Key Points
-
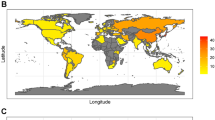
Since 1994, H. pylori infection has been associated with the development of some diseases localized outside the stomach
-
H. pylori can trigger a low-grade inflammatory state and induce molecular mimicry mechanisms by expressing virulence peptides that mimic host proteins
-
H. pylori might interfere with the absorbance of different nutrients and drugs, potentially influencing the development or clinical evolution of many diseases outside the gastrointestinal tract
-
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, unexplained iron deficiency anaemia and vitamin B12 deficiency are believed to be caused by H. pylori infection
-
The association of H. pylori with some cardiovascular, hepatobiliary, pancreatic and neurodegenerative diseases as well as colorectal cancer is currently under investigation, with interesting results
Abstract
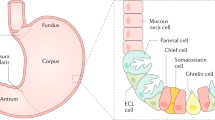
The discovery of Helicobacter pylori infection in the stomach could be considered as one of the most important events of modern gastroenterology. Understanding of the natural history of many disorders of the upper gastrointestinal tract, including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastric cancer and MALT lymphoma, was altered by this discovery. Interestingly, epidemiological studies have also revealed a correlation between H. pylori infection and some diseases localized outside the stomach, especially those characterized by persistent and low-grade systemic inflammation. Of note, H. pylori has an important role in iron deficiency anaemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and vitamin B12 deficiency. Moreover, the association of this bacterial pathogen with many other diseases, including hepatobiliary, pancreatic, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders is currently under investigation. In this Review, we summarize the results of the most important studies performed to date surrounding the association of H. pylori infection with extragastric diseases, as well as the strength of the evidence. We also provide information concerning bacterial–host interactions and the mechanisms implicated in the pathogenesis of each of these extragastric diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franceschi, F., Genta, R. M. & Sepulveda, A. R. Gastric mucosa: long-term outcome after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Gastroenterol. 37 (Suppl. 13), 17–23 (2002).
Dooley, C. P. et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and histologic gastritis in asymptomatic persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 321, 1562–1566 (1989).
Calvet, X., Ramirex Lazaro, M. J., Lehours, P. & Megraud, F. Diagnosis and epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 18 (Suppl. 1), 5–11 (2013).
Moyaert, H. et al. Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: other Helicobacters. Helicobacter 13 (Suppl. 1), 47–57 (2008).
Figura, N. et al. Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 15 (Suppl. 1), 60–68 (2010).
Mendall, M. A. et al. Relation of Helicobacter pylori infection and coronary heart disease. Br. Heart J. 71, 437–439 (1994).
Whincup, P. et al. Prospective study of potentially virulent strains of Helicobacter pylori and coronary heart disease in middle-aged men. Circulation 101, 1647–1652 (2000).
Rathbone, B., Martin, D., Stephens, J., Thompson, J. R. & Samani, N. J. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity in subjects with acute myocardial infarction. Heart 76, 308–311 (1996).
Pasceri, V. et al. Association of virulent Helicobacter pylori strains with ischemic heart disease. Circulation 97, 1675–1679 (1998).
Pasceri, V. et al. Virulent strains of Helicobacter pylori and vascular diseases: a meta-analysis. Am. Heart J. 151, 1215–1222 (2006).
Pellicano, R., Mladenova, I., Broutet, N., Salmi, L. R. & Mégraud, F. Is there an association between Helicobacter pylori infection and coronary heart disease? Eur. J. Epidemiol. 15, 611–619 (1999).
Franceschi, F. et al. CagA antigen of Helicobacter pylori and coronary instability: insight from a clinico-pathological study and a meta-analysis of 4241 cases. Atherosclerosis 202, 535–542 (2009).
Carter, A. M. et al. The influence of Helicobacter pylori status on circulating levels of the coagulation factors fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, factor VII, and factor VIII. Helicobacter 1, 65–69 (1996).
Satoh, H., Saijo, Y., Yoshioka, E. & Tsutsui, H. Helicobacter pylori infection is a significant risk for modified lipid profile in Japanese male subjects. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 17, 1041–1048 (2010).
Jia, E. Z. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with decreased serum levels of high density lipoprotein, but not with the severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 8, 59 (2009).
Kountouras, J., Polyzos, S. A., Deretzi, G., Katsinelos, P. & Kyriakou, P. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk for cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 22, e146–e147 (2011).
