Abstract
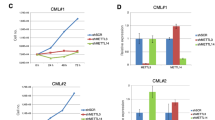
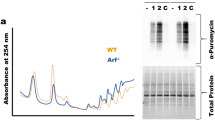
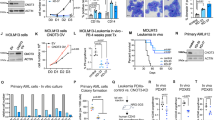
The 5′ untranslated region of the proto-oncogene c-myc contains an internal ribosome entry segment (IRES) and c-myc translation can therefore be initiated by internal ribosome entry as well as by cap-dependent mechanisms. It has been shown previously that in patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and in MM-derived cell lines there is a C to T mutation in the c-myc IRES that increases IRES activity and the corresponding synthesis of c-myc protein although it is not fully understood how this occurs. Our data show that two recently identified c-myc IRES trans-acting factors, Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) and polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (PTB-1), bind more strongly (approximately 3.5- and 2-fold respectively) to the mutated version of the c-myc IRES and in vitro these proteins exert their effect synergistically to stimulate IRES activity of the mutant IRES 4.5-fold more than the wild-type version. Importantly, we show that there is a strong correlation between the expression of PTB-1, YB-1 and c-myc in MM-derived cell lines, suggesting that by reducing either PTB-1 or YB-1 protein levels it is possible to decrease c-myc expression and inhibit cell proliferation of MM-derived cell lines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bader AG, Vogt PK . (2008). Phosphorylation by Akt disables the anti-oncogenic activity of YB-1. Oncogene 27: 1179–1182.
Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN . (1991). Max; a helix–loop–helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science 251: 1211–1217.
Boutz PL, Stoilov P, Li Q, Lin CH, Chawla G, Ostrow K et al. (2007). A post-transcriptional regulatory switch in polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins reprograms alternative splicing in developing neurons. Genes Dev 21: 1636–1652.
Chappell SA, Le Quesne JPC, Paulin FEM, deSchoolmeester ML, Stoneley M, Soutar RL et al. (2000). A mutation in the c-myc IRES leads to enhanced internal ribosome entry in multiple myelome: a novel mechanism of oncogene de-regulation. Oncogene 19: 4437–4440.
Chatterjee M, Rancso C, Stuhmer T, Eckstein N, Andrulis M, Gerecke C et al. (2008). The Y-box protein YB-1 is associated with progressive disease and mediates survival and drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Blood 111: 3714–3772.
Cobbold LC, Spriggs KA, Haines SJ, Dobbyn HC, Hayes C, de Moor CH et al. (2008). Identification of internal ribosome entry segment (IRES)-trans-acting factors for the Myc family of IRESs. Mol Cell Biol 28: 40–49.
Dalton WS, Durie BGM, Alberts DS, Gerlach JH, Cress AE . (1986). Characterisation of a new drug-resistant human myeloma cell line that expresses P-glycoprotein. Cancer Res 46: 5125–5130.
Drach J, Kaufmann H, Urbauer E, Schreiber S, Ackermann J, Huber H . (2000). The biology of multiple myeloma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126: 441–447.
Evans JR, Mitchell SA, Spriggs KA, Ostrowski J, Bomsztyk K, Ostarek D et al. (2003). Members of the poly (rC) binding protein family stimulate the activity of the c-myc internal ribosome entry segment in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 22: 6068–6076.
Evdokimova V, Tognon C, Ng T, Ruzanov P, Melnyk N, Fink D et al. (2009). Translational activation of snail1 and other developmentally regulated transcription factors by YB-1 promotes an epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell 15: 402–415.
He X, Pool M, Darcy KM, Lim SB, Auersperg N, Coon JS et al. (2007). Knockdown of polypyrimidine tract-binding protein suppresses ovarian tumor cell growth and invasiveness in vitro. Oncogene 26: 4961–4968.
Herold S, Herkert B, Eilers M . (2009). Facilitating replication under stress: an oncogenic function of MYC? Nat Rev Cancer 9: 441–444.
Ho PJ, Campbell LJ, Gibson J, Brown R, Joshua D . (2002). The biology and cytogenetics of multiple myeloma. Rev Clin Exp Hematol 6: 276–300.
Jo OD, Martin J, Bernath A, Masri J, Lichtenstein A, Gera J . (2008). Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 regulates cyclin D1 and c-myc internal ribosome entry site function through Akt signaling. J Biol Chem 283: 23274–23287.
Johannes G, Sarnow P . (1998). Cap-independent polysomal association of natural mRNAs encoding c-myc, Bip, and eIF4G conferred by internal ribosome entry sites. RNA 4: 1500–1513.
Kuehl WM, Bergsagel PL . (2002). Multiple myeloma: evolving genetic events and host interactions. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 175–187.
Le Quesne JPC, Stoneley M, Fraser GA, Willis AE . (2001). Derivation of a structural Model for the c-myc IRES. J Mol Biol 310: 111–126.
