Abstract
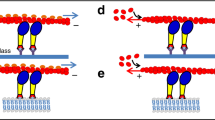
Myosin is an actin-based molecular motor that constitutes a diverse superfamily1,2. In contrast to conventional myosin, which binds to actin for only a short time during cross-bridge cycling, recent studies have demonstrated that class V myosin moves along actin filaments for a long distance without dissociating3,4. This would make it suitable for supporting cargo movement in cells. Because myosin V has a two-headed structure with an expanded neck domain, it has been postulated to 'walk' along the 36-nm helical repeat of the actin filament, with one head attached to the actin and leading the other head to the neighbouring helical pitch5. Here, we report that myosin IXb, a single-headed myosin, moves processively on actin filaments. Furthermore, we found that myosin IXb is a minus-end-directed motor. In addition to class VI myosin, this is the first myosin superfamily member identified that moves in the reverse direction6. The processive movement of the single-headed myosin IXb cannot be explained by a 'hand-over-hand' mechanism. This suggests that an alternative mechanism must be operating for the processive movement of single-headed myosin IXb.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mooseker, M. S. & Cheney, R. E. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 633–675 (1995).
Hodge, T. & Cope, M. J. J. Cell Sci. 113, 3353–3354 (2000).
Mehta, A. D. et al. Nature 400, 590–593 (1999).
Sakamoto, T., Amitani, I., Yokota, E. & Ando, T. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 272, 586–590 (2000).
Walker, M. L. et al. Nature 405, 804–807 (2000).
Wells, A. L. et al. Nature 401, 505–508 (1999).
Reinhard, J. et al. EMBO J. 14, 697–704 (1995).
Chieregatti, E., Gartner, A., Stofler, H. E. & Bahler, M. J. Cell Sci. 111, 3597–3608 (1998).
Wirth, J. A., Jensen, P. L., Post, W. M., Bement, M. S. & Mooseker, M. S. J. Cell Sci. 109, 653–661 (1996).
Kalhammer, G., Bahler, M., Schmitz, F., Jockel, J. & Block, C. FEBS Lett. 414, 599–602 (1997).
Schroder, R.R et al. Nature 364, 171–174 (1993).
Bahler, M. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1496, 52–59 (2000).
Sellers, J. R. Myosins (2nd ed.) Oxford University Press, New York (1999).
Cross, R. A. Curr. Biol. 18, R854–R856 (1999).
Rief, M. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9482–9486 (2000).
Post, P. L., Bokoch, G. M. & Mooseker, M. S. J. Cell Sci. 111, 941–950 (1998).
Rock, R. S., Rief, M., Mehta, A. D. & Spudich, J. A. Methods, 22, 373–381 (2000).
Uyeda, T. Q. P., Warrick, H. M., Kron, S. J. & Spudich, J. A. Nature, 352, 307–311 (1991).
Howard, J., Hudspeth, A. J. & Vale, R. D. Nature 342, 154–158 (1989).
Homma, K., Yoshimura, M., Saito, J., Ikebe, R. & Ikebe, M. Nature, 412, 831–834 (2001).
Okada, Y. & Hirokawa, N. Scinece 283, 1152–1157 (1999).
Okada, Y. & Hirokawa, N. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 640–645 (2000).
Kikkawa, M. et al. Nature, 411, 439–445 (2001).
Spudich, J. A. & Watt, J. J. Biol. Chem. 246, 4866–4871 (1971).
Zhu, T., Sata, M. & Ikebe, M. Biochemistry 35, 513–522 (1996).
Homma, K., Saito, J., Ikebe, R. & Ikebe, M. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 34766–34771 (2000).
Ikebe, M. & Hartshorne, D. J. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 13146–13153 (1985).
Ikebe, M., Stepinska, M., Kemp, B. E., Means, A. R., & Hartshorne, D. J. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 13828–13834 (1987).
Hoh, J. F. Y., McGrath, P. A. & White, R. I. Biochem. J. 157, 87–95 (1976).
Sata, M., Matsu-ura, M. & Ikebe, M. Biochemistry 35, 11113–11118 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Homma for his technical advice and valuable discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Movie 1
Video clips of Fig. 2b. Playback speed and scale are shown in the upper left and the lower left, respectively. (MOV 2806 kb)
Movie 2
Video clips of Fig. 3. Playback speed and scale are shown in the upper left and the lower left, respectively. (MOV 421 kb)
Movie 3
Video clips of Fig. 4a. Playback speed and scale are shown in the upper left and the lower left, respectively. (MOV 1887 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, A., Saito, J., Ikebe, R. et al. Myosin IXb is a single-headed minus-end-directed processive motor. Nat Cell Biol 4, 302–306 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb774
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb774
This article is cited by
-
Conformational changes at the nucleotide site in the presence of bound ADP do not set the velocity of fast Drosophila myosins
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2013)
-
Myosin VI: an innovative motor that challenged the swinging lever arm hypothesis
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2010)