Harvey, R. et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on blood pressure: a community based cross sectional study. BMJ 323, 264–265 (2001).
Liu, L. et al. Pathogen burden in essential hypertension. Circ. J. 71, 1761–1764 (2007).
Vahdat, K. et al. Association of pathogen burden and hypertension: The Persian Gulf Healthy Heart Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 26, 1140–1147 (2013).
Migneco, A. et al. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection improves blood pressure values in patients affected by hypertension. Helicobacter 8, 585–589 (2003).
Takenaka, R. et al. Helicobacter pylori heat-shock protein 60 induces inflammatory responses through the Toll-like receptor-triggered pathway in cultured human gastric epithelial cells. Microbiology 150, 3913–3922 (2004).
Lenzi, C. et al. H. pylori infection and systemic antibodies to CagA and heat shock protein 60 in patients with coronary heart disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 12, 7815–7820 (2006).
Birnie, D. H. et al. Association between antibodies to heat shock protein 65 and coronary atherosclerosis. Possible mechanism of action of Helicobacter pylori and other bacterial infections in increasing cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 19, 387–394 (1998).
Bourantas, C. V., Garcia-Garcia, H. M., Diletti, R., Muramatsu, T. & Serruys, P. W. Early detection and invasive passivation of future culprit lesions: a future potential or an unrealistic pursuit of chimeras? Am. Heart J. 165, 869–881.e4 (2013).
Franceschi, F. et al. Cross-reactivity of anti-CagA antibodies with vascular wall antigens: possible pathogenic link between Helicobacter pylori infection and atherosclerosis. Circulation 106, 430–434 (2002).
Rozankociv, P. B. et al. Influence of CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains on atherosclerotic carotid disease. J. Neurol. 258, 753–761 (2011).
Wang, Z. W. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection contributes to high risk of ischemic stroke: evidence from a meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 259, 2527–2537 (2012).
De Bastiani, R. et al. High prevalence of Cag-A positive H. pylori strains in ischemic stroke: a primary care multicenter study. Helicobacter 13, 274–277 (2008).
Chen, B. F. et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and serum interleukin-18 in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Helicobacter 18, 124–128 (2013).
Corcoran, P. A. et al. The effect of different strains of Helicobacter pylori on platelet aggregation. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 21, 367–370 (2007).
Chen, Y., Segers, S. & Blaser, M. J. Association between Helicobacter pylori and mortality in the NHANES III study. Gut 62, 1262–1269 (2013).
Cremonini, F., Gabrielli, M., Gasbarrini, G., Pola, P. & Gasbarrini, A. The relationship between chronic H. pylori infection, CagA seropositivity and stroke: meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 173, 253–259 (2004).
Shenoy, V., Kanasaki, K. & Kalluri, R. Pre-eclampsia: connecting angiogenic and metabolic pathways. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 21, 529–536 (2010).
Steegers E. A. et al. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 376, 631–644 (2010).
Cardaropoli, S., Rolfo, A., Piazzese, A., Ponzetto, A. & Todros, T. Helicobacter pylori's virulence and infection persistence define pre-eclampsia complicated by fetal growth retardation. World J. Gastroenterol. 17, 5156–5165 (2011).
Franceschi, F. et al. Antibodies anti-CagA cross-react with trophoblast cells: a risk factor for pre-eclampsia? Helicobacter 17, 426–434 (2012).
Gasbarrini, A., Serricchio, M., Tondi, P., Gasbarrini, G. & Pola, P. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with primary Raynaud phenomenon. Lancet 348, 966–967 (1996).
Gasbarrini, A. et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication ameliorates primary Raynaud's phenomenon. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43, 1641–1645 (1998).
Gasbarrini, A. et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori cytotoxic type I CagA-positive strains and migraine with aura. Cephalalgia 20, 561–565 (2000).
Faraji, F., Zarinfar, N., Zanjani, A. T. & Morteza, A. The effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on migraine: a randomized, double blind, controlled trial. Pain Physician 15, 495–498 (2012).
Tunca, A., Ardiçog˘lu, Y., Kargili, A. & Adam, B. Migraine, Helicobacter pylori, and oxidative stress. Helicobacter 12, 59–62 (2007).
Marignani, M. et al. Reversal of long-standing iron deficiency anaemia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 32, 617–622 (1997).
