Abstract
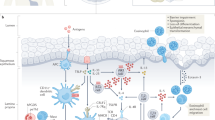
Eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) was first described in the early 1990s. Although initially reported to be a rare entity, EoE has rapidly become a regularly diagnosed disease with a prevalence of approximately 1 in 2,000 individuals in the USA and Europe. The disease is characterized by a combination of oesophageal dysfunction and predominant eosinophilic infiltration of the oesophageal tissue. At diagnosis, other diseases that can be associated with oesophageal eosinophilic infiltration must be ruled out. Children with EoE present with a wide variety of symptoms, whereas adults mostly present with dysphagia for solid food and chest pain. Histologic features of EoE resemble those of T-helper type 2 inflammation. Endoscopy should be carried out to establish the diagnosis, but endoscopic abnormalities are not pathognomonic for EoE and the examination might not show histologic abnormality. Treatment modalities for EoE include drugs (corticosteroids, PPIs, antiallergic and biologic agents), hypoallergenic diets and oesophageal dilatation for strictures that are unresponsive to medical therapy. Unresolved eosinophilic inflammation leads to the formation of oesophageal strictures, which probably increase the risk of food bolus impactions. To date, long-term strategies for the therapeutic management of this chronic inflammatory disease remain poorly defined.
Key Points
-
The incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) is increasing in Western countries
-
A combination of clinical, endoscopic and histologic findings are used to diagnose EoE
-
Patients with EoE should be treated to improve quality of life, to reduce the risk of oesophageal injury associated with food impaction and to prevent or reduce oesophageal remodelling
-
Treatment modalities include drugs (such as corticosteroids, antiallergic agents, immunomodulators and biologic agents), food elimination diets and oesophageal dilatation
-
Treatment with corticosteroids consists of an induction and maintenance phase
-
Long-term management approaches for EoE (>1 year) remain poorly defined
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liacouras, C. A. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 128, 3–20 (2011).
Kelley, M. L. Jr & Frazer, J. P. Symptomatic mid-esophageal webs. JAMA 197, 143–146 (1966).
Landres, R. T., Kuster, G. G. & Strum, W. B. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 74, 1298–1301 (1978).
Bousvaros, A., Antonioli, D. A. & Winter, H. S. Ringed esophagus: an association with esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 87, 1187–1190 (1992).
Langdon, D. E. Corrugated ringed esophagus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 88, 1461 (1993).
Attwood, S. E., Smyrk, T. C., Demeester, T. R. & Jones, J. B. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia, a distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 38, 109–116 (1993).
Straumann, A., Spichtin, H. P., Bernoulli, R., Loosli, J. & Vögtlin, J. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis: a frequently overlooked disease with typical clinical aspects and discrete endoscopic findings [article in German with English abstract]. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 124, 1419–1429 (1994).
Rothenberg, M. E., Mishra, A., Collins, M. H. & Putnam, P. E. Pathogenesis and clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108, 891–894 (2001).
Prasad, G. A. et al. Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 1055–1061 (2009).
Hruz, P. et al. Escalating incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis: a 20-year prospective, population-based study in Olten County, Switzerland. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 128, 1349–1350 (2011).
DeBrosse, C. W. et al. Identification, epidemiology, and chronicity of pediatric esophageal eosinophilia, 1982–1999. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 126, 112–119 (2010).
Straumann, A. et al. Fragility of the esophageal musoca: a pathognomonic endoscopic sign of primary eosinophilic esophagitis? Gastrointest. Endosc. 57, 407–412 (2003).
Straumann, A. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: analysis of food impaction and perforation in 251 adolescent and adult patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 598–600 (2008).
Noel, R. J., Putnam, P. E. & Rothenberg, M. E. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 940–941 (2004).
Croese, J. et al. Clinical and endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Gastrointest. Endosc. 58, 516–522 (2003).
Franciosi, J. P., Tam, V., Liacouras, C. A. & Spergel, J. M. A case-control study of sociodemographic and geographic characteristics of 335 children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 415–419 (2009).
Collins, M. H. et al. Clinical, pathologic and molecular characterization of familial eosinophilic esophagitis compared with sporadic cases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 621–629 (2008).
Blanchard, C. et al. Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 536–547 (2006).
Palmer, C. N. et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 38, 441–446 (2006).
Blanchard, C. et al. Coordinate interaction between IL-13 and epithelial differentiation cluster genes in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Immunol. 184, 4033–4041 (2010).
Rothenberg, M. E. et al. Common variants at 5q22 associate with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat. Genet. 42, 289–291 (2010).
Gudbjartsson, D. F. et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 41, 342–347 (2009).
Yan, B. M. & Shaffer, E. A. Primary eosinophilic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Gut 58, 721–732 (2009).
Yamaguchi, Y. et al. Purified interleukin 5 supports the terminal differentiation and proliferation of murine eosinophilic precursors. J. Exp. Med. 167, 43–56 (1988).
Rothenberg, M. E., Mishra, A., Brandt, E. B. & Hogan, S. P. Gastrointestinal eosinophils in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 78, 291–328 (2001).
