Abstract
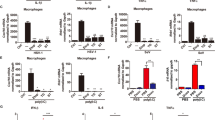
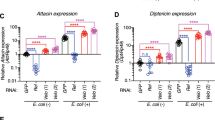
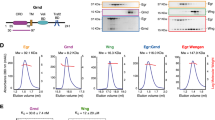
The extracellular protein Spätzle is required for activation of the Toll signaling pathway in the embryonic development and innate immune defense of Drosophila. Spätzle is synthesized as a pro-protein and is processed to a functional form by a serine protease. We show here that the mature form of Spätzle triggers a Toll-dependent immune response after injection into the hemolymph of flies. Spätzle specifically bound to Drosophila cells and to Cos-7 cells expressing Toll. Furthermore, in vitro experiments showed that the mature form of Spätzle bound to the Toll ectodomain with high affinity and with a stoichiometry of one Spätzle dimer to two receptors. The Spätzle pro-protein was inactive in all these assays, indicating that the pro-domain sequence, which is natively unstructured, acts to prevent interaction of the cytokine and its receptor Toll. These results show that, in contrast to the human Toll-like receptors, Drosophila Toll requires only an endogenous protein ligand for activation and signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janeway, C.A. & Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 197–216 (2002).
Kaisho, T. & Akira, S. Toll-like receptors as adjuvant receptors. Bba-Mol. Cell. Res. 1589, 1–13 (2002).
Krutzik, S.R., Sieling, P.A. & Modlin, R.L. The role of Toll-like receptors in host defense against microbial infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 104–108 (2001).
Underhill, D.M. & Ozinsky, A. Toll-like receptors: key mediators of microbe detection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14, 103–110 (2002).
Imler, J.L. & Hoffmann, J.A. Toll receptors in innate immunity. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 304–311 (2001).
Belvin, M.P. & Anderson, K.V. A conserved signaling pathway: The Drosophila Toll-Dorsal pathway. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 12, 393–416 (1996).
Irving, P. et al. A genome-wide analysis of immune responses in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 15119–15124 (2001).
Rutschmann, S. et al. The Rel protein DIF mediates the antifungal but not the antibacterial host defense in Drosophila. Immunity 12, 569–580 (2000).
De Gregorio, E., Spellman, P.T., Tzou, P., Rubin, G.M. & Lemaitre, B. The Toll and Imd pathways are the major regulators of the immune response in Drosophila. EMBO J. 21, 2568–2579 (2002).
Mizuguchi, K., Parker, J.S., Blundell, T.L. & Gay, N.J. Getting knotted: a model for the structure and activation of Spatzle. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 239–242 (1998).
LeMosy, E.K., Tan, Y.Q. & Hashimoto, C. Activation of a protease cascade involved in patterning the Drosophila embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5055–5060 (2001).
Dissing, M., Giordano, H. & DeLotto, R. Autoproteolysis and feedback in a protease cascade directing Drosophila dorsal-ventral cell fate. EMBO J. 20, 2387–2393 (2001).
DeLotto, Y. & DeLotto, R. Proteolytic processing of the Drosophila Spatzle protein by Easter generates a dimeric NGF-like molecule with ventralising activity. Mech. Develop. 72, 141–148 (1998).
Levashina, E.A. et al. Constitutive activation of toll-mediated antifungal defense in serpin-deficient Drosophila. Science 285, 1917–1919 (1999).
Ligoxygakis, P., Pelte, N., Hoffmann, J.A. & Reichhart, J.M. Activation of Drosophila Toll during fungal infection by a blood serine protease. Science 297, 114–116 (2002).
Schneider, D.S., Hudson, K.L., Lin, T.Y. & Anderson, K.V. Dominant and recessive mutations define functional domains of Toll, a transmembrane protein required for dorsal ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 5, 797–807 (1991).
Tauszig, S., Jouanguy, E., Hoffmann, J.A. & Imler, J.L. Toll-related receptors and the control of antimicrobial peptide expression in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 10520–10525 (2000).
Ooi, J.Y., Yagi, Y., Hu, X.D. & Ip, Y.T. The Drosophila Toll-9 activates a constitutive antimicrobial defense. EMBO Rep. 3, 82–87 (2002).
Luo, C., Shen, B., Manley, J.L. & Zheng, L. Tehao functions in the Toll pathway in Drosophila melanogaster: possible roles in development and innate immunity. Insect Mol. Biol. 10, 457–464 (2001).
Livnah, O. et al. Crystallographic evidence for preformed dimers of erythropoietin receptor before ligand activation. Science 283, 987–990 (1999).
