Abstract
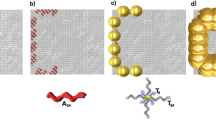
The next step in the maturing field of nanotechnology is to develop ways to introduce unusual architectural changes to simple building blocks. For nanowires, on-wire lithography (OWL) has emerged as a powerful way of synthesizing a segmented structure and subsequently introducing architectural changes through post-chemical treatment. In the OWL protocol presented here, multisegmented nanowires are grown and a support layer is deposited on one side of each nanostructure. After selective chemical etching of sacrificial segments, structures with gaps as small as 2 nm and disks as thin as 20 nm can be created. These nanostructures are highly tailorable and can be used in electrical transport, Raman enhancement and energy conversion. Such nanostructures can be functionalized with many types of adsorbates, enabling the use of OWL-generated structures as bioactive probes for diagnostic assays and molecular transport junctions. The process takes 13–36 h depending on the type of adsorbate used to functionalize the nanostructures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hurst, S.J., Payne, E.K., Qin, L. & Mirkin, C.A. Multisegmented one-dimensional nanorods prepared by hard-template synthetic methods. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 45, 2672–2692 (2006).
Ozin, G.A. & Arsenault, A.C. Nanochemistry: A Chemical Approach to Nanomaterials (RSC Publishing, Cambridge, 2005).
Gates, B.D. et al. New approaches to nanofabrication: molding, printing, and other techniques. Chem. Rev. 105, 1171–1196 (2005).
Lieber, C.M. & Wang, Z.L. Functional nanowires. MRS Bull. 32, 99–108 (2007).
Xia, Y. et al. One-dimensional nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mat. 15, 353–389 (2003).
Melosh, N.A. et al. Ultrahigh-density nanowire lattices and circuits. Science 300, 112–115 (2003).
Hu, J., Ouyang, M., Yang, P. & Lieber, C.M. Controlled growth and electrical properties of heterojunctions of carbon nanotubes and silicon nanowires. Nature 399, 48–51 (1999).
Wu, Y., Fan, R. & Yang, P. Block-by-block growth of single-crystalline Si/Si-Ge superlattice nanowires. Nano Lett. 2, 83–86 (2002).
Gudiksen, M.S., Lauhon, L.J., Wang, J., Smith, D.C. & Lieber, C.M. Growth of nanowire superlattice structures for nanoscale photonics and electronics. Nature 415, 617–620 (2002).
Nicewarner-Pena, S.R. et al. Submicrometer metallic barcodes. Science 294, 137–141 (2001).
Martin, C.R. Nanomaterials: a membrane-based synthetic approach. Science 266, 1961–1966 (1994).
Piner, R.D., Zhu, J., Xu, F., Hong, S. & Mirkin, C.A. Dip-pen nanolithography. Science 283, 661–663 (1999).
Manna, L., Scher, E.C. & Alivisatos, A.P. Synthesis of soluble and processable rod-, arrow-, teardrop-, and tetrapod-shaped CdSe nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 12700–12706 (2000).
Xiang, J. et al. Ge/Si nanowire heterostructures as high-performance field-effect transistors. Nature 441, 489–493 (2006).
Jiang, X. et al. InAs/InP radial nanowire heterostructures as high electron mobility devices. Nano Lett. 7, 3214–3218 (2007).
Sioss, J.A. & Keating, C.D. Batch preparation of linear Au and Ag nanoparticle chains via wet chemistry. Nano Lett. 5, 1779–1783 (2005).
Qian, F., Gradecak, S., Li, Y., Wen, C.-Y. & Lieber, C.M. Core/multishell nanowire heterostructures as multicolor, high-efficiency light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett. 5, 2287–2291 (2005).
Hu, J., Bando, Y., Zhan, J. & Golberg, D. Fabrication of silica-shielded Ga-ZnS metal-semiconductor nanowire heterojunctions. Adv. Mat. 17, 1964–1969 (2005).
