Key Points
-
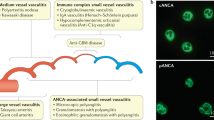
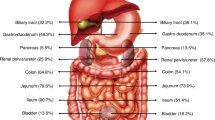
Gastrointestinal manifestations are rarely the predominating features of systemic vasculitides but can rapidly become life-threatening
-
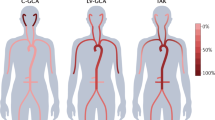
Gastrointestinal involvement is rare in large-vessel vasculitides and is mainly due to large-vessel stenosis or occlusion, with long-segment gastrointestinal tract ischaemic manifestations
-
Small-vessel vasculitides can cause various gastrointestinal manifestations, including mucosal purpura (risk of haemorrhage), patchy granulomatous or ischaemic ulcerations that can mimic IBD and can perforate
-
Liver involvement is rarely clinically significant in systemic vasculitides, except for rare infarcts due to large or medium-sized vasculitic occlusions and Budd–Chiari syndrome in patients with Behçet's disease
-
Treatment of gastrointestinal manifestations must be prompt, adapted to the severity of the disease and conducted in collaboration with general surgery and interventional radiology as needed
-
Patients with single-organ gastrointestinal vasculitis must be followed closely for the development of systemic vasculitis, although such a progression is observed in a maximum of one-quarter of patients over the subsequent 5 years
Abstract
Systemic vasculitides are caused by inflammation of blood vessels and can affect any organ and any part of the gastrointestinal tract, hepatic and biliary system, as well as the pancreas. These disorders can cause a wide array of gastrointestinal manifestations, from asymptomatic elevated transaminase levels and mild abdominal pain to potentially life-threatening bowel perforations and peritonitis. A diagnosis based solely on gastrointestinal symptoms is challenging as these manifestations are not specific. Conversely, diagnostic and therapeutic delays can be rapidly detrimental. In this article, we review the epidemiology, characteristics and management of the main gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic vasculitides, including polyarteritis nodosa and antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitides, as well as isolated vasculitides limited to the gastrointestinal tract.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jennette, J. C. et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 1–11 (2013).
Bailey, M., Chapin, W., Licht, H. & Reynolds, J. C. The effects of vasculitis on the gastrointestinal tract and liver. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 27, 747–782 (1998).
Guillevin, L. et al. Prognostic factors in polyarteritis nodosa and Churg–Strauss syndrome. A prospective study in 342 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 75, 17–28 (1996).
Mason, J. C. Takayasu arteritis: surgical interventions. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 27, 45–52 (2015).
Alibaz-Oner, F. & Direskeneli, H. Update on Takayasu's arteritis. Presse Med. 44, e259–e265 (2015).
Terao, C., Yoshifuji, H. & Mimori, T. Recent advances in Takayasu arteritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 17, 238–247 (2014).
Hall, S. et al. Takayasu arteritis. A study of 32 North American patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 64, 89–99 (1985).
Schmidt, J. et al. Diagnostic features, treatment, and outcomes of Takayasu arteritis in a US cohort of 126 patients. Mayo Clin. Proc. 88, 822–830 (2013).
Reddi, A. & Chetty, R. Primary aorto-esophageal fistula due to Takayasu's aortitis. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 12, 112–114 (2003).
Cohen, C. D., Kirsch, R. E., Saunders, S. J., Campbell, J. A. & Terblanche, J. Takayasu's syndrome — evidence for a liver lesion. S. Afr. Med. J. 57, 1076–1078 (1980).
Sy, A. et al. Vasculitis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: a study of 32 patients and systematic review of the literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 45, 475–482 (2016).
Terao, C. et al. Takayasu arteritis and ulcerative colitis: high rate of co-occurrence ratio and genetic overlap. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67, 2226–2232 (2015)
Hoffman, G. S. et al. Treatment of glucocorticoid-resistant or relapsing Takayasu arteritis with methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 37, 578–582 (1994).
Koster, M. J., Matteson, E. L. & Warrington, K. J. Recent advances in the clinical management of giant cell arteritis and Takayasu arteritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 28, 211–217 (2016).
Goel, R., Danda, D., Mathew, J. & Edwin, N. Mycophenolate mofetil in Takayasu's arteritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 29, 329–332 (2010).
