Abstract
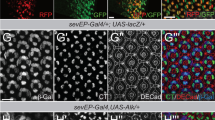
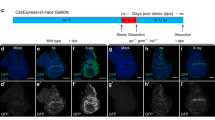
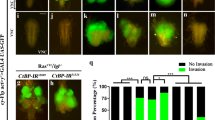
The Abelson (Abl) family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases has an important role in cell morphogenesis, motility, and proliferation. Although the function of Abl has been extensively studied in leukemia, its role in epithelial cell invasion remains obscure. Using the Drosophila wing epithelium as an in vivo model system, we show that overexpression (activation) of Drosophila Abl (dAbl) causes loss of epithelial apical/basal cell polarity and secretion of matrix metalloproteinases, resulting in a cellular invasion and apoptosis. Our in vivo data indicate that dAbl acts downstream of the Src kinases, which are known regulators of cell adhesion and invasion. Downstream of dAbl, Rac GTPases activate two distinct MAPK pathways: c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling (required for cell invasion and apoptosis) and ERK signaling (inducing cell proliferation). Activated Abl also increases the activity of Src members through a positive feedback loop leading to signal amplification. Thus, targeting Src-Abl, using available dual inhibitors, could be of therapeutic importance in tumor cell metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo J, Logothetis C . (2010). Dasatinib: a potent SRC inhibitor in clinical development for the treatment of solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev (doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.02.015).
Biscardi JS, Ishizawar RC, Silva CM, Parsons SJ . (2000). Tyrosine kinase signalling in breast cancer: epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Src interactions in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2: 203–210.
Boureux A, Furstoss O, Simon V, Roche S . (2005). Abl tyrosine kinase regulates a Rac/JNK and a Rac/Nox pathway for DNA synthesis and Myc expression induced by growth factors. J Cell Sci 118: 3717–3726.
Brand AH, Perrimon N . (1993). Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118: 401–415.
Coso OA, Chiariello M, Yu JC, Teramoto H, Crespo P, Xu N et al. (1995). The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 81: 1137–1146.
Coussens LM, Werb Z . (2002). Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420: 860–867.
Das J, Chen P, Norris D, Padmanabha R, Lin J, Moquin RV et al. (2006). 2-aminothiazole as a novel kinase inhibitor template. Structure-activity relationship studies toward the discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1- piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide (dasatinib, BMS-354825) as a potent pan-Src kinase inhibitor. J Med Chem 49: 6819–6832.
Davis RJ . (2000). Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103: 239–252.
Debant A, Serra-Pages C, Seipel K, O'Brien S, Tang M, Park SH et al. (1996). The multidomain protein Trio binds the LAR transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase, contains a protein kinase domain, and has separate rac-specific and rho-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 5466–5471.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP . (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25: 9–34.
Dolfi F, Garcia-Guzman M, Ojaniemi M, Nakamura H, Matsuda M, Vuori K . (1998). The adaptor protein Crk connects multiple cellular stimuli to the JNK signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15394–15399.
Golas JM, Arndt K, Etienne C, Lucas J, Nardin D, Gibbons J et al. (2003). SKI-606, a 4-anilino-3-quinolinecarbonitrile dual inhibitor of Src and Abl kinases, is a potent antiproliferative agent against chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in culture and causes regression of K562 xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res 63: 375–381.
Hall A . (1998). Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279: 509–514.
Harden N, Loh HY, Chia W, Lim L . (1995). A dominant inhibitory version of the small GTP-binding protein Rac disrupts cytoskeletal structures and inhibits developmental cell shape changes in Drosophila. Development 121: 903–914.
Hirohashi S . (1998). Inactivation of the E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in human cancers. Am J Pathol 153: 333–339.
Huh JR, Guo M, Hay BA . (2004). Compensatory proliferation induced by cell death in the Drosophila wing disc requires activity of the apical cell death caspase Dronc in a nonapoptotic role. Curr Biol 14: 1262–1266.
Igaki T, Pagliarini RA, Xu T . (2006). Loss of cell polarity drives tumor growth and invasion through JNK activation in Drosophila. Curr Biol 16: 1139–1146.
Irby RB, Yeatman TJ . (2000). Role of Src expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene 19: 5636–5642.
Kennedy NJ, Davis RJ . (2003). Role of JNK in tumor development. Cell Cycle 2: 199–201.
Lanier LM, Gertler FB . (2000). From Abl to actin: Abl tyrosine kinase and associated proteins in growth cone motility. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10: 80–87.
Lin J, Arlinghaus R . (2008). Activated c-Abl tyrosine kinase in malignant solid tumors. Oncogene 27: 4385–4391.
Luster AD, Alon R, von Andrian UH . (2005). Immune cell migration in inflammation: present and future therapeutic targets. Nat Immunol 6: 1182–1190.
Martin-Blanco E, Gampel A, Ring J, Virdee K, Kirov N, Tolkovsky AM et al. (1998). puckered encodes a phosphatase that mediates a feedback loop regulating JNK activity during dorsal closure in Drosophila. Genes Dev 12: 557–570.
Navarro P, Gomez M, Pizarro A, Gamallo C, Quintanilla M, Cano A . (1991). A role for the E-cadherin cell-cell adhesion molecule during tumor progression of mouse epidermal carcinogenesis. J Cell Biol 115: 517–533.
