Abstract
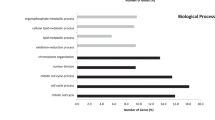
Comparing normal colorectal mucosa and adenomas focusing on deregulated pathways obtains insight into the biological processes of early colorectal carcinogenesis. Publicly available microarray expression data from 26 normal mucosa and 47 adenoma samples were analyzed. Biological pathways enriched in adenomas were identified with Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). The analysis revealed 10, 11 and 16 gene sets distinguishing adenomas from normal mucosa according to Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), Gene Map Annotator and Pathway Profiler (GenMAPP) and Biocarta databases, respectively. Biological pathways known to be involved in colon carcinogenesis such as cell cycle (P=0.002) and Wnt signaling (P=0.007) were enriched in adenomas. In addition, we found enrichment of novel pathways such as retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway (P=0.002), Src pathway (P=0.004), folate biosynthesis (P=0.019) and Hedgehog signaling (P=0.037) in adenomas. Microarray results for Rb and Src pathway genes were validated by quantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (qRT–PCR) on mRNA isolated from an independent set of adenoma and normal colon samples. A high correlation between microarray data and qRT–PCR expression data was found. The relevance of targeting of identified pathways was shown using the Rb pathway inhibitors roscovitine and PD-0332991 and the Src pathway inhibitor dasatinib. All inhibitors used induced cell growth reduction in adenoma cells. This study shows a bioinformatical and functional approach leading to potentially new options for chemoprevention of colorectal cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldoss IT, Tashi T, Ganti AK . (2009). Seliciclib in malignancies. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 18: 1957–1965.
Alter O, Brown PO, Botstein D . (2000). Singular value decomposition for genome-wide expression data processing and modeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 10101–10106.
Arber N, Hibshoosh H, Moss SF, Sutter T, Zhang Y, Begg M et al. (1996). Increased expression of cyclin D1 is an early event in multistage colorectal carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 110: 669–674.
Arber N, Levin B . (2008). Chemoprevention of colorectal neoplasia: the potential for personalized medicine. Gastroenterology 134: 1224–1237.
Arhel NJ, Packham G, Townsend PA, Collard TJ, Zadeh AM, Sharp A et al. (2003). The retinoblastoma protein interacts with Bag-1 in human colonic adenoma and carcinoma derived cell lines. Int J Cancer 106: 364–371.
Arima Y, Inoue Y, Shibata T, Hayashi H, Nagano O, Saya H et al. (2008). Rb depletion results in deregulation of E-cadherin and induction of cellular phenotypic changes that are characteristic of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68: 5104–5112.
Bartkova J, Thullberg M, Slezak P, Jaramillo E, Rubio C, Thomassen LH . (2001). Aberrant expression of G1-phase cell cycle regulators in flat and exophytic adenomas of the human colon. Gastroenterology 120: 1680–1688.
Bild AH, Potti A, Nevins JR . (2006). Linking oncogenic pathways with therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 735–741.
Boquoi A, Chen T, Enders GH . (2009). Chemoprevention of mouse intestinal tumorigenesis by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor SNS-032. Cancer Prev Res 2: 800–806.
Carey R, Jurickova I, Ballard E, Bonkowski E, Han X, Xu H et al. (2008). Activation of an IL-6:STAT3-dependent transcriptome in pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 14: 446–457.
Cartwright CA, Meisler AI, Eckhart W . (1990). Activation of the pp60c-Src protein kinase is an early event in colonic carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 558–562.
Chen R, Wierda WG, Chubb S, Hawtin RE, Fox JA, Keating MJ et al. (2009). Mechanism of action of SNS-032, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 113: 4637–4645.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N . (1987). Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159.
Cole AM, Myant K, Reed KR, Ridgway RA, Athineos D, van den Brink GR et al. (2010). Cyclin D2–cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 is required for efficient proliferation and tumorigenesis following Apc loss. Cancer Res 70: 8149–8158.
Crijns AP, Fehrmann RS, de Jong S, Gerbens F, Meersma GJ, Klip HG et al. (2009). Survival-related profile, pathways, and transcription factors in ovarian cancer. PLoS Med 6: 181–193.
Crijns AP, Gerbens F, Plantinga AE, Meersma GJ, de Jong S, Hofstra RM et al. (2006). A biological question and a balanced (orthogonal) design: the ingredients to efficiently analyze two-color microarrays with confirmatory factor analysis. BMC Genomics 7: 232.