Keser, G., Direskeneli, H. & Aksu, K. Management of Takayasu arteritis: a systematic review. Rheumatology 53, 793–801 (2014).
Mekinian, A. et al. Efficacy of biological-targeted treatments in Takayasu arteritis: multicenter, retrospective study of 49 patients. Circulation 132, 1693–1700 (2015).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00556439?term (2015).
Gonzalez-Gay, M. A. et al. Epidemiology of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Arthritis Rheum. 61, 1454–1461 (2009).
Gonzalez-Gay, M. A. & Pina, T. Giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: an update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 17, 6 (2015).
Scola, C. J., Li, C. & Upchurch, K. S. Mesenteric involvement in giant cell arteritis. An underrecognized complication? Analysis of a case series with clinicoanatomic correlation. Medicine (Baltimore) 87, 45–51 (2008).
Evans, J. M., O'Fallon, W. M. & Hunder, G. G. Increased incidence of aortic aneurysm and dissection in giant cell (temporal) arteritis: a population-based study. Ann. Intern. Med. 122, 502–507 (1995).
Bienvenu, B. et al. Management of giant cell arteritis: recommendations of the French Study Group for Large Vessel Vasculitis (GEFA). Rev. Med. Interne 37, 154–165 (2016).
Ilan, Y. & Ben-Chetrit, E. Liver involvement in giant cell arteritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 12, 219–222 (1993).
Xu, J., Bjornsson, E. S. & Sundaram, V. Severe cholestatic hepatitis due to large vessel vasculitis: report of two cases. Gastroenterol. Rep. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/gastro/gov061 (2015).
Lee, S., Childerhouse, A. & Moss, K. Gastrointestinal symptoms and granulomatous vasculitis involving the liver in giant cell arteritis: a case report and review of the literature. Rheumatology 50, 2316–2317 (2011).
Heneghan, M. A., Feeley, K. M., DeFaoite, N., Little, M. P. & O'Gorman, T. A. Granulomatous liver disease and giant-cell arteritis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43, 2164–2167 (1998).
Furuta, S., Cousins, C., Chaudhry, A. & Jayne, D. Clinical features and radiological findings in large vessel vasculitis: are Takayasu arteritis and giant cell arteritis 2 different diseases or a single entity? J. Rheumatol. 42, 300–308 (2015).
Mahr, A. D. et al. Adjunctive methotrexate for treatment of giant cell arteritis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 2789–2797 (2007).
Villiger, P. M. et al. Tocilizumab for induction and maintenance of remission in giant cell arteritis: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 387, 1921–1927 (2016).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01791153?term (2016).
Langford, C. A. et al. A randomized double-blind trial of abatacept and glucocorticoids for the treatment of giant cell arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 67 (Suppl. 10), 9L (2015).
De Virgilio, A. et al. Polyarteritis nodosa: a contemporary overview. Autoimmun. Rev. 15, 564–570 (2016).
Levine, S. M., Hellmann, D. B. & Stone, J. H. Gastrointestinal involvement in polyarteritis nodosa: presentation and outcomes in 24 patients (1986–2000). Am. J. Med. 112, 386–391 (2002).
Pagnoux, C., Mahr, A., Cohen, P. & Guillevin, L. Presentation and outcome of gastrointestinal involvement in systemic necrotizing vasculitides: analysis of 62 patients with polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener granulomatosis, Churg–Strauss syndrome, or rheumatoid arthritis-associated vasculitis. Medicine (Baltimore) 84, 115–128 (2005).
Singhal, M. et al. Role of multidetector abdominal CT in the evaluation of abnormalities in polyarteritis nodosa. Clin. Radiol. 71, 222–227 (2016).
Li, S. J. et al. Clinical and morphologic spectrum of renal involvement in patients with HBV-associated cryoglobulinemia. Nephrology http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/nep.12795 (2016).
Guillevin, L. et al. Hepatitis B virus-associated polyarteritis nodosa: clinical characteristics, outcome, and impact of treatment in 115 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 84, 313–322 (2005).
Forbess, L. & Bannykh, S. Polyarteritis nodosa. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 41, 33–46 (2015).
Mahr, A., Guillevin, L., Poissonnet, M. & Ayme, S. Prevalences of polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener's granulomatosis, and Churg–Strauss syndrome in a French urban multiethnic population in 2000: a capture–recapture estimate. Arthritis Rheum. 51, 92–99 (2004).
