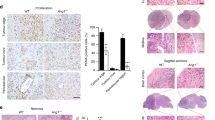
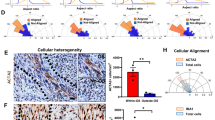
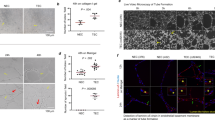
Abstract
Angiogenesis involves a complex set of cell–cell and cell–extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions that coordinately promote and inhibit blood vessel growth and sprouting. Although many factors that promote angiogenesis have been characterized, the identities and mechanisms of action of endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis remain unclear. Furthermore, little is known about how cancer cells selectively circumvent the actions of these inhibitors to promote pathological angiogenesis, a requisite event for tumor progression. Using mosaic mouse models of the malignant brain cancer, astrocytoma, we report that tumor cells induce pathological angiogenesis by suppressing expression of the ECM protein receptor αvβ8 integrin. Diminished integrin expression in astrocytoma cells leads to reduced activation of latent TGFβs, resulting in impaired TGFβ receptor signaling in tumor-associated endothelial cells. These data reveal that astrocytoma cells manipulate their angiogenic balance by selectively suppressing αvβ8 integrin expression and function. Finally, these results show that an adhesion and signaling axis normally involved in developmental brain angiogenesis is pathologically exploited in adult brain tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Harpel JG, Metz CN, Nunes I, Loskutoff DJ, Rifkin DB . (1994). An assay for transforming growth factor-beta using cells transfected with a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter-luciferase construct. Anal Biochem 216: 276–284.
Adams RH, Alitalo K . (2007). Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 464–478.
Alcantara Llaguno S, Chen J, Kwon CH, Jackson EL, Li Y, Burns DK et al. (2009). Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model. Cancer Cell 15: 45–56.
Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ et al. (2002). Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell 1: 269–277.
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al. (2006a). Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444: 756–760.
Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li Z, Hjelmeland AB et al. (2006b). Stem cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res 66: 7843–7848.
Bautch VL, James JM . (2009). Neurovascular development: the beginning of a beautiful friendship. Cell Adh Migr 3: 199–204.
Benjamin LE, Keshet E . (1997). Conditional switching of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in tumors: induction of endothelial cell shedding and regression of hemangioblastoma-like vessels by VEGF withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 8761–8766.
Bogler O, Huang HJ, Cavenee WK . (1995). Loss of wild-type p53 bestows a growth advantage on primary cortical astrocytes and facilitates their in vitro transformation. Cancer Res 55: 2746–2751.
Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, Hogg TL, Fuller C, Hamner B et al. (2007). A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell 11: 69–82.
Cambier S, Gline S, Mu D, Collins R, Araya J, Dolganov G et al. (2005). Integrin alpha(v)beta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta by perivascular astrocytes: an angiogenic control switch. Am J Pathol 166: 1883–1894.
Cheng SY, Huang HJ, Nagane M, Ji XD, Wang D, Shih CC et al. (1996). Suppression of glioblastoma angiogenicity and tumorigenicity by inhibition of endogenous expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 8502–8507.
Cheng SY, Nagane M, Huang HS, Cavenee WK . (1997). Intracerebral tumor-associated hemorrhage caused by overexpression of the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF121 and VEGF165 but not VEGF189. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12081–12087.
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA . (2010). Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 9–22.
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A et al. (2007). Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21: 2683–2710.
Holland EC, Celestino J, Dai C, Schaefer L, Sawaya RE, Fuller GN . (2000). Combined activation of Ras and Akt in neural progenitors induces glioblastoma formation in mice. Nat Genet 25: 55–57.
Ishii N, Maier D, Merlo A, Tada M, Sawamura Y, Diserens AC et al. (1999). Frequent co-alterations of TP53, p16/CDKN2A, p14ARF, PTEN tumor suppressor genes in human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol 9: 469–479.
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT . (2007). Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci 8: 610–622.
Kanamori M, Vanden Berg SR, Bergers G, Berger MS, Pieper RO . (2004). Integrin beta3 overexpression suppresses tumor growth in a human model of gliomagenesis: implications for the role of beta3 overexpression in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 64: 2751–2758.
Kaur B, Tan C, Brat DJ, Post DE, Van Meir EG . (2004). Genetic and hypoxic regulation of angiogenesis in gliomas. J Neurooncol 70: 229–243.
Massague J . (2008). TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 134: 215–230.
McCarty JH . (2009a). Cell adhesion and signaling networks in brain neurovascular units. Curr Opin Hematol 16: 209–214.
McCarty JH . (2009b). Integrin-mediated regulation of neurovascular development, physiology and disease. Cell Adh Migr 3: 211–215.
McCarty JH, Barry M, Crowley D, Bronson RT, Lacy-Hulbert A, Hynes RO . (2008). Genetic ablation of alphav integrins in epithelial cells of the eyelid skin and conjunctiva leads to squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol 172: 1740–1747.
McCarty JH, Cook AA, Hynes RO . (2005). An interaction between {alpha}v\{beta}8 integrin and Band 4.1B via a highly conserved region of the Band 4.1 C-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 13479–13483.
McCarty JH, Lacy-Hulbert A, Charest A, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Housman D et al. (2004). Selective ablation of {alpha}v integrins in the central nervous system leads to cerebral hemorrhage, seizures, axonal degenerat. Development 132: 165–176.