Dahlquist KD, Salomonis N, Vranizan K, Lawlor SC, Conklin BR . (2002). GenMAPP, a new tool for viewing and analyzing microarray data on biological pathways. Nat Genet 31: 19–20.
de Hoon MJ, Imoto S, Nolan J, Miyano S . (2004). Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 20: 1453–1454.
Du W, Searle JS . (2009). The rb pathway and cancer therapeutics. Curr Drug Targets 10: 581–589.
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE . (2002). Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res 30: 207–210.
Einspahr JG, Martinez ME, Jiang R, Hsu CH, Rashid A, Bhattacharrya AK et al. (2006). Associations of Ki-ras proto-oncogene mutation and p53 gene overexpression in sporadic colorectal adenomas with demographic and clinicopathologic characteristics. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15: 1443–1450.
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL, Meade MA, Trachet E et al. (2004). Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 1428–1437.
Fujita T, Liu W, Doihara H, Wan Y . (2008). Regulation of Skp2-p27 axis by the Cdh1/anaphase-promoting complex pathway in colorectal tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol 173: 217–228.
Galamb O, Gyorffy B, Sipos F, Spisak S, Nemeth AM, Miheller P et al. (2008). Inflammation, adenoma and cancer: objective classification of colon biopsy specimens with gene expression signature. Dis Markers 25: 1–16.
Giacinti C, Giordano A . (2006). RB and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 25: 5220–5227.
Guillen-Ahlers H, Buechler SA, Suckow MA, Castellino FJ, Ploplis VA . (2008). Sulindac treatment alters collagen and matrilysin expression in adenomas of ApcMin/+ mice. Carcinogenesis 29: 1421–1427.
Hao X, Du M, Bishop AE, Talbot IC . (1998). Imbalance between proliferation and apoptosis in the development of colorectal carcinoma. Virchows Arch 433: 523–527.
Hong Y, Ho KS, Eu KW, Cheah PY . (2007). A susceptibility gene set for early onset colorectal cancer that integrates diverse signaling pathways: implication for tumorigenesis. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1107–1114.
Imazeki F, Yokosuka O, Yamaguchi T, Ohto M, Isono K, Omata M . (1996). Expression of variant CD44-messenger RNA in colorectal adenocarcinomas and adenomatous polyps in humans. Gastroenterology 110: 362–368.
Jalving M, de Jong S, Koornstra JJ, Boersma-van Ek W, Zwart N, Wesseling J et al. (2006). TRAIL induces apoptosis in human colorectal adenoma cell lines and human colorectal adenomas. Clin Cancer Res 12: 4350–4356.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Hattori M, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Itoh M, Kawashima S et al. (2006). From genomics to chemical genomics: new developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 354–357.
Kantarjian H, Pasquini R, Hamerschlak N, Rousselot P, Holowiecki J, Jootar S et al. (2007). Dasatinib or high-dose imatinib for chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of first-line imatinib: a randomized phase 2 trial. Blood 109: 5143–5150.
Kita H, Hikichi Y, Hikami K, Tsuneyama K, Cui ZG, Osawa H et al. (2006). Differential gene expression between flat adenoma and normal mucosa in the colon in a microarray analysis. J Gastroenterol 41: 1053–1063.
Knudsen ES, Wang JY . (2010). Targeting the RB-pathway in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 16: 1094–1099.
Koornstra JJ, Rijcken FE, de Jong S, Hollema H, de Vries EG, Kleibeuker JH . (2004). Assessment of apoptosis by M30 immunoreactivity and the correlation with morphological criteria in normal colorectal mucosa, adenomas and carcinomas. Histopathology 44: 9–17.
Kopetz S, Lesslie DP, Dallas NA, Park SI, Johnson M, Parikh NU et al. (2009). Synergistic activity of the SRC family kinase inhibitor dasatinib and oxaliplatin in colon carcinoma cells is mediated by oxidative stress. Cancer Res 69: 3842–3849.
Kwong LN, Weiss KR, Haigis KM, Dove WF . (2008). Atm is a negative regulator of intestinal neoplasia. Oncogene 27: 1013–1018.
LaPointe LC, Dunne R, Brown GS, Worthley DL, Molloy PL, Wattchow D et al. (2008). Map of differential transcript expression in the normal human large intestine. Physiol Genomics 33: 50–64.
Li J, Rix U, Fang B, Bai Y, Edwards A, Colinge J et al. (2010). A chemical and phosphoproteomic characterization of dasatinib action in lung cancer. Nat Chem Biol 6: 291–299.
Lin YM, Furukawa Y, Tsunoda T, Yue CT, Yang KC, Nakamura Y . (2002). Molecular diagnosis of colorectal tumors by expression profiles of 50 genes expressed differentially in adenomas and carcinomas. Oncogene 21: 4120–4128.