Meyer N, Penn LZ . (2008). Myc-timeline reflecting on 25 years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 976–990.
Mitchell SA, Spriggs KA, Bushell M, Evans JR, Stoneley M, Le Quesne JPC et al. (2005). Identification of a motif that mediates polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-dependent internal ribosome entry. Genes Dev 19: 1556–1571.
Mitchell SA, Spriggs KA, Coldwell MJ, Jackson RJ, Willis AE . (2003). The Apaf-1 internal ribosome entry segment attains the correct structural conformation for function via interactions with PTB and unr. Mol Cell 11: 757–711.
Nanbru C, Lafon I, Audiger S, Gensac G, Vagner S, Huez G et al. (1997). Alternative translation of the proto-oncogene c-myc by an internal ribosome entry site. J Biol Chem 272: 32061–32066.
Paulin FEM, Chappell SA, Willis AE . (1998). A single nucleotide change in the c-myc internal ribosome entry segment leads to enhanced binding of a group of protein factors. Nucleic Acids Res 26: 3097–3103.
Paulin FEM, West MJ, Sullivan NF, Whitney RL, Lyne L, Willis AE . (1996). Aberrant translational control of the c-myc gene in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 13: 505–513.
Shi YJ, Frost PJ, Hoang BQ, Benavides A, Sharma S, Gera JF et al. (2008). IL-6-induced stimulation of c-myc translation in multiple myeloma cells is mediated by myc internal ribosome entry site function and the RNA-binding protein, hnRNP A1. Cancer Res 68: 10215–10222.
Sonenberg N, Hinnebusch AG . (2009). Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: mechanisms and biological targets. Cell 136: 731–745.
Spriggs KA, Cobbold LC, Jopling CL, Cooper RE, Wilson LA, Stoneley M et al. (2009). Canonical initiation factor requirements of the myc family of internal ribosome entry segments. Mol Cell Biol 29: 1565–1574.
Stoneley M, Chappell S, Jopling C, Dickens M, MacFarlane M, Willis A . (2000). c-Myc protein synthesis is initiated from the internal ribosome entry segment during apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 20: 1162–1169.
Stoneley M, Paulin FEM, Le Quesne JPC, Chappell SA, Willis AE . (1998). C-Myc 5′ untranslated region contains an internal ribosome entry segment. Oncogene 16: 423–428.
Stoneley M, Willis AE . (2004a). Cellular internal ribosome entry segments: structures, trans-acting factors and regulation of gene expression. Oncogene 23: 3200–3207.
Stoneley M, Willis AE . (2004b). Cellular internal ribosome entry segments; structures, trans-acting factors and regulation of gene expression. Oncogene 23: 3200–3207.
Subkhankulova T, Mitchell SA, Willis AE . (2001). Internal ribosome entry segment mediated initiation of c-Myc protein synthesis following genotoxic stress. Biochem J 359: 183–192.
Sutherland BW, Kucab J, Wu J, Lee C, Cheang MCU, Yorida E et al. (2005). Akt phosphorylates the Y-box binding protein 1 at Ser102 located in the cold shock domain and affects the anchorage-independent growth of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 4281–4292.
Vafa O, Wade M, Kern S, Beeche M, Pandita TK, Hampton GM et al. (2002). c-Myc can induce DNA damage, increase reactive oxygen species, and mitigate p53 function: a mechanism for oncogene-induced genetic instability. Mol Cell 9: 1031–1044.
Wang C, Norton JT, Ghosh S, Kim J, Fushimi K, Wu JY et al. (2008). Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTB) differentially affects malignancy in a cell line-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 283: 20277–20287.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by grants from the BBSRC (LCC, HAK) and CRUK (LAW, AVK). Martin Bushell is a BBSRC David Philips fellow and Anne Willis holds a BBSRC professorial fellowship. We thank Professor Dalton (Moffitt Cancer Center, Florida, USA) for providing the cell line 8226/R5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobbold, L., Wilson, L., Sawicka, K. et al. Upregulated c-myc expression in multiple myeloma by internal ribosome entry results from increased interactions with and expression of PTB-1 and YB-1. Oncogene 29, 2884–2891 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.31
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The plasticity of mRNA translation during cancer progression and therapy resistance
Nature Reviews Cancer (2021)
-
Functional 5′ UTR mRNA structures in eukaryotic translation regulation and how to find them
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2018)
-
Human rhinovirus internal ribosome entry site element enhances transgene expression in transfected CHO-S cells
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Uncoupling of EGFR–RAS signaling and nuclear localization of YBX1 in colorectal cancer
Oncogenesis (2016)
-
TGF-β1 Induces Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein to Alter Fibroblasts Proliferation and Fibronectin Deposition in Keloid
Scientific Reports (2016)