Bourgarit, A. et al. Deaths occurring during the first year after treatment onset for polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg–Strauss syndrome: a retrospective analysis of causes and factors predictive of mortality based on 595 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 84, 323–330 (2005).
Pagnoux, C. et al. Clinical features and outcomes in 348 patients with polyarteritis nodosa: a systematic retrospective study of patients diagnosed between 1963 and 2005 and entered into the French Vasculitis Study Group Database. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 616–626 (2010).
Sharma, A. et al. Uncommon presentations of primary systemic necrotizing vasculitides: the Great Masquerades. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 17, 562–572 (2014).
Guillevin, L. et al. Treatment of polyarteritis nodosa and microscopic polyangiitis with poor prognosis factors: a prospective trial comparing glucocorticoids and six or twelve cyclophosphamide pulses in sixty-five patients. Arthritis Rheum. 49, 93–100 (2003).
Samson, M. et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized trial on 118 patients with polyarteritis nodosa or microscopic polyangiitis without poor-prognosis factors. Autoimmun. Rev. 13, 197–205 (2014).
Puechal, X. et al. Does adding azathioprine to glucocorticoid induction increase the remission rate and prevent relapses in patients with systemic necrotizing vasculitides without poor-prognosis factors? A multicenter, double-blind randomized controlled trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 67 (Suppl. 10), 1086 (2015).
Guillevin, L. et al. Short-term corticosteroids then lamivudine and plasma exchanges to treat hepatitis B virus-related polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 51, 482–487 (2004).
Pagnoux, C., Cohen, P. & Guillevin, L. Vasculitides secondary to infections. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 24, S71–S81 (2006).
Makino, N. et al. Descriptive epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in Japan, 2011-2012: from the results of the 22nd nationwide survey. J. Epidemiol. 25, 239–245 (2015).
Singh, S., Vignesh, P. & Burgner, D. The epidemiology of Kawasaki disease: a global update. Arch. Dis. Child. 100, 1084–1088 (2015).
Fraison, J. B. et al. Kawasaki disease in adults: observations in France and literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 15, 242–249 (2016).
Gomard-Mennesson, E. et al. Kawasaki disease in adults: report of 10 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 89, 149–158 (2010).
Baker, A. L. et al. Associated symptoms in the ten days before diagnosis of Kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. 154, 592–595. e2 (2009).
Zulian, F. et al. Acute surgical abdomen as presenting manifestation of Kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. 142, 731–735 (2003).
Singh, R., Ward, C., Walton, M. & Persad, R. Atypical Kawasaki disease and gastrointestinal manifestations. Paediatr. Child Health 12, 235–237 (2007).
Yim, D., Curtis, N., Cheung, M. & Burgner, D. An update on Kawasaki disease II: clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and outcomes. J. Paediatr. Child Health 49, 614–623 (2013).
Newburger, J. W. et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114, 1708–1733 (2004).
Shulman, S. T. & Rowley, A. H. Kawasaki disease: insights into pathogenesis and approaches to treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 11, 475–482 (2015).
Ha, H. K. et al. Radiologic features of vasculitis involving the gastrointestinal tract. Radiographics 20, 779–794 (2000).
Lhote, F. & Guillevin, L. Polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg–Strauss syndrome. Clinical aspects and treatment. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 21, 911–947 (1995).
Gibelin, A., Maldini, C. & Mahr, A. Epidemiology and etiology of Wegener granulomatosis, microscopic polyangiitis, Churg–Strauss syndrome and Goodpasture syndrome: vasculitides with frequent lung involvement. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 32, 264–273 (2011).
Akbulut, S. Multiple ileal perforations in a patient with Wegener's granulomatosis: a case report and literature review. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 16, 857–862 (2012).
Nay, J., Menias, C. O., Mellnick, V. M. & Balfe, D. M. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic disease: a multimodality review. Abdom. Imaging. 40, 1926–1943 (2015).
Schneider, A., Merikhi, A. & Frank, B. B. Autoimmune disorders: gastrointestinal manifestations and endoscopic findings. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 16, 133–151 (2006).
Humbert, S. et al. Inflammatory bowel diseases in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: 11 retrospective cases from the French Vasculitis Study Group. Rheumatology 54, 1970–1975 (2015).