Lockhart DJ, Dong H, Byrne MC, Follettie MT, Gallo MV, Chee MS et al. (1996). Expression monitoring by hybridization to high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat Biotechnol 14: 1675–1680.
Michaud K, Solomon D, Oermann E, Kim J-S, Zhong W-Z, Prados MD et al. (2010). Pharmacologic inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 arrests the growth of glioblastoma multiforme intracranial xenografts. Cancer Res 70: 3228–3238.
Midgley R, Kerr D . (1999). Colorectal cancer. Lancet 353: 391–399.
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF, Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J et al. (2003). PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet 34: 267–273.
Nielsen TO, West RB, Linn SC, Alter O, Knowling MA, O'Connell JX et al. (2002). Molecular characterisation of soft tissue tumours: a gene expression study. Lancet 359: 1301–1307.
Paulson QX, Pusapati RV, Hong S, Weaks RL, Conti CJ, Johnson DG . (2008). Transgenic expression of E2F3a causes DNA damage leading to ATM-dependent apoptosis. Oncogene 27: 4954–4961.
Payne SR, Zhang S, Tsuchiya K, Moser R, Gurley KE, Longton G et al. (2008). p27kip1 deficiency impairs G2/M arrest in response to DNA damage, leading to an increase in genetic instability. Mol Cell Biol 28: 258–268.
Rencher A . (1998). Mutivariate Statistical Interference and Applications. John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, USA.
Sabates-Bellver J, van der Flier LG, de Palo M, Cattaneo E, Maake C, Rehrauer H et al. (2007). Transcriptome profile of human colorectal adenomas. Mol Cancer Res 5: 1263–1275.
Senderowicz AM . (2003). Small-molecule cyclin-dependent kinase modulators. Oncogene 22: 6609–6620.
Serrels A, Macpherson IR, Evans TR, Lee FY, Clark EA, Sansom OJ et al. (2006). Identification of potential biomarkers for measuring inhibition of Src kinase activity in colon cancer cells following treatment with dasatinib. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 3014–3022.
Sherlock G . (2001). Analysis of large-scale gene expression data. Brief Bioinform 2: 350–362.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 15545–15550.
Timmerbeul I, Garrett-Engele CM, Kossatz U, Chen X, Firpo E, Grunwald V et al. (2006). Testing the importance of p27 degradation by the SCFskp2 pathway in murine models of lung and colon cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 14009–14014.
van Geelen CM, de Vries EG, Le PT, van Weeghel RP, de Jong S . (2003). Differential modulation of the TRAIL receptors and the CD95 receptor in colon carcinoma cell lines. Br J Cancer 89: 363–373.
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M et al. (1988). Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med 319: 525–532.
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . (2004). Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med 10: 789–799.
Wai PY, Mi Z, Gao C, Guo H, Marroquin C, Kuo PC . (2006). Ets-1 and runx2 regulate transcription of a metastatic gene, osteopontin, in murine colorectal cancer cells. J Biol Chem 281: 18973–18982.
Wesierska-Gadek J, Maurer M, Zulehner N, Komina O . (2011). Whether to target single or multiple CDKs for therapy? That is the question. J Cell Physiol 226: 341–349.
Whittaker SR, Walton MI, Garrett MD, Workman P . (2004). The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine) inhibits retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, causes loss of cyclin D1, and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cancer Res 64: 262–272.
Yeatman TJ . (2004). A renaissance for Src. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 470–480.
Zhao P, Mao X, Talbot IC . (2006). Aberrant cytological localization of p16 and CDK4 in colorectal epithelia in the normal adenoma carcinoma sequence. World J Gastroenterol 12: 6391–6396.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant RUG 2005-3361 from the Dutch Cancer Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heijink, D., Fehrmann, R., de Vries, E. et al. A bioinformatical and functional approach to identify novel strategies for chemoprevention of colorectal cancer. Oncogene 30, 2026–2036 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.578
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.578
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Liver glycogen phosphorylase is upregulated in glioblastoma and provides a metabolic vulnerability to high dose radiation
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
A prognostic index based on an eleven gene signature to predict systemic recurrences in colorectal cancer
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
Identification of Key Genes Associated with Colorectal Cancer Based on the Transcriptional Network
Pathology & Oncology Research (2015)
-
Design, synthesis and experimental validation of novel potential chemopreventive agents using random forest and support vector machine binary classifiers
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (2014)
-
Targeting cell cycle and hormone receptor pathways in cancer
Oncogene (2013)