McCarty JH, Monahan-Earley RA, Brown LF, Keller M, Gerhardt H, Rubin K et al. (2002). Defective associations between blood vessels and brain parenchyma lead to cerebral hemorrhage in mice lacking alphav integrins. Mol Cell Biol 22: 7667–7677.
Milner R, Relvas JB, Fawcett J, ffrench-Constant C . (2001). Developmental regulation of alphav integrins produces functional changes in astrocyte behavior. Mol Cell Neurosci 18: 108–118.
Mobley AK, Tchaicha JH, Shin J, Hossain MG, McCarty JH . (2009). {beta}8 integrin regulates neurogenesis and neurovascular homeostasis in the adult brain. J Cell Sci 122: 1842–1851.
Mori T, Buffo A, Gotz M . (2005). The novel roles of glial cells revisited: the contribution of radial glia and astrocytes to neurogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol 69: 67–99.
Mu Z, Yang Z, Yu D, Zhao Z, Munger JS . (2008). TGFbeta1 and TGFbeta3 are partially redundant effectors in brain vascular morphogenesis. Mech Dev 125: 508–516.
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S, Dick JE . (2007). A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature 445: 106–110.
Petersen M, Pardali E, van der Horst G, Cheung H, van den Hoogen C, van der Pluijm G et al 2010. Smad2 and Smad3 have opposing roles in breast cancer bone metastasis by differentially affecting tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 29: 1351–1361.
Proctor JM, Zang K, Wang D, Wang R, Reichardt LF . (2005). Vascular development of the brain requires beta8 integrin expression in the neuroepithelium. J Neurosci 25: 9940–9948.
Ramsauer M, D'Amore PA . (2007). Contextual role for angiopoietins and TGFbeta1 in blood vessel stabilization. J Cell Sci 120: 1810–1817.
Riemenschneider MJ, Mueller W, Betensky RA, Mohapatra G, Louis DN . (2005). In situ analysis of integrin and growth factor receptor signaling pathways in human glioblastomas suggests overlapping relationships with focal adhesion kinase activation. Am J Pathol 167: 1379–1387.
Rietze RL, Reynolds BA . (2006). Neural stem cell isolation and characterization. Methods Enzymol 419: 3–23.
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T et al. (2004). Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432: 396–401.
Skuli N, Monferran S, Delmas C, Favre G, Bonnet J, Toulas C et al. (2009). Alphavbeta3/alphavbeta5 integrins–FAK–RhoB: a novel pathway for hypoxia regulation in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 69: 3308–3316.
Sonoda Y, Kanamori M, Deen DF, Cheng SY, Berger MS, Pieper RO . (2003). Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms drives oxygenation and growth but not progression to glioblastoma multiforme in a human model of gliomagenesis. Cancer Res 63: 1962–1968.
Sonoda Y, Ozawa T, Aldape KD, Deen DF, Berger MS, Pieper RO . (2001a). Akt pathway activation converts anaplastic astrocytoma to glioblastoma multiforme in a human astrocyte model of glioma. Cancer Res 61: 6674–6678.
Sonoda Y, Ozawa T, Hirose Y, Aldape KD, McMahon M, Berger MS et al. (2001b). Formation of intracranial tumors by genetically modified human astrocytes defines four pathways critical in the development of human anaplastic astrocytoma. Cancer Res 61: 4956–4960.
Stipursky J, Gomes FC . (2007). TGF-beta1/SMAD signaling induces astrocyte fate commitment in vitro: implications for radial glia development. Glia 55: 1023–1033.
Uchida N, Buck DW, He D, Reitsma MJ, Masek M, Phan TV et al. (2000). Direct isolation of human central nervous system stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 14720–14725.
Uhrbom L, Dai C, Celestino JC, Rosenblum MK, Fuller GN, Holland EC . (2002). Ink4a-Arf loss cooperates with KRas activation in astrocytes and neural progenitors to generate glioblastomas of various morphologies depending on activated Akt. Cancer Res 62: 5551–5558.
Zheng H, Ying H, Yan H, Kimmelman AC, Hiller DJ, Chen AJ et al. (2008). p53 and Pten control neural and glioma stem/progenitor cell renewal and differentiation. Nature 455: 1129–1133.
Zhu J, Motejlek K, Wang D, Zang K, Schmidt A, Reichardt LF . (2002). beta8 integrins are required for vascular morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development 129: 2891–2903.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Nami McCarty for providing assistance with FACS analysis and Dr Russell Pieper for generously providing E6/E7 and G12VH-Ras plasmids. This research was supported by grants awarded to JHM from the National Institutes of Neurological Disease and Stroke (R01NS059876), the National Cancer Institute (P50CA127001) and the Ellison Medical Foundation (AG-NS-0324-06). This work was also supported in part by a National Cancer Institute core grant (CA-16672) awarded to The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tchaicha, J., Mobley, A., Hossain, M. et al. A mosaic mouse model of astrocytoma identifies αvβ8 integrin as a negative regulator of tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 29, 4460–4472 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.199
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of adhesion molecules in cancer and targeted therapy
Science China Life Sciences (2024)
-
ITGA2B and ITGA8 are predictive of prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
The role of integrins in TGFβ activation in the tumour stroma
Cell and Tissue Research (2016)
-
αvβ3, αvβ5 and αvβ6 integrins in brain metastases of lung cancer
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2014)
-
TGF-β signaling in endothelial cells, but not neuroepithelial cells, is essential for cerebral vascular development
Laboratory Investigation (2011)