Pastor-Pareja JC, Grawe F, Martin-Blanco E, Garcia-Bellido A . (2004). Invasive cell behavior during Drosophila imaginal disc eversion is mediated by the JNK signaling cascade. Dev Cell 7: 387–399.
Pedraza LG, Stewart RA, Li DM, Xu T . (2004). Drosophila Src-family kinases function with Csk to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncogene 23: 4754–4762.
Pendergast AM . (2002). The Abl family kinases: mechanisms of regulation and signaling. Adv Cancer Res 85: 51–100.
Raitano AB, Halpern JR, Hambuch TM, Sawyers CL . (1995). The Bcr-Abl leukemia oncogene activates Jun kinase and requires Jun for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11746–11750.
Ren R, Ye ZS, Baltimore D . (1994). Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev 8: 783–795.
Ryoo HD, Gorenc T, Steller H . (2004). Apoptotic cells can induce compensatory cell proliferation through the JNK and the Wingless signaling pathways. Dev Cell 7: 491–501.
Salhia B, Tran NL, Chan A, Wolf A, Nakada M, Rutka F et al. (2008). The guanine nucleotide exchange factors trio, Ect2, and Vav3 mediate the invasive behavior of glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 173: 1828–1838.
Sanchez-Madrid F, del Pozo MA . (1999). Leukocyte polarization in cell migration and immune interactions. EMBO J 18: 501–511.
Sawyers CL . (1999). Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 340: 1330–1340.
Shindo M, Wada H, Kaido M, Tateno M, Aigaki T, Tsuda L et al. (2008). Dual function of Src in the maintenance of adherens junctions during tracheal epithelial morphogenesis. Development 135: 1355–1364.
Sirvent A, Boureux A, Simon V, Leroy C, Roche S . (2007). The tyrosine kinase Abl is required for Src-transforming activity in mouse fibroblasts and human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26: 7313–7323.
Skorski T, Wlodarski P, Daheron L, Salomoni P, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Majewski M et al. (1998). BCR/ABL-mediated leukemogenesis requires the activity of the small GTP-binding protein Rac. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 11858–11862.
Srinivasan D, Plattner R . (2006). Activation of Abl tyrosine kinases promotes invasion of aggressive breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66: 5648–5655.
Srivastava A, Pastor-Pareja JC, Igaki T, Pagliarini R, Xu T . (2007). Basement membrane remodeling is essential for Drosophila disc eversion and tumor invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 2721–2726.
Stevens TL, Rogers EM, Koontz LM, Fox DT, Homem CC, Nowotarski SH et al. (2008). Using Bcr-Abl to examine mechanisms by which abl kinase regulates morphogenesis in Drosophila. Mol Biol Cell 19: 378–393.
Sugimura M, Kobayashi K, Sagae S, Nishioka Y, Ishioka S, Terasawa K et al. (2000). Mutation of the SRC gene in endometrial carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 91: 395–398.
Taagepera S, McDonald D, Loeb JE, Whitaker LL, McElroy AK, Wang JY et al. (1998). Nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of C-ABL tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7457–7462.
Thiery JP . (2003). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 740–746.
Van Etten RA . (1999). Cycling, stressed-out and nervous: cellular functions of c-Abl. Trends Cell Biol 9: 179–186.
Vidal M, Larson DE, Cagan RL . (2006). Csk-deficient boundary cells are eliminated from normal Drosophila epithelia by exclusion, migration, and apoptosis. Dev Cell 10: 33–44.
Vleminckx K, Vakaet Jr L, Mareel M, Fiers W, van Roy F . (1991). Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role. Cell 66: 107–119.
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ, Greenberg ME . (1995). Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 270: 1326–1331.
Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J, Condeelis J . (2005). Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 559–564.
Yang JH, Wylie-Sears J, Bischoff J . (2008). Opposing actions of Notch1 and VEGF in post-natal cardiac valve endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374: 512–516.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Bloomington Stock Center, DSHB, Ed Giniger, and Ross Cagan for fly stocks and antibodies. We are grateful to members of the Mlodzik lab for helpful suggestions, discussions, and criticism, Ross Cagan and members of the Cagan lab for discussion and reagents, in particular Tirtha Das. We also thank William Gault for critical reading of the manuscript, Nadinath Nillegoda, and Maneesha Chhikara for helpful comments and suggestions, and Joyce Lau, Sophy Okello, and Andrea Blitzer for technical help. Confocal laser microscopy was performed at the MSSM Microscopy SRF, supported by an NIH/NCI shared instrumentation grant. This research was supported by NIH/National Eye Institute Grant R01 EY14597 to MM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J., Aaronson, S. & Mlodzik, M. Drosophila Abelson kinase mediates cell invasion and proliferation through two distinct MAPK pathways. Oncogene 29, 4033–4045 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.155
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.155
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Basolateral protrusion and apical contraction cooperatively drive Drosophila germ-band extension
Nature Cell Biology (2017)
-
Adherens Junction and E-Cadherin complex regulation by epithelial polarity
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2016)
-
Src42A modulates tumor invasion and cell death via Ben/dUev1a-mediated JNK activation in Drosophila
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
Sds22/PP1 links epithelial integrity and tumor suppression via regulation of myosin II and JNK signaling
Oncogene (2011)