Yuan, W. et al. Iron deficiency anemia in Helicobacter pylori infection: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 45, 665–676 (2010).
Huang, X. et al. Iron deficiency anaemia can be improved after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Postgrad. Med. J. 86, 272–278 (2010).
Huang, X. et al. Iron deficiency anaemia can be improved after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Postgrad. Med. J. 86, 272–278 (2010).
Franceschi, F. & Gasbarrini, A. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 21, 325–334 (2007).
Gasbarrini, A. et al. Regression of autoimmune thrombocytopenia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet 352, 878 (1998).
Tsumoto, C. et al. Long-term efficacy of Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: 7-year follow-up prospective study. Ann. Hematol. 88, 789–793 (2009).
Veneri, D. et al. Analysis of B- and T-cell clonality and HLA class II alleles in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: correlation with Helicobacter pylori infection and response to eradication treatment. Platelets 16, 307–311 (2005).
Veneri, D., Krampera, M. & Franchini, M. High prevalence of sustained remission of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura after Helicobacter pylori eradication: a long-term follow-up study. Platelets 16, 117–119 (2005).
Veneri, D. et al. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Helicobacter pylori infection, and HLA class II alleles. Blood 100, 1925–1926 (2002).
Godeau, B. & Michel, M. Treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura in adults. Ann. Hematol. 89 (Suppl.), 55–60 (2010).
Franceschi, F., Christodoulides, N., Kroll, M. H. & Genta, R. M. Helicobacter pylori and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann. Intern. Med. 140, 766–767 (2004).
Diamantidis, M. D. et al. High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Greek patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Acta Haematol. 124, 141–149 (2010).
Malik, A. A., Ganti, A. K., Potti, A., Levitt, R. & Hanley, J. F. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in the incidence and clinical course of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 97, 1371–1374 (2002).
Soler, J. A. et al. H. pylori eradication does not reduce paraprotein levels in monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS): a prospective cohort study. Ann. Hematol. 88, 769–773 (2009).
Asadi-Pooya, A. A., Dehghani, S. M., Petramfar, P., Emami, M. & Mahmoodi, M. Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with epilepsy. Seizure 21, 21–23 (2012).
Long, Y. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection in neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation 20, 107–112 (2012).
Yoshimura, S. et al. Distinct genetic and infectious profiles in Japanese neuromyelitis optica patients according to anti-aquaporin 4 antibody status. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 84, 29–34 (2013).
Kountouras, J. et al. Potential implications of Helicobacter pylori-related neutrophil-activating protein. World J. Gastroenterol. 18, 489–490 (2012).
Kountouras, J. et al. Aquaporin 4, Helicobacter pylori and potential implications for neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroimmunol. 263, 162–163 (2013).
Nielsen, H. H., Qiu, J., Friis, S., Wermuth, L. & Ritz, B. Treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of Parkinson's disease in Denmark. Eur. J. Neurol. 19, 864–869 (2012).
Dobbs, S. M. et al. Differential effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on time-trends in brady/hypokinesia and rigidity in idiopathic parkinsonism. Helicobacter 15, 279–294 (2010).
Kountouras, J. et al. Five-year survival after Helicobacter pylori eradication in Alzheimer disease patients. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 23, 199–204 (2010).
Roubaud-Baudron, C., Krolak-Salmon, P., Quadrio, I., Megraud, F. & Salles N. Impact of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection on Alzheimer's disease: preliminary results. Neurobiol. Aging 33, 1009.e11–19 (2012).
Roubaud Baudron, C. et al. Does Helicobacter pylori infection increase incidence of dementia? The Personnes Agees QUID Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 61, 74–78 (2013).
Beydoun, M. A., Beydoun, H. A., Shroff, M. R., Kitner-Triolo, M. H. & Zonderman, A. B. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and cognitive performance among US adults: evidence from a large national survey. Psychosom. Med. 75, 486–496 (2013).
Katan, M. et al. Infectious burden and cognitive function: the Northern Manhattan Study. Neurology 80, 1209–1215 (2013).
Zhou, X., Wu, J. & Zhang, G. Association between Helicobacter pylori and asthma: a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 25, 460–468 (2013).
Oertli, M. & Müller, A. Helicobacter pylori targets dendritic cells to induce immune tolerance, promote persistence and confer protection against allergic asthma. Gut Microbes 3, 566–571 (2012).
