Abstract
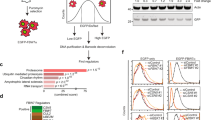
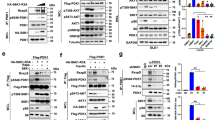
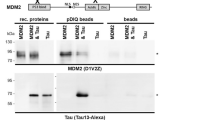
The neurofibromatosis-2 (NF2) tumour-suppressor gene encodes an intracellular membrane-associated protein, called merlin, whose growth-suppressive function is dependent on its ability to form interactions through its intramolecular amino-terminal domain (NTD) and carboxy-terminal domain (CTD)1,2,3. Merlin phosphorylation plays a critical part in dictating merlin NTD/CTD interactions as well as in controlling binding to its effector proteins4,5,6,7. Merlin is partially regulated by phosphorylation of Ser 518, such that hyperphosphorylated merlin is inactive and fails to form productive intramolecular and intermolecular interactions8,9. Here, we show that the protein kinase Akt directly binds to and phosphorylates merlin on residues Thr 230 and Ser 315, which abolishes merlin NTD/CTD interactions and binding to merlin's effector protein PIKE-L and other binding partners. Furthermore, Akt-mediated phosphorylation leads to merlin degradation by ubiquitination. These studies demonstrate that Akt-mediated merlin phosphorylation regulates the function of merlin in the absence of an inactivating mutation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gutmann, D. H., Haipek, C. A. & Hoang Lu, K. Neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein, merlin, forms two functionally important intramolecular associations. J. Neurosci. Res. 58, 706–716 (1999).
Gonzalez-Agosti, C., Wiederhold, T., Herndon, M. E., Gusella, J. & Ramesh, V. Interdomain interaction of merlin isoforms and its influence on intermolecular binding to NHE-RF. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 34438–34442 (1999).
Meng, J. J. et al. Interaction between two isoforms of the NF2 tumor suppressor protein, merlin, and between merlin and ezrin, suggests modulation of ERM proteins by merlin. J. Neurosci. Res. 62, 491–502 (2000).
Kissil, J. L., Johnson, K. C., Eckman, M. S. & Jacks, T. Merlin phosphorylation by p21-activated kinase 2 and effects of phosphorylation on merlin localization. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10394–10399 (2002).
Xiao, G. H., Beeser, A., Chernoff, J. & Testa, J. R. p21-activated kinase links Rac/Cdc42 signaling to merlin. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 883–886 (2002).
Morrison, H. et al. The NF2 tumor suppressor gene product, merlin, mediates contact inhibition of growth through interactions with CD44. Genes Dev. 15, 968–980 (2001).
Rong, R., Surace, E. I., Haipek, C. A., Gutmann, D. H. & Ye, K. Serine 518 phosphorylation modulates merlin intramolecular association and binding to critical effectors important for NF2 growth suppression. Oncogene 23, 8447–8454 (2004).
Shaw, R. J., McClatchey, A. I. & Jacks, T. Regulation of the neurofibromatosis type 2 tumor suppressor protein, merlin, by adhesion and growth arrest stimuli. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7757–7764 (1998).
Jin, H., Sperka, T., Herrlich, P. & Morrison, H. Tumorigenic transformation by CPI-17 through inhibition of a merlin phosphatase. Nature 442, 576–579 (2006).
Hu, Y. et al. Akt phosphorylates acinus and inhibits its proteolytic cleavage, preventing chromatin condensation. EMBO J. 24, 3543–3554 (2005).
Sarbassov, D. D., Guertin, D. A., Ali, S. M. & Sabatini, D. M. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307, 1098–1101 (2005).
Sarbassov, D. D. et al. Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol. Cell 22, 159–168 (2006).
Shiota, C., Woo, J. T., Lindner, J., Shelton, K. D. & Magnuson, M. A. Multiallelic disruption of the rictor gene in mice reveals that mTOR complex 2 is essential for fetal growth and viability. Dev. Cell 11, 583–589 (2006).