Camilleri, M., Pusey, C. D., Chadwick, V. S. & Rees, A. J. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic vasculitis. Q. J. Med. 52, 141–149 (1983).
Valerieva, Y., Golemanov, B., Tzolova, N. & Mitova, R. Pancreatic mass as an initial presentation of severe Wegener's granulomatosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 26, 267–269 (2013).
Schirmer, J. H. et al. Clinical presentation and long-term outcome of 144 patients with microscopic polyangiitis in a monocentric German cohort. Rheumatology 55, 71–79 (2016).
Groh, M. et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg–Strauss) (EGPA) Consensus Task Force recommendations for evaluation and management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 26, 545–553 (2015).
Comarmond, C. et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg–Strauss): clinical characteristics and long-term followup of the 383 patients enrolled in the French Vasculitis Study Group cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 270–281 (2013).
Moosig, F. et al. A vasculitis centre based management strategy leads to improved outcome in eosinophilic granulomatosis and polyangiitis (Churg–Strauss, EGPA): monocentric experiences in 150 patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 1011–1017 (2013).
Pagnoux, C. Churg–Strauss syndrome: evolving concepts. Discov. Med. 9, 243–252 (2010).
Gayraud, M. et al. Long-term followup of polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg–Strauss syndrome: analysis of four prospective trials including 278 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 44, 666–675 (2001).
Holle, J. U. et al. Improved outcome in 445 patients with Wegener's granulomatosis in a German vasculitis center over four decades. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 257–266 (2011).
Flossmann, O. et al. Long-term patient survival in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 488–494 (2011).
Stone, J. H. et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 221–232 (2010).
Kim, S., Marigowda, G., Oren, E., Israel, E. & Wechsler, M. E. Mepolizumab as a steroid-sparing treatment option in patients with Churg–Strauss syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 125, 1336–1343 (2010).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02020889?term (2016).
Pagnoux, C. et al. Azathioprine or methotrexate maintenance for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 2790–2803 (2008).
Hiemstra, T. F. et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus azathioprine for remission maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 304, 2381–2388 (2010).
Guillevin, L. et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 1771–1780 (2014).
McGeoch, L. et al. CanVasc recommendations for the management of antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitides. J. Rheumatol. 43, 97–120 (2016).
Audemard-Verger, A., Pillebout, E., Guillevin, L., Thervet, E. & Terrier, B. IgA vasculitis (Henoch–Shönlein purpura) in adults: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Autoimmun. Rev. 14, 579–585 (2015).
Pillebout, E. & Verine, J. [Henoch–Schönlein purpura in the adult]. Rev. Med. Interne 35, 372–381 (in French) (2014).
Ebert, E. C. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53, 2011–2019 (2008).
Esaki, M. et al. Gastrointestinal involvement in Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Gastrointest. Endosc. 56, 920–923 (2002).
Nam, E. J. et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding in adult patients with Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Endoscopy 46, 981–986 (2014).
Chao, H. C., Kong, M. S. & Lin, S. J. Hepatobiliary involvement of Henoch–Schönlein purpura in children. Acta Paediatr. Taiwan 41, 63–68 (2000).
Pillebout, E. et al. Addition of cyclophosphamide to steroids provides no benefit compared with steroids alone in treating adult patients with severe Henoch Schönlein purpura. Kidney Int. 78, 495–502 (2010).
Pillebout, E. et al. Successful outcome using rituximab as the only immunomodulation in Henoch–Schönlein purpura: case report. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 26, 2044–2046 (2011).
Chou, T. et al. Successful treatment of Henoch–Schönlein purpura with recurrent gastrointestinal involvement with mycophenolate mofetil: a brief report. Clin. Pediatr. 54, 900–903 (2015).
Ferri, C. et al. Mixed cryoglobulinemia: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 231 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 33, 355–374 (2004).
Ghetie, D., Mehraban, N. & Sibley, C. H. Cold hard facts of cryoglobulinemia: updates on clinical features and treatment advances. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 41, 93–108 (2015).
Dammacco, F., Racanelli, V., Russi, S. & Sansonno, D. The expanding spectrum of HCV-related cryoglobulinemic vasculitis: a narrative review. Clin. Exp. Med. 16, 233–242 (2016).
Cacoub, P., Terrier, B. & Saadoun, D. Hepatitis C virus-induced vasculitis: therapeutic options. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 24–30 (2014).