Deshpande, N. et al. Helicobacter pylori IgG antibodies in aqueous humor and serum of subjects with primary open angle and pseudo-exfoliation glaucoma in a South Indian population. J. Glaucoma 17, 605–610 (2008).
Zavos, C. et al. Histological presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the trabeculum and iris of patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmic Res. 47, 150–156 (2012).
Zullo, A. et al. Glaucoma and Helicobacter pylori: eyes wide shut? Dig. Liver Dis. 44, 627–628 (2012).
Pajic´-Penavic´, I., Danic´, D., Maslovara, S. & Gall-Trošelj, K. Absence of Helicobacter pylori in healthy laryngeal mucosa. J. Laryngol. Otol. 126, 196–199 (2012).
Gong, H. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection of the larynx may be an emerging risk factor for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 14, 905–910 (2012).
Ki, M. R. et al. Helicobacter pylori accelerates hepatic fibrosis by sensitizing transforming growth factor-β1-induced inflammatory signaling. Lab. Invest. 90, 1507–1516 (2010).
Le Roux-Goglin, E. et al. Helicobacter infection induces podosome assembly in primary hepatocytes in vitro. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 91, 161–170 (2012).
Polyzos, S. A. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 62, 121–126 (2013).
Esmat, G., El-Bendary, M., Zakarya, S., Ela, M. A. & Zalata, K. Role of Helicobacter pylori in patients with HCV-related chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis with or without hepatocellular carcinoma: possible association with disease progression. J. Viral Hepat. 19, 473–479 (2012).
Sakr, S. A., Badrah, G. A. & Sheir, R. A. Histological and histochemical alterations in liver of chronic hepatitis C patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 67, 367–374 (2013).
Hu, B. L., Wang, H. Y. & Yang, G. Y. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with hepatic encephalopathy risk: a systematic review. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2013.05.004.
Kountouras, J., Zavos, C. & Deretzi, G. Helicobacter pylori might contribute to persistent cognitive impairment after resolution of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 9, 624 (2011).
Kountouras, J. et al. Helicobacter pylori induced cognitive dysfunction might be associated with falls and fractures in cirrhosis. Hepatology 57, 1284 (2013).
Kountouras, J., Zavos, C. & Chatzopoulos, D. A concept on the role of Helicobacter pylori infection in autoimmune pancreatitis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 9, 196–207 (2005).
Shinji, A. et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis is closely associated with gastric ulcer presenting with abundant IgG4-bearing plasma cell infiltration. Gastrointest. Endosc. 59, 506–511 (2004).
Guarneri, F., Guarneri, C. & Benvenga, S. Helicobacter pylori and autoimmune pancreatitis: role of carbonic anhydrase via molecular mimicry? J. Cell. Mol. Med. 9, 741–744 (2005).
Okazaki, K., Uchida, K. & Fukui, T. Recent advances in autoimmune pancreatitis: concept, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. J. Gastroenterol. 43, 409–418 (2008).
Frulloni, L. et al. Identification of a novel antibody associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 2135–2142 (2009).
Takayama, S., Takahashi, H., Matsuo, Y., Okada, Y. & Manabe, T. Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on human pancreatic cancer cell line. Hepatogastroenterology 54, 2387–2391 (2007).
de Martel, C. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and development of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 17, 1188–1194 (2008).
Risch, H. A., Yu, H., Lu, L. & Kidd, M. S. ABO blood group, Helicobacter pylori seropositivity, and risk of pancreatic cancer: a case–control study. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 102, 502–505 (2010).
Risch, H. A. Pancreatic cancer: Helicobacter pylori colonization, N-nitrosamine exposures, and ABO blood group. Mol. Carcinog. 51, 109–118 (2012).
Risch, H. A. et al. ABO blood group and risk of pancreatic cancer: a study in Shanghai and meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 177, 1326–1337 (2013).
Malfertheiner, P., Selgrad, M. & Bornschein, J. Helicobacter pylori: clinical management. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 28, 608–614 (2012).
Kountouras, J., Kapetanakis, N., Zavos, C. & Romiopoulos, I. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on normal colorectal mucosa, adenomatous polyps and the adenocarcinoma sequence. Colorectal Dis. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/codi.12356.
Machida-Montani, A. et al. Atrophic gastritis, Helicobacter pylori, and colorectal cancer risk: a case–control study. Helicobacter. 12, 328–332 (2007).
