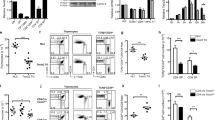
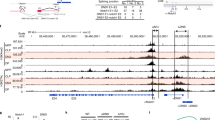
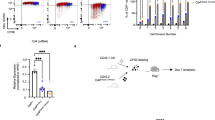
Abstract
CD4 and the transcription factor ThPOK are essential for the differentiation of major histocompatibility complex class II–restricted thymocytes into the helper T cell lineage; their genes (Cd4 and Zbtb7b (called 'ThPOK' here)) are repressed by transcriptional silencer elements in cytotoxic T cells. The molecular mechanisms regulating expression of these genes during helper T cell lineage differentiation remain unknown. Here we showed that inefficient upregulation of ThPOK, induced by removal of the proximal enhancer from the ThPOK locus, resulted in the transdifferentiation of helper lineage–specified cells into the cytotoxic T cell lineage. Furthermore, direct antagonism by ThPOK of the Cd4 and ThPOK silencers generated two regulatory loops that initially inhibited Cd4 downregulation and later stabilized ThPOK expression. Our results show how an initial lineage–specification signal can be amplified and stabilized during the lineage–commitment process.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothenberg, E.V. & Dionne, C.J. Lineage plasticity and commitment in T-cell development. Immunol. Rev. 187, 96–115 (2002).
Singh, H., Medina, K.L. & Pongubala, J.M. Contingent gene regulatory networks and B cell fate specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 4949–4953 (2005).
Laiosa, C.V., Stadtfeld, M. & Graf, T. Determinants of lymphoid-myeloid lineage diversification. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 24, 705–738 (2006).
Ellmeier, W., Sawada, S. & Littman, D.R. The regulation of CD4 and CD8 coreceptor gene expression during T cell development. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 523–554 (1999).
Suzuki, H., Punt, J.A., Granger, L.G. & Singer, A. Asymmetric signaling requirements for thymocyte commitment to the CD4+ versus CD8+ T cell lineages: a new perspective on thymic commitment and selection. Immunity 2, 413–425 (1995).
Lundberg, K., Heath, W., Kontgen, F., Carbone, F.R. & Shortman, K. Intermediate steps in positive selection: differentiation of CD4+8int TCRint thymocytes into CD4−8+TCRhi thymocytes. J. Exp. Med. 181, 1643–1651 (1995).
Brugnera, E. et al. Coreceptor reversal in the thymus: signaled CD4+8+ thymocytes initially terminate CD8 transcription even when differentiating into CD8+ T cells. Immunity 13, 59–71 (2000).
Bosselut, R., Guinter, T.I., Sharrow, S.O. & Singer, A. Unraveling a revealing paradox: Why major histocompatibility complex I-signaled thymocytes “paradoxically” appear as CD4+8lo transitional cells during positive selection of CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 197, 1709–1719 (2003).
Chan, S., Correia-Neves, M., Dierich, A., Benoist, C. & Mathis, D. Visualization of CD4/CD8 T cell commitment. J. Exp. Med. 188, 2321–2333 (1998).
Singer, A. & Bosselut, R. CD4/CD8 coreceptors in thymocyte development, selection, and lineage commitment: analysis of the CD4/CD8 lineage decision. Adv. Immunol. 83, 91–131 (2004).
Yasutomo, K., Doyle, C., Miele, L., Fuchs, C. & Germain, R.N. The duration of antigen receptor signalling determines CD4+ versus CD8+ T-cell lineage fate. Nature 404, 506–510 (2000).
Liu, X. & Bosselut, R. Duration of TCR signaling controls CD4–CD8 lineage differentiation in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 5, 280–288 (2004).
Sarafova, S.D. et al. Modulation of coreceptor transcription during positive selection dictates lineage fate independently of TCR/coreceptor specificity. Immunity 23, 75–87 (2005).
Sawada, S., Scarborough, J.D., Killeen, N. & Littman, D.R. A lineage-specific transcriptional silencer regulates CD4 gene expression during T lymphocyte development. Cell 77, 917–929 (1994).
Leung, R.K. et al. Deletion of the CD4 silencer element supports a stochastic mechanism of thymocyte lineage commitment. Nat. Immunol. 2, 1167–1173 (2001).
Zou, Y.R. et al. Epigenetic silencing of CD4 in T cells committed to the cytotoxic lineage. Nat. Genet. 29, 332–336 (2001).
Siu, G., Wurster, A.L., Duncan, D.D., Soliman, T.M. & Hedrick, S.M. A transcriptional silencer controls the developmental expression of the CD4 gene. EMBO J. 13, 3570–3579 (1994).
Bilic, I. & Ellmeier, W. The role of BTB domain-containing zinc finger proteins in T cell development and function. Immunol. Lett. 108, 1–9 (2007).
Dave, V.P., Allman, D., Keefe, R., Hardy, R.R. & Kappes, D.J. HD mice: a novel mouse mutant with a specific defect in the generation of CD4+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8187–8192 (1998).
Keefe, R., Dave, V., Allman, D., Wiest, D. & Kappes, D.J. Regulation of lineage commitment distinct from positive selection. Science 286, 1149–1153 (1999).
He, X. et al. The zinc finger transcription factor Th-POK regulates CD4 versus CD8 T-cell lineage commitment. Nature 433, 826–833 (2005).
Sun, G. et al. The zinc finger protein cKrox directs CD4 lineage differentiation during intrathymic T cell positive selection. Nat. Immunol. 6, 373–381 (2005).
Setoguchi, R. et al. Repression of the transcription factor Th-POK by Runx complexes in cytotoxic T cell development. Science 319, 822–825 (2008).
He, X. et al. CD4–CD8 lineage commitment is regulated by a silencer element at the ThPOK transcription-factor locus. Immunity 28, 346–358 (2008).
Taniuchi, I. et al. Differential requirements for Runx proteins in CD4 repression and epigenetic silencing during T lymphocyte development. Cell 111, 621–633 (2002).
Woolf, E. et al. Runx3 and Runx1 are required for CD8 T cell development during thymopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 7731–7736 (2003).
Koller, B.H., Marrack, P., Kappler, J.W. & Smithies, O. Normal development of mice deficient in β2M, MHC class I proteins, and CD8+ T cells. Science 248, 1227–1230 (1990).
Grusby, M.J., Johnson, R.S., Papaioannou, V.E. & Glimcher, L.H. Depletion of CD4+ T cells in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Science 253, 1417–1420 (1991).
Kawamoto, H., Ikawa, T., Ohmura, K., Fujimoto, S. & Katsura, Y. T cell progenitors emerge earlier than B cell progenitors in the murine fetal liver. Immunity 12, 441–450 (2000).
Egawa, T., Tillman, R.E., Naoe, Y., Taniuchi, I. & Littman, D.R. The role of the Runx transcription factors in thymocyte differentiation and in homeostasis of naive T cells. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1945–1957 (2007).
Pearce, E.L. et al. Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor Eomesodermin. Science 302, 1041–1043 (2003).
Taniuchi, I., Sunshine, M.J., Festenstein, R. & Littman, D.R. Evidence for distinct CD4 silencer functions at different stages of thymocyte differentiation. Mol. Cell 10, 1083–1096 (2002).
Kappes, D.J., He, X. & He, X. Role of the transcription factor Th-POK in CD4:CD8 lineage commitment. Immunol. Rev. 209, 237–252 (2006).
Djuretic, I.M. et al. Transcription factors T-bet and Runx3 cooperate to activate Ifng and silence Il4 in T helper type 1 cells. Nat. Immunol. 8, 145–153 (2007).
Jenkinson, S.R. et al. Expression of the transcription factor cKrox in peripheral CD8 T cells reveals substantial postthymic plasticity in CD4–CD8 lineage differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 204, 267–272 (2007).
Bilic, I. et al. Negative regulation of CD8 expression via Cd8 enhancer-mediated recruitment of the zinc finger protein MAZR. Nat. Immunol. 7, 392–400 (2006).
Wildt, K.F. et al. The transcription factor zbtb7b promotes CD4 expression by antagonizing runx-mediated activation of the CD4 silencer. J. Immunol. 179, 4405–4414 (2007).
Ogawa, H., Ishiguro, K., Gaubatz, S., Livingston, D.M. & Nakatani, Y. A complex with chromatin modifiers that occupies E2F- and Myc-responsive genes in G0 cells. Science 296, 1132–1136 (2002).
Naoe, Y. et al. Repression of interleukin-4 in T helper type 1 cells by Runx/Cbf beta binding to the Il4 silencer. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1749–1755 (2007).
Intlekofer, A.M. et al. Effector and memory CD8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1236–1244 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank D.J. Kappes (Fox Chase Cancer Center) for cDNA encoding helper-deficient mutant ThPOK; Y. Nakatani (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute) for the pOZ-FH-N vector; M. Matsuda for aggregation of embryonic stem cells; I. Hisanaga for microinjection of transgenes; H. Fujimoto and Y. Hachiman for cell sorting; and W. Ellmeier and S.L. Reiner for critical reading of the manuscript. Supported by Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology, Japan Science and Technology Agency (I.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.M. generated all mice with mutations at the ThPOK locus and did phenotypic analyses with assistance from C.M.; Y.N. did ChIP assays with tiling arrays with assistance from K.A.; T.I., K.M. and H.K. did in vitro culture in thymic lobes; and I.T. designed the experiments, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 956 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muroi, S., Naoe, Y., Miyamoto, C. et al. Cascading suppression of transcriptional silencers by ThPOK seals helper T cell fate. Nat Immunol 9, 1113–1121 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1650
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1650
This article is cited by
-
Downregulation of chemokine receptor 9 facilitates CD4+CD8αα+ intraepithelial lymphocyte development
Nature Communications (2023)
-
TCF-1: a maverick in T cell development and function
Nature Immunology (2022)
-
CD4 expression in effector T cells depends on DNA demethylation over a developmentally established stimulus-responsive element
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Chemokine receptor CCR9 suppresses the differentiation of CD4+CD8αα+ intraepithelial T cells in the gut
Mucosal Immunology (2022)
-
Essential role of a ThPOK autoregulatory loop in the maintenance of mature CD4+ T cell identity and function
Nature Immunology (2021)