Liu, S., Tok Jeffrey, B.H. & Bao, Z. Nanowire lithography: fabricating controllable electrode gaps using Au–Ag–Au nanowires. Nano Lett. 5, 1071–1076 (2005).
Qin, L., Park, S., Huang, L. & Mirkin, C.A. On-wire lithography. Science 309, 113–115 (2005).
Chou, S.Y., Krauss, P.R. & Renstrom, P.J. Imprint lithography with 25-nanometer resolution. Science 272, 85–87 (1996).
Qin, L., Banholzer, M.J., Millstone, J.E. & Mirkin, C.A. Nanodisk codes. Nano Lett. 7, 3849–3853 (2007).
Zheng, G., Qin, L. & Mirkin, C.A. Spectroscopically enhancing electrical nanotraps. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47, 1938–1941 (2008).
Wei, W. et al. Surface plasmon-mediated energy transfer in heterograp Au–Ag nanowires. Nano Lett. 8, 3446–3449 (2008).
Banholzer, M.J., Millstone, J.E., Qin, L. & Mirkin, C.A. Rationally designed nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 885–897 (2008).
Patolsky, F., Zheng, G. & Lieber, C.M. Fabrication of silicon nanowire devices for ultrasensitive, label-free, real-time detection of biological and chemical species. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1711–1724 (2006).
Zheng, G., Patolsky, F., Cui, Y., Wang, W.U. & Lieber, C.M. Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1294–1301 (2005).
Nie, S., Xing, Y., Kim, G.J. & Simons, J.W. Nanotechnology applications in cancer. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 9, 257–288 (2007).
Qin, L., Jang, J.-W., Huang, L. & Mirkin, C.A. Sub-5-nm gaps prepared by on-wire lithography: correlating gap size with electrical transport. Small 3, 86–90 (2006).
Qin, L., Banholzer, M.J., Xu, H., Huang, L. & Mirkin, C.A. Rational design and synthesis of catalytically driven nanorotors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 14870–14871 (2007).
Chen, X. et al. On-wire lithography-generated molecule-based transport junctions: a new testbed for molecular electronics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 8166–8168 (2008).
Qin, L. et al. Designing, fabricating, and imaging Raman hot spots. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 13300–13303 (2006).
Masuda, H. & Fukuda, K. Ordered metal nanohole arrays made by a two-step replication of honeycomb structures of anodic alumina. Science 268, 1466–1468 (1995).
Payne, E.K., Shuford, K.L., Park, S., Schatz, G.C. & Mirkin, C.A. Multipole plasmon resonances in gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 2150–2154 (2006).
Hill, H.D. & Mirkin, C.A. The bio-barcode assay for the detection of protein and nucleic acid targets using DTT-induced ligand exchange. Nat. Protoc. 1, 324–336 (2006).
Li, Z. & Mirkin, C.A. G-quartet-induced nanoparticle assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 11568–11569 (2005).
Mirkin, C.A., Letsinger, R.L., Mucic, R.C. & Storhoff, J.J. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticle into macroscopic materials. Nature 382, 607–609 (1996).
Goldstein, J. et al. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-ray Microanalysis 3rd ed. (Springer Science & Business Media, Inc., New York, 2003).
Acknowledgements
C.A.M. acknowledges the National Science Foundation (NSF), the NSSEFF and the AFSOR for support of this research. C.A.M. is also grateful for a NIH Director's Pioneer Award. M.J.B. acknowledges the 2008 Edward G. Weston ECS Summer Fellowship and NU for a Ryan Fellowship. J.E.M. acknowledges NU for a Presidential Fellowship. K.D.O. acknowledges the NSF for a Graduate Research Fellowship and NU for a Ryan Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banholzer, M., Qin, L., Millstone, J. et al. On-wire lithography: synthesis, encoding and biological applications. Nat Protoc 4, 838–848 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.52
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.52
This article is cited by
-
Nanoreactors for particle synthesis
Nature Reviews Materials (2022)
-
Application of electrochemistry to single-molecule junctions: from construction to modulation
Science China Chemistry (2019)
-
Coaxial lithography
Nature Nanotechnology (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.