Zhang, Y., Hoffmeister, M., Weck, M. N., Chang-Claude, J. & Brenner, H. Helicobacter pylori infection and colorectal cancer risk: evidence from a large population-based case–control study in Germany. Am. J. Epidemiol. 175, 441–450 (2012).
Wu, Q., Yang, Z. P., Xu, P., Gao, L. C. & Fan, D. M. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of colorectal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis. 15, e352–e364 (2013).
Sonnenberg, A. & Genta, R. M. Helicobacter pylori is a risk factor for colonic neoplasms. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 108, 208–215 (2013).
Zhou, X., Zhang, C., Wu, J. & Zhang, G. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 99, 200–208 (2013).
Jeon, C. Y. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with an increased rate of diabetes. Diabetes Care 35, 520–525 (2012).
Shin, D. W. et al. Association between metabolic syndrome and Helicobacter pylori infection diagnosed by histologic status and serological status. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 46, 840–845 (2012).
Chen, Y. & Blaser, M. J. Association between gastric Helicobacter pylori colonization and glycated hemoglobin levels. J. Infect. Dis. 205, 1195–1202 (2012).
Akanuma, M. et al. Influence of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the management of type 2 diabetes. Hepatogastroenterology 59, 641–645 (2012).
Tseng, C. H. Diabetes, insulin use and Helicobacter pylori eradication: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 9, 12–46 (2012).
Chung, G. E. et al. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity in diabetic patients is associated with microalbuminuria. World J. Gastroenterol. 19, 97–102 (2013).
Zhou, X., Zhang, C., Wu, J. & Zhang, G. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 99, 200–208 (2013).
Candelli, M. et al. High reinfection rate of Helicobacter pylori in young type 1 diabetic patients: a three-year follow-up study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 16, 1468–1472 (2012).
Shi, W., Liu, W., Zhou, X., Ye, F. & Zhang, G. Associations of Helicobacter pylori infection and cytotoxin-associated gene A status with autoimmune thyroid diseases: a meta-analysis. Thyroid 23, 1294–1300 (2013).
Franceschi, F. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Helicobacter 9, 369 (2004).
Ram, M. et al. Helicobacter pylori serology in autoimmune diseases—fact or fiction? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 51, 1075–1082 (2012).
Cicconi, V. et al. Disappearance of antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Am. J. Med. 111, 163–164 (2001).
Tüzün, Y., Keskin, S. & Kote, E. The role of Helicobacter pylori infection in skin diseases: facts and controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 28, 478–482 (2010).
Di Campli, C. et al. Beneficial effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on idiopathic chronic urticaria. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43, 1226–1229 (1998).
Ojetti, V. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection affects eosinophilic cationic protein in the gastric juice of patients with idiopathic chronic urticaria. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 125, 66–72 (2001).
Magen, E. & Mishal, J. Possible benefit from treatment of Helicobacter pylori in antihistamine-resistant chronic urticaria. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 38, 7–12 (2013).
El-Khalawany, M. et al. Role of Helicobacter pylori in common rosacea subtypes: a genotypic comparative study of Egyptian patients. J. Dermatol. 39, 989–995 (2012).
Malfertheiner, P. et al. European Helicobacter Study Group. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht IV/ Florence Consensus Report. Gut 61, 646–664 (2012).
Vitale, G. et al. Nutritional aspects of Helicobacter pylori infection. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 57, 369–377 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D. Roccarina and G. Zuccalà researched the data for the article. F. Franceschi wrote the article. A. Gasbarrini reviewed and edited it. All authors discussed the content of the article before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franceschi, F., Zuccalà, G., Roccarina, D. et al. Clinical effects of Helicobacter pylori outside the stomach. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11, 234–242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.243
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.243
This article is cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori infection
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2023)
-
Helicobacter pylori infection and gut microbiota in adolescents: Is there a relation?
Journal of Biosciences (2023)
-
Relationship between active Helicobacter pylori infection and risk factors of cardiovascular diseases, a cross-sectional hospital-based study in a Sub-Saharan setting
BMC Infectious Diseases (2022)
-
Helicobacter pylori infection is not an independent risk factor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China
BMC Gastroenterology (2022)
-
Association Between Helicobacter pylori and Periampullary and Pancreatic Cancer: a Case–Control Study
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer (2022)