Mishra, A., Hogan, S. P., Lee, J. J., Foster, P. S. & Rothenberg, M. Fundamental signals that regulate eosinophil homing to the gastrointestinal tract. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 1719–1727 (1999).
Garcia-Zepeda, E. A. et al. Human eotaxin is a specific chemoattractant for eosinophil cells and provides a new mechanism to explain tissue eosinophilia. Nat. Med. 2, 449–456 (1996).
Forssmann, U. et al. Eotaxin-2, a novel CC chemokine that is selective for the chemokine receptor CCR3, and acts like eotaxin on human eosinophil and basophil leukocytes. J. Exp. Med. 185, 2171–2176 (1997).
Shinkai, A. et al. A novel human CC chemokine, eotaxin-3, which is expressed in IL-4 stimulated vascular endothelial cells, exhibits potent activity toward eosinophils. J. Immunol. 163, 1602–1610 (1999).
Bochner, B. S. & Schleimer, R. P. The role of adhesion molecules in human eosinophil and basophil recruitment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 94, 427–438 (1994).
Powell, N., Walker, M. M. & Talley, N. J. Gastrointestinal eosinophils in health, disease and functional disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 146–156 (2010).
Mishra, A. et al. Esophageal remodeling develops as a consequence of tissue specific IL-5 induced eosinophilia. Gastroenterology 134, 204–214 (2008).
Aceves, S. S., Newbury, R. O., Dohil, R., Bastian, J. F. & Broide, D. H. Esophageal remodeling in paediatric eosinophilic oesophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119, 206–212 (2007).
Kagalwalla, A. F. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: epithelial mesenchymal transition contributes to esophageal remodeling and reverses with treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129, 1387–1396 (2012).
Aceves, S. S. et al. Resolution of remodeling in eosinophilic oesophagitis correlates with epithelial response to topical corticosteroids. Allergy 65, 109–116 (2010).
Straumann, A. et al. Budesonide is effective in adolescent and adult patients with active eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gastroenterology 139, 1526–1537 (2010).
Straumann, A. et al. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: a follow-up of thirty patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology 125, 1660–1669 (2003).
DeBrosse, C. W. et al. Long-term outcomes in pediatric-onset esophageal eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 128, 132–138 (2011).
Aceves, S. S. et al. Resolution of remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis correlates with epithelial response to topical corticosteroids. Allergy 65, 109–116 (2010).
Lucendo, A. J. et al. Subepithelial collagen deposition, profibrogenic cytokine gene expression, and changes after prolonged fluticasone propionate treatment in adult eosinophilic esophagitis: a prospective study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 128, 1037–1046 (2011).
Abu-Sultaneh, S. M., Durst, P., Maynard, V. & Elitsur, Y. Fluticasone and food allergen elimination reverse sub-epithelial fibrosis in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 56, 97–102 (2011).
Furuta, G. T. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 133, 1342–1363 (2007).
Kelly, K. J. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis attributed to gastroesophageal reflux: improvement with an amino acid-based formula. Gastroenterology 109, 1503–1512 (1995).
Arora, A. S. & Yamazaki, K. Eosinophilic esophagitis: asthma of the esophagus? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2, 523–530 (2004).
Straumann, A., Bauer, M., Fischer, B., Blaser, K. & Simon, H. U. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with a TH 2-type allergic inflammatory response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108, 954–961 (2001).
Krarup, A. L. et al. Acid hypersensitivity in patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 45, 273–281 (2010).
Molina-Infante, J. et al. Esophageal eosinophilic infiltration responds to proton pump inhibition in most adults. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 9, 110–117 (2011).
Sayej, W. N., Patel, R., Baker, R. D., Tron, E. & Baker, S. S. Treatment with high-dose proton pump inhibitors helps distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from noneosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 49, 393–399 (2009).
Liacouras, C. A., Wenner, W. J., Brown, K. & Ruchelli, E. Primary eosinophilic esophagitis in children: successful treatment with oral corticosteroids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 26, 380–385 (1998).
Faubion, W. A. et al. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with inhaled corticosteroids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 27, 90–93 (1998).
Schaefer, E. T. et al. Comparison of oral prednisone and topical fluticasone in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: a randomized trial in children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 165–173 (2008).
Konikoff, M. R. et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 131, 1381–1391 (2006).
Remedios, M., Campbell, C., Jones, D. M. & Kerlin, P. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings and response to treatment with fluticasone proprionate. Gastrointest. Endosc. 63, 3–12 (2006).
Lucendo, A. J. et al. Endoscopic, bioptic, and manometric findings in eosinophilic esophagitis before and after steroid therapy: a case series. Endoscopy 39, 765–771 (2007).
Dohil, R., Newbury, R., Fox, L., Bastian, J. & Aceves, S. S. Oral viscous budesonide is effective in children with eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 139, 418–429 (2010).
Straumann, A. et al. Budesonide is effective in adolescent and adult patients with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 139, 1526–1537 (2010).
Peterson, K. A. et al. Comparison of esomeprazole to aerosolized, swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 55, 1313–1319 (2010).