Lemmon, M.A. et al. Two EGF molecules contribute additively to stabilization of the EGFR dimer. EMBO J. 16, 281–294 (1997).
Holbrook, M.R., Slakey, L.L. & Gross, D.J. Thermodynamic mixing of molecular states of the epidermal growth factor receptor modulates macroscopic ligand binding affinity. Biochem. J. 352, 99–108 (2000).
Huizinga, E.G. et al. Structures of glycoprotein Ibα and its complex with von Willebrand factor A1 domain. Science 297, 1176–1179 (2002).
Liu, J., Tan, H. & Rost, B. Loopy proteins appear conserved in evolution. J. Mol. Biol. 322, 53–64 (2002).
Cuff, J.A., Clamp, M.E., Siddiqui, A.S., Finlay, M. & Barton, G.J. JPred: a consensus secondary structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 14, 892–893 (1998).
Lee, R., Kermani, P., Teng, K.K. & Hempstead, B.L. Regulation of cell survival by secreted proneurotrophins. Science 294, 1945–1948 (2001).
Rattenholl, A. et al. The pro-sequence facilitates folding of human nerve growth factor from Escherichia coli inclusion bodies. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 3296–3303 (2001).
Zuany-Amorim, C., Hastewell, J. & Walker, C. Toll-like receptors as potential therapeutic targets for multiple diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 1, 797–807 (2002).
Lien, E. et al. Toll-like receptor 4 imparts ligand-specific recognition of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 497–504 (2000).
Poltorak, A., Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P., Citterio, S. & Beutler, B. Physical contact between lipopolysaccharide and Toll-like receptor 4 revealed by genetic complementation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2163–2167 (2000).
da Silva Correia, J., Soldau, K., Christen, U., Tobias, P.S. & Ulevitch, R.J. Lipopolysaccharide is in close proximity to each of the proteins in its membrane receptor complex - Transfer from CD14 to TLR4 and MD-2. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 21129–21135 (2001).
Mitsuzawa, H. et al. Extracellular toll-like receptor 2 region containing Ser(40)-Ile(64) but not Cys(30)-Ser(39) is critical for the recognition of Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 41350–41356 (2001).
Takeuchi, O. et al. Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int. Immunol. 13, 933–940 (2001).
Singh, P.K. et al. Production of β-defensins by human airway epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14961–14966 (1998).
Liu, L.D., Roberts, A.A. & Ganz, T. By IL-1 signaling, monocyte-derived cells dramatically enhance the epidermal antimicrobial response to lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 170, 575–580 (2003).
Michel, T., Reichhart, J.M., Hoffmann, J.A. & Royet, J. Drosophila Toll is activated by Gram-positive bacteria through a circulating peptidoglycan recognition protein. Nature 414, 756–759 (2001).
Rutschmann, S. et al. Role of Drosophila IKKγ in a Toll-independent antibacterial immune response. Nat. Immunol. 1, 342–347 (2000).
Lemaitre, B., Reichhart, J.M. & Hoffmann, J.A. Drosophila host defense: Differential induction of antimicrobial peptide genes after infection by various classes of microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14614–14619 (1997).
Clemens, J.C. et al. Use of double-stranded RNA interference in Drosophila cell lines to dissect signal transduction pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6499–6503 (2000).
Gascan, H. et al. Constitutive production of human interleukin for Da-cells leukemia inhibitory factor by human tumor-cell lines derived from various tissues. J. Immunol. 144, 2592–2598 (1990).
Robledo, O. et al. Signaling of the cardiotrophin-1 receptor - Evidence for a third receptor component. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4855–4863 (1997).
DeLotto, Y., Smith, C. & DeLotto, R. Multiple isoforms of the Drosophila Spatzle protein are encoded by alternatively spliced maternal mRNAs in the precellular blastoderm embryo. Mol. Gen. Genet. 264, 643–652 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Shah, T. Chapman, P. Lowe, G. Praefcke and M. Moncrieffe for advice on baculovirus expression and biophysical techniques, as well as J. Royet for reagents and advice for hemolymph transfer experiments. We also thank J. Ladbury and T. Blundell for discussions and critical reading of this manuscript. We thank M. Sims for access to facilities in the GlaxoSmithKline Immunology Department in Stevenage. This work was supported by Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and the National Institutes of Health (grant 5P01AI44220-02). S.T.-D. was supported by a short-term fellowship from La Ligue Contre le Cancer. A.W. was supported by GlaxoSmithKline, The Cambridge European Trust and St. John's College, Cambridge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, A., Tauszig-Delamasure, S., Hoffmann, J. et al. Binding of the Drosophila cytokine Spätzle to Toll is direct and establishes signaling. Nat Immunol 4, 794–800 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni955
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni955