Abstract
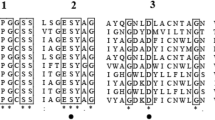
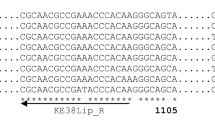
The nucleotide sequence of the gene from Pseudomonas diminuta MG encoding parathion hydrolase was determined, and a single open reading frame located. Comparison of the deduced N-terminal amino acid sequence with that determined by protein sequence analysis of the enzyme from P. diminuta MG indicated that parathion hydrolase is synthesized as a 365 amino acid precursor from which 29 amino acids are removed. Expression of the processed parathion hydrolase coding sequence in Escherichia coli under the control of lambda PL promoter results in the production of high-level enzyme activity. Furthermore, addition of metal salts to the growth medium enhanced specific activity. The N-terminal amino acid sequence, C-terminal amino acid sequence and the amino acid composition of the purified enzyme were in agreement to those expected from the translated DNA sequence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eto, M. 1974. Organophosphorus pesticides: organic and biological chemistry. CRC Press Inc. Cleveland, Ohio.
Munnecke, D.M. and Hsieh, D.P.H. 1976. Pathways of microbial metabolism of parathion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31:63–69.
Munnecke, D.M. 1980. Enzymatic detoxification of waste organo-phosphate pesticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 28:105–111.
Barik, S. and Munnecke, D.M. 1982. Enzymatic hydrolysis of concentrated diazinon in soil. Bull. Environm. Contam. Toxicol. 29:235–239.
Honeycutt, R., Ballantine, L., LeBaron, H., Paulson, D., Seim, V., Ganz, C., and Milad, G. 1984. Degradation of high concentrations of a phosphorothioic ester by hydrolase. ACS Symposium Series, No. 259. Treatment & Disposal of Pesticide Wastes, p. 343–352.
Serdar, C.M., Gibson, D.T., Munnecke, D.M., and Lancaster, J.H. 1982. Plasmid involvement in parathion hydrolysis by Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44:246–249.
Mulbry, W.W., Karns, J.S., Kearney, P.C., Nelson, J.O., McDaniels, C.S., and Wild, J.R. 1986. Identification of a plamid-borne parathion hydrolase gene from Flavobacterium sp. by Southern hybridization with opd from Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 51:926–930.
Mulbry, W.W., Kearney, P.C., Nelson, J.O., and Karns, J.S. 1987. Physical comparison of parathion hydrolase plasmids from Pseudomonas diminuta and Flavobacterium sp. Plasmid 18:173–177.
Serdar, C.M. and Murdock, D.M. 1989. Plasmid encoded parathion hydrolase activity, p. 143–154. In: Enzymes Hydrolysing Organophosphorus Compounds. E. Reiner, W. Aldridge, and F. Hoskin (Eds.). Ellis Horwood Publishers, NY.
Serdar, C. M. and Gibson, D. T. 1985. Enzymatic hydrolysis of organophosphates: cloning and expression of a parathion hydrolase gene from Pseudomonas diminuta. Nature Biotechnology. 3:567–571.
von Heijne, G. 1984. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 173:243–251.
Konigsberg, W. and Godson, G.N. 1983. Evidence for use of rare codons in the dnaG gene and other regulatory genes of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:687–691.
McDaniel, C.S., Harper, L.L., and Wild, J.R. 1988. Cloning and sequencing of a plasmid-borne gene (opd) encoding a phosphodiesterase. J. Bacteriol. 170:2306–2311.
Harper, L.L., McDaniel, C.S., Miller, C.E., and Wild, J.R. 1988. Dissimilar plasmids isolated from Pseudomonas diminuta MG and a Flavobacterium sp. (ATCC 27551) contain identical opd genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44:246–249.
Steiert, J.G., Pogell, B.M., Speedie, M.K., and Laredo J. 1989. A gene coding for a membrane-bound hydrolase is expressed as a secreted, soluble enzyme in Streptomyces lividans. Nature Biotechnology. 7:65–68.
Morris, C.F. 1987. DNA plasmids. United States Patent 4,710,474.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Sambrook . 1982. J. Molecular Cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Heidecker, G., Messing, J., and Gronenborn, B. 1980. A versatile primer for DNA sequencing in the M13mp2 cloning system. Gene 10:69–73.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulsen, R.R. 1977. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74:5463–5467.
Lu, H.S., Klein, M.L., and Lai, P.-H. 1988. Narrow-bore high-performance chromatography of phenylthiocarbamyl amino acids and carboxypeptidase P digestion for protein C-terminal sequence analysis. Journal Chromatog. 447:351–364.
Caruthers, M.H. 1982. Chemical synthesis of DNA, p. 71–79. In: Chemical and Enzymatic Synthesis of Gene Fragments. Gassen, H. G. and Lang, A. (Eds.). Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, FRG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serdar, C., Murdock, D. & Rohde, M. Parathion Hydrolase Gene from Pseudomonas diminuta MG: Subcloning, Complete Nucleotide Sequence, and Expression of the Mature Portion of the Enzyme in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 7, 1151–1155 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1189-1151
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1189-1151