Guertin, D. A. et al. Ablation in mice of the mTORC components raptor, rictor, or mLST8 reveals that mTORC2 is required for signaling to Akt-FOXO and PKCalpha, but not S6K1. Dev. Cell 11, 859–871 (2006).
Rong, R., Tang, X., Gutmann, D. H. & Ye, K. Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) tumor suppressor merlin inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase through binding to PIKE.-L. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 18200–18205 (2004).
Pearson, M. A., Reczek, D., Bretscher, A. & Karplus, P. A. Structure of the ERM protein moesin reveals the FERM domain fold masked by an extended actin binding tail domain. Cell 101, 259–270 (2000).
Kim, H. et al. Merlin neutralizes the inhibitory effect of Mdm2 on p53. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7812–7818 (2004).
Lee, J. Y. et al. Merlin facilitates ubiquitination and degradation of transactivation-responsive RNA-binding protein. Oncogene 25, 1143–1152 (2006).
Zhou, B. P. et al. HER-2/neu induces p53 ubiquitination via Akt-mediated MDM2 phosphorylation. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 973–982 (2001).
Brazil, D. P., Park, J. & Hemmings, B. A. PKB binding proteins. Getting in on the Akt. Cell 111, 293–303 (2002).
Gautreau, A. et al. Mutant products of the NF2 tumor suppressor gene are degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 31279–31282 (2002).
Alfthan, K., Heiska, L., Gronholm, M., Renkema, G. H. & Carpen, O. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates Merlin at serine 518 independently of P21-activated kinase and promotes Merlin-Ezrin heterodimerization. J. Biol. Chem. (2004).
Scoles, D. R. et al. Neurofibromatosis 2 tumour suppressor schwannomin interacts with betaII-spectrin. Nature Genet. 18, 354–359 (1998).
Neill, G. W. & Crompton, M. R. Binding of the merlin-I product of the neurofibromatosis type 2 tumour suppressor gene to a novel site in beta-fodrin is regulated by association between merlin domains. Biochem. J. 358, 727–735 (2001).
Chen, Y., Yu, P., Lu, D., Tagle, D. A. & Cai, T. A novel isoform of beta-spectrin II localizes to cerebellar Purkinje-cell bodies and interacts with neurofibromatosis type 2 gene product schwannomin. J. Mol. Neurosci. 17, 59–70 (2001).
Kakhniashvili, D. G. et al. Erythrocyte spectrin is an E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme. Biochemistry 40, 11630–11642 (2001).
Cichowski, K., Santiago, S., Jardim, M., Johnson, B. W. & Jacks, T. Dynamic regulation of the Ras pathway via proteolysis of the NF1 tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 17, 449–454 (2003).
Ahn, J. Y. et al. Nuclear Akt associates with PKC-phosphorylated Ebp1, preventing DNA fragmentation by inhibition of caspase-activated DNase. EMBO J. 25, 2083–2095 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Research-Initiated Award from the Department of Defense (NF05009) and RO1 (CA117872) from NIH to K.Y. as well as an Investigator-Initiated Award from Department of Defense (DAMD-17-04-0266) to D.H.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1, S2 and S3 (PDF 235 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Jang, SW., Wang, X. et al. Akt phosphorylation regulates the tumour-suppressor merlin through ubiquitination and degradation. Nat Cell Biol 9, 1199–1207 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1641
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1641
This article is cited by
-
The genetic landscape and possible therapeutics of neurofibromatosis type 2
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 4B induces lipogenesis via the Hippo pathway
Archives of Virology (2023)
-
Molecular profiling reveals primary mesothelioma cell lines recapitulate human disease
Cell Death & Differentiation (2016)
-
Role of Merlin/NF2 inactivation in tumor biology
Oncogene (2016)
-
The combination of sorafenib and everolimus shows antitumor activity in preclinical models of malignant pleural mesothelioma
BMC Cancer (2015)