Cacoub, P., Comarmond, C., Domont, F., Savey, L. & Saadoun, D. Cryoglobulinemia vasculitis. Am. J. Med. 128, 950–955 (2015).
Retamozo, S. et al. Life-threatening cryoglobulinemic patients with hepatitis C: clinical description and outcome of 279 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0b013e3182a5cf71 (2013).
Terrier, B. et al. Prognostic factors in patients with hepatitis C virus infection and systemic vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 1748–1757 (2011).
Terrier, B. et al. Prognostic factors of survival in patients with non-infectious mixed cryoglobulinaemia vasculitis: data from 242 cases included in the CryoVas survey. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 374–380 (2013).
Sise, M. E. et al. Treatment of hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia with direct-acting antiviral agents. Hepatology 63, 408–417 (2016).
Quartuccio, L. et al. Efficacy of rituximab in severe and mild abdominal vasculitis in the course of mixed cryoglobulinemia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 28, 84–87 (2010).
Saadoun, D. et al. Peg-IFNα/ribavirin/protease inhibitor combination in hepatitis C virus associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis: results at week 24. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 831–837 (2014).
Ho, A. C., Roat, M. I., Venbrux, A. & Hellmann, D. B. Cogan's syndrome with refractory abdominal aortitis and mesenteric vasculitis. J. Rheumatol. 26, 1404–1407 (1999).
Mahr, A. & Maldini, C. [Epidemiology of Behçet's disease]. Rev. Med. Interne 35, 81–89 (in French) (2014).
Skef, W., Hamilton, M. J. & Arayssi, T. Gastrointestinal Behçet's disease: a review. World J. Gastroenterol. 21, 3801–3812 (2015).
Sibley, C. et al. Behçet syndrome manifestations and activity in the United States versus Turkey — a cross-sectional cohort comparison. J. Rheumatol. 41, 1379–1384 (2014).
Lee, S. K., Kim, B. K., Kim, T. I. & Kim, W. H. Differential diagnosis of intestinal Behçet's disease and Crohn's disease by colonoscopic findings. Endoscopy 41, 9–16 (2009).
Vaiopoulos, A. G., Sfikakis, P. P., Kanakis, M. A., Vaiopoulos, G. & Kaklamanis, P. G. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behçet's disease: advances in evaluation and management. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 32, S140–S148 (2014).
Zeidan, M. J. et al. Behçet's disease physiopathology: a contemporary review. Auto Immun. Highlights 7, 4 (2016).
Orikasa, H. et al. A case of Behçet's disease with occlusion of both caval veins and “downhill” esophageal varices. J. Gastroenterol. 29, 506–510 (1994).
Ozenc, A., Bayraktar, Y. & Baykal, A. Pyloric stenosis with esophageal involvement in Behçet's syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 85, 727–728 (1990).
Moon, C. M. et al. Prediction of free bowel perforation in patients with intestinal Behçet's disease using clinical and colonoscopic findings. Dig. Dis. Sci. 55, 2904–2911 (2010).
Bayraktar, Y., Balkanci, F., Bayraktar, M. & Calguneri, M. Budd–Chiari syndrome: a common complication of Behçet's disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 92, 858–862 (1997).
Tanida, S. et al. Adalimumab for the treatment of Japanese patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13, 940–948. e3 (2015).
Hatemi, G. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 1656–1662 (2008).
Han, S. W., Kim, G. W., Lee, J., Kim, Y. J. & Kang, Y. M. Successful treatment with stent angioplasty for Budd–Chiari syndrome in Behçet's disease. Rheumatol. Int. 25, 234–237 (2005).
Naganuma, M. et al. Analysis of clinical course and long-term prognosis of surgical and nonsurgical patients with intestinal Behçet's disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 95, 2848–2851 (2000).
Fawzy, M., Edrees, A., Okasha, H., El Ashmaui, A. & Ragab, G. Gastrointestinal manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 25, 1456–1462 (2016).
Barile-Fabris, L., Hernandez-Cabrera, M. F. & Barragan-Garfias, J. A. Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 16, 440 (2014).
Ju, J. H. et al. Lupus mesenteric vasculitis can cause acute abdominal pain in patients with SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 5, 273–281 (2009).
Janssens, P. et al. Lupus enteritis: from clinical findings to therapeutic management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 8, 67 (2013).