Schroeder, S. et al. Successful treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with ciclesonide. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129, 1419–1421 (2012).
Dellon, E. S. et al. Viscous topical is more effective than nebulized steroid therapy for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 143, 321–324e1 (2012).
Straumann, A. et al. Long-term budesonide maintenance treatment is partially effective for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 9, 400–409 (2011).
Attwood, S. E. et al. Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast. Gut 52, 181–185 (2003).
Lucendo, A. J. et al. Montelukast was inefficient in maintaining steroid-induced remission in adult eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 56, 3551–3558 (2011).
Gupta, S. K., Fitzgerald, J. F., Kondratyuk, T. & HogenEsch, H. Cytokine expression in normal and inflamed esophageal mucosa: a study into the pathogenesis of allergic eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 42, 22–26 (2006).
Pettipher, R., Hansel, T. T. & Armer, R. Antagonism of the prostaglandin D2 receptors DP1 and CRTH2 as an approach to treat allergic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6, 313–325 (2007).
Straumann, A. et al. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with the CRTH2-antagonist OC000459: a novel therapeutic principle [abstract A856]. Gastroenterology 142 (Suppl. 1), S-439 (2012).
Straumann, A. et al. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody treatment (mepolizumab) in active eosinophilic esophagitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gut 59, 21–30 (2010).
Assa'ad, A. H. et al. An antibody against IL-5 reduces numbers of esophageal intraepithelial eosinophils in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 141, 1593–1604 (2011).
Spergel, J. M. et al. Reslizumab in children and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis: Results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129, 456–463 (2012).
Straumann, A., Bussmann, C., Conus, S., Beglinger, C. & Simon, H. U. Anti-TNF-α (infliximab) therapy for severe adult eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 122, 425–427 (2008).
Netzer, P. et al. Corticosteroid-dependent eosinophilic oesophagitis: azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine can induce and maintain long-term remission. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 19, 865–869 (2007).
Spergel, J. M. et al. 14 years of eosinophilic espophagitis: clinical features and prognosis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 48, 30–36 (2009).
Markowitz, J. E., Spergel, J. M., Ruchelli, E. & Liacouras, C. A. Elemental diet is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 98, 777–782 (2003).
Liacouras, C. A. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a 10-year experience in 381 children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 3, 1198–1206 (2005).
Spergel, J. M., Andrews, T., Brown-Whitehorn, T. F., Beausoleil, J. L. & Liacouras, C. A. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with specific food elimination diet directed by a combination of skin prick and patch tests. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 95, 336–343 (2005).
Spergel, J. M., Beausoleil, J. L., Mascarenhas, M. & Liacouras, C. A. The use of skin prick tests and patch tests to identify causative foods in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 109, 363–368 (2002).
Kagalwalla, A. F. et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 4, 1097–1102 (2006).
Kagalwalla, A. F. et al. Identification of specific foods responsible for inflammation in children with eosinophilic esophagitis successfully treated with empiric elimination diet. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 53, 145–149 (2011).
Gonsalves, N. et al. Elimination diet effectively treats eosinophilic esophagitis in adults; food reintroduction identifies causative factors. Gastroenterology 142, 1451–1459 (2012).
Henderson, C. J. et al. Comparative dietary therapy effectiveness in remission of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129, 1570–1578 (2012).
Schoepfer, A. M., Gschossmann, J., Scheurer, U., Seibold, F. & Straumann, A. Esophageal strictures in adult eosinophilic oesophagitis: dilation is an effective and safe alternative after failure of topical corticosteroids. Endoscopy 40, 161–164 (2008).
Schoepfer, A. M. et al. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic oesophagitis: effectiveness, safety, and impact on the underlying inflammation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 105, 1062–1070 (2010).
Dellon, E. S. et al. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic oesophagitis: safety and predictors of clinical response and complications. Gastrointest. Endosc. 71, 706–712 (2010).
Robles-Medranda, C. et al. Severe dysphagia in children with eosinophilic esophagitis and esophageal stricture : an indication for balloon dilation? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 50, 516–520 (2010).
Jacobs, J. W. Jr & Spechler, S. J. A systematic review of the risk of perforation during esophageal dilation for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 55, 1512–1525 (2010).
University of Oxford Centre for Evidence based Medicine. Levels of evidence [online], (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ekaterina Safroneeva, PhD, for editorial assistance. The authors' research is supported by a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation to AS and AMS (Grant No. 32003B_135665/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to all aspects of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Straumann, A., Schoepfer, A. Therapeutic concepts in adult and paediatric eosinophilic oesophagitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9, 697–704 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.182
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.182
This article is cited by
-
Quail egg homogenate alleviates food allergy induced eosinophilic esophagitis like disease through modulating PAR-2 transduction pathway in peanut sensitized mice
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2018)
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: published evidences for disease subtypes, indications for patient subpopulations, and how to translate patient observations to murine experimental models
World Allergy Organization Journal (2016)
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin–elicited basophil responses promote eosinophilic esophagitis
Nature Medicine (2013)