Abstract
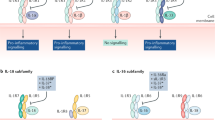
The IL-12 family members, IL-12, IL-23, IL-27 and IL-35, are heterodimeric cytokines that share subunits and have important roles in autoimmunity. As well as their structural relationship the IL-12 family cytokines share some biological characteristics but have functional differences. These cytokines contribute to immune-mediated inflammation and our improved knowledge of their actions has led to alteration of the TH1–TH2 paradigm. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), leukocyte migration, bone erosions and angiogenesis are modulated by an IL-23–IL-17 cascade, which can be negated in part by IL-12, IL-27 and IL-35 function. However, the IL-12 family members are a relatively new area of research and data have been generated mostly at the preclinical stage. Further studies in patients with RA are, therefore, required to determine whether these cytokines are valid targets for RA therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collison, L. W. & Vignali, D. A. Interleukin-35: odd one out or part of the family? Immunol. Rev. 226, 248–262 (2008).
Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 133–146 (2003).
Collison, L. W. et al. The composition and signaling of the IL-35 receptor are unconventional. Nat. Immunol. 13, 290–299 (2012).
Hunter, C. A. New IL-12-family members: IL-23 and IL-27, cytokines with divergent functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 521–531 (2005).
Weaver, C. T., Hatton, R. D., Mangan, P. R. & Harrington, L. E. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 821–852 (2007).
Nakanishi, K., Yoshimoto, T., Tsutsui, H. & Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 is a unique cytokine that stimulates both TH1 and TH2 responses depending on its cytokine milieu. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 12, 53–72 (2001).
Petrovic-Rackov, L. & Pejnovic, N. Clinical significance of IL-18, IL-15, IL-12 and TNFα measurement in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 25, 448–452 (2006).
Yin, Z. et al. The elevated ratio of interferon γ-/interleukin-4-positive T cells found in synovial fluid and synovial membrane of rheumatoid arthritis patients can be changed by interleukin-4 but not by interleukin-10 or transforming growth factor β. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38, 1058–1067 (1999).
Leipe, J. et al. Role of TH17 cells in human autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 2876–2885 (2010).
Shahrara, S., Huang, Q., Mandelin, A. M. 2nd & Pope, R. M. TH17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 10, R93 (2008).
Holmdahl, R. et al. Collagen induced arthritis as an experimental model for rheumatoid arthritis. Immunogenetics, pathogenesis and autoimmunity. APMIS 97, 575–584 (1989).
Germann, T. et al. Administration of interleukin 12 in combination with type II collagen induces severe arthritis in DBA/1 mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 4823–4827 (1995).
Joosten, L. A., Lubberts, E., Helsen, M. M. & van den Berg, W. B. Dual role of IL-12 in early and late stages of murine collagen type II arthritis. J. Immunol. 159, 4094–4102 (1997).
Paunovic, V., Carroll, H. P., Vandenbroeck, K. & Gadina, M. Signalling, inflammation and arthritis: crossed signals: the role of interleukin (IL)-12, -17, -23 and -27 in autoimmunity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47, 771–776 (2008).
Sarkar, S. & Fox, D. A. Targeting IL-17 and TH17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 36, 345–366 (2010).
Iwakura, Y. & Ishigame, H. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1218–1222 (2006).
Paradowska-Gorycka, A., Grzybowska-Kowalczyk, A., Wojtecka-Lukasik, E. & Maslinski, S. IL-23 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Immunol. 71, 134–145 (2010).
Murphy, C. A. et al. Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1951–1957 (2003).
Brentano, F. et al. Abundant expression of the interleukin (IL)23 subunit p19, but low levels of bioactive IL23 in the rheumatoid synovium: differential expression and Toll-like receptor-(TLR) dependent regulation of the IL23 subunits, p19 and p40, in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 143–150 (2009).
Stamp, L. K., Easson, A., Pettersson, L., Highton, J. & Hessian, P. A. Monocyte derived interleukin (IL)-23 is an important determinant of synovial IL-17A expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 36, 2403–2408 (2009).
Langrish, C. L. et al. IL-12 and IL-23: master regulators of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 202, 96–105 (2004).
Liu, F. L. et al. Interleukin (IL)-23 p19 expression induced by IL-1β in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes with rheumatoid arthritis via active nuclear factor-κB and AP-1 dependent pathway. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46, 1266–1273 (2007).
Kim, H. R. et al. The clinical role of IL-23p19 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 36, 259–264 (2007).
Chen, L., Wei, X. Q., Evans, B., Jiang, W. & Aeschlimann, D. IL-23 promotes osteoclast formation by up-regulation of receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK) expression in myeloid precursor cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 2845–2854 (2008).
Li, X. et al. IL-23 induces receptor activator of NF-κB ligand expression in fibroblast-like synoviocytes via STAT3 and NF-κB signal pathways. Immunol. Lett. 127, 100–107 (2010).
Sato, K. et al. TH17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2673–2682 (2006).
Kotake, S. et al. IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 1345–1352 (1999).
Nakae, S., Nambu, A., Sudo, K. & Iwakura, Y. Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 171, 6173–6177 (2003).