Yuan, S. et al. Lupus mesenteric vasculitis: clinical features and associated factors for the recurrence and prognosis of disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 43, 759–766 (2014).
Mok, C. C. Investigations and management of gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 19, 741–766 (2005).
Matsumoto, T. et al. The liver in systemic lupus erythematosus: pathologic analysis of 52 cases and review of Japanese autopsy registry data. Hum. Pathol. 23, 1151–1158 (1992).
Makol, A. et al. Vasculitis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a case–control study. Rheumatology 53, 890–899 (2014).
Bartels, C., Bell, C., Rosenthal, A., Shinki, K. & Bridges, A. Decline in rheumatoid vasculitis prevalence among US veterans: a retrospective cross-sectional study. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 2553–2557 (2009).
Ebert, E. C. & Hagspiel, K. D. Gastrointestinal and hepatic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 56, 295–302 (2011).
Hernandez-Rodriguez, J., Tan, C. D., Rodriguez, E. R. & Hoffman, G. S. Single-organ gallbladder vasculitis: characterization and distinction from systemic vasculitis involving the gallbladder. An analysis of 61 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 93, 405–413 (2014).
Salvarani, C. et al. Localized vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract: a case series. Rheumatology 49, 1326–1335 (2010).
Hernandez-Rodriguez, J. & Hoffman, G. S. Updating single-organ vasculitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 24, 38–45 (2012).
Miloslavsky, E. M., Stone, J. H. & Unizony, S. H. Challenging mimickers of primary systemic vasculitis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 41, 141–160 (2015).
Senatore, F. J. & McDonald, K. Gastrointestinal: ischemic gastrointestinal manifestations in a young adult: implicating a rare initial presentation of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 31, 1381 (2016).
Navon Elkan, P. et al. Mutant adenosine deaminase 2 in a polyarteritis nodosa vasculopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 370, 921–931 (2014).
Kamisawa, T., Zen, Y., Pillai, S. & Stone, J. H. IgG4-related disease. Lancet 385, 1460–1471 (2015).
Olin, J. W. Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease). N. Engl. J. Med. 343, 864–869 (2000).
Olin, J. W. & Shih, A. Thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease). Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 18, 18–24 (2006).
Puechal, X. & Fiessinger, J. N. Thromboangiitis obliterans or Buerger's disease: challenges for the rheumatologist. Rheumatology 46, 192–199 (2007).
Lee, K. S. et al. Colon ischemia associated with Buerger's disease: case report and review of the literature. Gut Liver 4, 287–291 (2010).
Hassoun, Z., Lacrosse, M. & De Ronde, T. Intestinal involvement in Buerger's disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 32, 85–89 (2001).
Cacione, D. G., Macedo, C. R. & Baptista-Silva, J. C. Pharmacological treatment for Buerger's disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 3, CD011033 (2016).
Cooper, L. T. et al. Long-term survival and amputation risk in thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 44, 2410–2411 (2004).
Acknowledgements
M.S. is supported by a Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium Fellowship grant (2015–2016). The Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium has received support from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (U54AR057319 and U01AR5187404), the National Center for Research Resources (U54RR019497), the Office of Rare Diseases Research, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.P. and M.S. contributed equally to researching data for the article, contributing to discussion of content and writing. All authors contributed equally to reviewing and/or editing the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
C.P. reports receiving fees for serving on advisory boards from Chemocentryx, GlaxoSmithKline and Hoffman-LaRoche; he also reports lecture fees and grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, EuroImmune, Hoffman-LaRoche and Terumo-BCT.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soowamber, M., Weizman, A. & Pagnoux, C. Gastrointestinal aspects of vasculitides. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14, 185–194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.179
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.179
This article is cited by
-
Management of granulomatosis with polyangiitis complicated by intestinal perforation and pancytopenia: a case report and literature review
Rheumatology International (2024)
-
Imaging of intestinal vasculitis focusing on MR and CT enterography: a two-way street between radiologic findings and clinical data
Insights into Imaging (2022)
-
Spectrum of Large and Medium Vessel Vasculitis in Adults: Primary Vasculitides, Arthritides, Connective Tissue, and Fibroinflammatory Diseases
Current Rheumatology Reports (2022)
-
Systemerkrankungen und Gastroenterologie
Die Gastroenterologie (2022)
-
Isolated duodenal ischemia of unknown etiology: a case report
BMC Surgery (2021)