatly appreciate the suggestions and feedback from Nada Jabado, Dan Brat, Sandra Dunn, Tracy Ann-Read, Renee Read and Tamara Caspary. This work has been supported by grants to AMK from the NIH (NINDS R01 NS061070), CURE Childhood Cancer Foundation and Winship Cancer Institute (P30 center grant—CA138292). AD acknowledges Alex Lemonade Stand Foundation and Northwestern Mutual Foundation for Young Investigator Award and Imaging studies were supported by a pilot grant to AD from the Integrated Cellular Imaging (ICI) core at Emory University.
Author contributions
AD and AMK designed the research. AD, MRo, MRe, CM and AM performed the experiments and analyzed the data. AG and JLW provided YAP(LoxP) mice and assisted with their husbandry. MRo, MRe, JLW, MDT and SA edited the manuscript before submission. AD and AMK wrote the paper. All the authors read and commented on the manuscript and approved the final version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, A., Robitaille, M., Remke, M. et al. YB-1 is elevated in medulloblastoma and drives proliferation in Sonic hedgehog-dependent cerebellar granule neuron progenitor cells and medulloblastoma cells. Oncogene 35, 4256–4268 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.491
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.491
This article is cited by
-
YB1 modulates the DNA damage response in medulloblastoma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Androgens increase excitatory neurogenic potential in human brain organoids
Nature (2022)
-
Pediatric brain tumor cell lines exhibit miRNA-depleted, Y RNA-enriched extracellular vesicles
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2022)
-
Ybx1 fine-tunes PRC2 activities to control embryonic brain development
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Upregulation of the chromatin remodeler HELLS is mediated by YAP1 in Sonic Hedgehog Medulloblastoma
Scientific Reports (2019)