Ratsimandresy, R. A. et al. Active immunization against IL-23p19 improves experimental arthritis. Vaccine 29, 9329–9336 (2011).
Wiekowski, M. T. et al. Ubiquitous transgenic expression of the IL-23 subunit p19 induces multiorgan inflammation, runting, infertility, and premature death. J. Immunol. 166, 7563–7570 (2001).
Niedbala, W. et al. Interleukin 27 attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 1474–1479 (2008).
Pflanz, S. et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4+ T cells. Immunity 16, 779–790 (2002).
Diveu, C., McGeachy, M. J. & Cua, D. J. Cytokines that regulate autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 20, 663–668 (2008).
Cao, Y., Doodes, P. D., Glant, T. T. & Finnegan, A. IL-27 induces a TH1 immune response and susceptibility to experimental arthritis. J. Immunol. 180, 922–930 (2008).
Batten, M. et al. Interleukin 27 limits autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing the development of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat. Immunol. 7, 929–936 (2006).
Stumhofer, J. S. et al. Interleukin 27 negatively regulates the development of interleukin 17-producing T helper cells during chronic inflammation of the central nervous system. Nat. Immunol. 7, 937–945 (2006).
Stumhofer, J. S. et al. Interleukins 27 and 6 induce STAT3-mediated T cell production of interleukin 10. Nat. Immunol. 8, 1363–1371 (2007).
Wojno, E. D. & Hunter, C. A. New directions in the basic and translational biology of interleukin-27. Trends Immunol. 33, 91–97 (2012).
Iyer, S. S., Ghaffari, A. A. & Cheng, G. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated IL-10 transcriptional regulation requires sequential induction of type I IFNs and IL-27 in macrophages. J. Immunol. 185, 6599–6607 (2010).
Kalliolias, G. D., Gordon, R. A. & Ivashkiv, L. B. Suppression of TNFα and IL-1 signaling identifies a mechanism of homeostatic regulation of macrophages by IL-27. J. Immunol. 185, 7047–7056 (2010).
Kalliolias, G. D., Zhao, B., Triantafyllopoulou, A., Park-Min, K. H. & Ivashkiv, L. B. Interleukin-27 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis by abrogating RANKL-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 and suppressing proximal RANK signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 402–413 (2010).
Pickens, S. R. et al. Local expression of IL-27 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 2289–2298 (2011).
Collison, L. W. et al. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature 450, 566–569 (2007).
Collison, L. W. et al. IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population. Nat. Immunol. 11, 1093–1101 (2010).
Niedbala, W. et al. IL-35 is a novel cytokine with therapeutic effects against collagen-induced arthritis through the expansion of regulatory T cells and suppression of TH17 cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 37, 3021–3029 (2007).
Kochetkova, I., Golden, S., Holderness, K., Callis, G. & Pascual, D. W. IL-35 stimulation of CD39+ regulatory T cells confers protection against collagen II-induced arthritis via the production of IL-10. J. Immunol. 184, 7144–7153 (2010).
Veys, E. M. et al. Interferon γ in rheumatoid arthritis—a double blind study comparing human recombinant interferon γ with placebo. J. Rheumatol. 15, 570–574 (1988).
Seitz, M., Franke, M. & Kirchner, H. Induction of antinuclear antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving treatment with human recombinant interferon γ. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 47, 642–644 (1988).
Krausz, S. et al. Brief report: a phase IIa, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of apilimod mesylate, an interleukin-12/interleukin-23 inhibitor, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 26, 1750–1755 (2012).
Leonardi, C. L. et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 76-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 1). Lancet 371, 1665–1674 (2008).
Gottlieb, A. et al. Ustekinumab, a human interleukin 12/23 monoclonal antibody, for psoriatic arthritis: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Lancet 373, 633–640 (2009).
Genovese, M. C. et al. LY2439821, a humanized anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a phase I randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept study. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 929–939 (2010).
Papp, K. A. et al. Brodalumab, an anti-interleukin-17-receptor antibody for psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1181–1189 (2012).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the NIH (AR056099 and AR055240), the American College of Rheumatology Research and Education Foundation (Within Our Reach: Finding a Cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis campaign), and the Department of Defense (PR093477) as well as the Arthritis Foundation (Innovative Research Grant).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Shahrara researched the data for the article and provided a substantial contribution to discussions of the content. R. Pope and S. Shahrara wrote the article and reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Table 1
The effect of IL 12 family cytokines in murine CIA. (DOC 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pope, R., Shahrara, S. Possible roles of IL-12-family cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9, 252–256 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.170
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.170
This article is cited by
-
Is adrenomedullin upregulation due to apical periodontitis independent of periodontal disease?
Odontology (2023)
-
Interleukin-35 pathobiology in periodontal disease: a systematic scoping review
BMC Oral Health (2021)
-
The role of IL-18 in addition to Th17 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis development and treatment in women
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
IL-35: a new immunomodulator in autoimmune rheumatic diseases
Immunologic Research (2018)
-
Interleukin-27 as a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis: has the time come?
Clinical Rheumatology (2013)