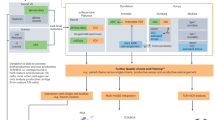
Abstract
The regulation of the cellular immune response in lung diseases is not yet fully understood. Isolating different subsets of immune cells directly from the lung is therefore an indispensable method of gaining detailed knowledge on the function of these cells in this organ. This protocol describes a method of isolating and magnetically labeling CD4+ lung T cells, which are then loaded and retained on the column while all other cells run through it (positive selection). The yield of this isolation is approximately 5 × 105 to 1.5 × 106 CD4+ cells from a murine lung. These cells can be further investigated by several methods such as flow cytometry, western blot analysis, RT-PCR, immunostaining and ELISA. In addition, lung CD4+ T cells alone or along with other immunologically important cells such as CD8+ T cells and T regulatory cells can be adoptively transferred into immune-deficient mice, and can influence important local parameters. This protocol can be completed in approximately 4 h 20 min.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Oosterhout, A.J. & Bloksma, N. Regulatory T-lymphocytes in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 26, 918–932 (2005).
Doganci, A., Sauer, K., Karwot, R. & Finotto, S. Pathological role of IL-6 in the experimental allergic bronchial asthma in mice. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 28, 257–270 (2005).
Sinigaglia, F. & D'Ambrosio, D. Regulation of helper T cell differentiation and recruitment in airway inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 162, S157–160 (2000).
Neurath M.F., Finotto, S & Glimcher, L.H. The role of Th1/Th2 polarization in mucosal immunity. Nat. Med. 8, 567–73 (2002).
Doganci, A. et al. The IL-6R alpha chain controls lung CD4+CD25+ Treg development and function during allergic airway inflammation in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 313–325 (2005).
Hausding, M. et al. A stage-specific functional role of the leucine zipper transcription factor c-Maf in lung Th2 cell differentiation. Eur. J. Immunol. 34, 3401–3412 (2004).
Yoo, J.K. et al. IL-12 Provides proliferation and survival signals to murine CD4 T cells through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 169, 3637–3643 (2002).
Yang, J. et al. Schistosoma japonicum egg antigens stimulate CD4 CD25 T cells and modulate airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. Immunology, published online 17 October 2006 (doi: 10.1111/j.1365–2567.2006.02472.x).
Quinn, K.M. et al. Inactivation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells during early mycobacterial infection increases cytokine production but does not affect pathogen load. Immunol. Cell Biol. 84, 467–474 (2006).
Finotto, S. et al. Asthmatic changes in mice lacking T-bet are mediated by IL-13. Int Immunol. 17, 993–1007 (2005).
Jelley-Gibbs, D.M. et al. Unexpected prolonged presentation of influenza antigens promotes CD4 T cell memory generation. J. Exp. Med. 202, 697–706 (2005).
Sakoda, Y. et al. Donor-derived thymic-dependent T cells cause chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood, published online 10 October 2006 (doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-042853).
Finotto, S. et al. Development of spontaneous airway changes consistent with human asthma in mice lacking T-bet. Science 295, 336–338 (2002).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by German grant SFB 548-B8-Z3. The authors thank Professor Jürgen Knop for his support to the Asthma Core Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauer, K., Scholtes, P., Karwot, R. et al. Isolation of CD4+ T cells from murine lungs: a method to analyze ongoing immune responses in the lung. Nat Protoc 1, 2870–2875 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.435
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.435
This article is cited by
-
Nuclear receptor Nr1d1 alleviates asthma by abating GATA3 gene expression and Th2 cell differentiation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
CARD9S12N facilitates the production of IL-5 by alveolar macrophages for the induction of type 2 immune responses
Nature Immunology (2018)
-
Cross-protective mucosal immunity mediated by memory Th17 cells against Streptococcus pneumoniae lung infection
Mucosal Immunology (2017)
-
Targeting TSLP With shRNA Alleviates Airway Inflammation and Decreases Epithelial CCL17 in a Murine Model of Asthma
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2016)
-
Increased expression of the Th17-IL-6R/pSTAT3/BATF/RorγT-axis in the tumoural region of adenocarcinoma as compared to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
Scientific Reports (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.