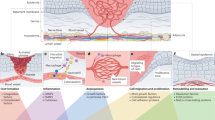
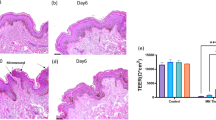
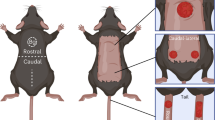
Abstract
The process of wound healing begins immediately following surface lesions or when skin proteins become exposed to radiation, chemical damage or extreme temperatures. Wound repair requires close control of degradative and regenerative processes, involving numerous cell types and complex interactions between multiple biochemical cascades. Growth factors released in the traumatized area promote cell migration into the wound area (chemotaxis), stimulate the growth of epithelial cells and fibroblasts (mitogenesis), initiate the formulation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), and stimulate matrix formation and remodeling of the affected region. Animal studies have shown that exogenously added growth factors can accelerate the normal healing process. Growth factors have also been used successfully in humans to treat previously incurable wounds. The most intensively studied growth factors are EGF, FGFs, PDGF, TGF-α, and TGF-βs. Each of these factors is currently the focus of intense commercial development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sporn, M.B. and Roberts, A.B. 1987. Peptide growth factors Current status and therapeutic opportunities, p. 75–86. In: Important Adv. Oncol. De Vita, V.T. (Ed.). J.B. Lippmcott Company, Philadelphia, PA.
Gray, A., Dal, T.J., and Ullrich, A. 1983. A nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature 303:722–725.
Shoyab, M., Plowman, G.D., McDonald, V.L., Bradley, J.G., and Todaro, G.J. 1989. Structure and function of human amphiregulin: a member of the epidermal growth factor family. Science 243:1074–1076.
Gregory, H. 1975. Isolation and structure of urogastrone and its relationship to epidermal growth factor. Nature 257:325–327.
Cohen, S. 1962. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J. Biol. Chem. 237:1555–1562.
Nakagawa, S., Yoshida, S., Hirao, Y., Kasuga, S., and Fuwa, T. 1985. Biological effects of biosynthetic human EGF on the growth of mammalian cells in vitro . Differentiation 29:284–288.
Blay, J., and Brown, K.D. 1985. Epidermal growth factor promotes the chemotactic migration of cultured rat intestinal epithelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 124:107–112.
Downward, J., Yarden, Y., Mayes, E., Scrace, G., Totty, N., Stockwell, P., Ullrich, A., Schlessmger, J., and Wakefield, M.D. 1984. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erbB oncogene protein sequences. Nature 307:521–527.
Derynck, R., Roberts, A.B., Winkler, M.E., Chen, E.Y., and Goeddel, D.V. 1984. Human transforming growth factor -α: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. . Cell 38:287–297.
Todaro, G.J., Fryling, C., and DeLarco, J.E. 1980. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:5258–5262.
Anzano, M.A., Roberts, A.B., Smith, J.M., Sporn, M.B., and DeLarco, J.E. 1983. Sarcoma growth factor from conditioned medium of virally transformed cells is composed of both type α and type β transforming growth factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:6264–6268.
Ross, R., and Vogel, A. 1978. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 14:203–210.
Hammacher, A., Hellman, U., Johnsson, A., Ostman, A., Gunnarson, K., Westermark, B., Wateson, A., and Heldin, C.-H. 1988. A major part of platelet-derived growth factor purified from human platelets is a heterodimer of one A and one B chain. J. Biol. Chem. 263:16493–16498.
Owen, A.J., Pantazis, P., and Antoniades, H.N. 1984. Simian sarcoma virus-transformed cells secrete a mitogen identical to platelet-derived growth factor. Science 225:54–56.
Ross, R., Raines, E.W., and Bowen-Pope, D.F. 1986. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 45:155–169.
Seppa, H., Grotendorst, G., Seppa, S., Schiffmann, E., and Martin, G.R. 1982. Platelet-derived growth factor is chemotactic for fibro blasts. J. Cell. Biol. 92:584–588.
Deuel, T.F., Senior, R.M., Huang, J.S., and Griffin, G.L. 1982. Chemotaxis of monocytes and neutrophils to platelet-derived growth factor. J. Clin. Invest. 69:1046–1049.
Tzeng, D.Y., Deuel, T.F., Huang, J.S., and Baehner, R.L. 1985. Platelet-derived growth factor promotes human peripheral monocyte activation. Blood 66:179–183.
Ek, B., Heldin, C.-H. 1982. Characterization of a tyrosine-specific kinase activity in human fibroblast membranes stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 257:10486–10492.
Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Wakefield, L.M., and de Crombrugghe, B. 1987. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor beta. J. Cell. Biol. 105:1039–1045.
Derynck, R., Jarrett, J.A., Chen, E.Y., Eaton, D.H., Bell, J.R., Assoian, R.K., Roberts, A.B., Sporn, M.B., and Goeddel, D.V. 1985. Human transforming growth factor-β cDNA sequence and expression in tumor cell lines. Nature 316:701–705.
de Martin, R., Haendler, B., Hofer-Warbinek, R., Gaugitisch, H., Wrann, M., Schusener, H., Seifert, J.M., Bodmer, S., Fontana, A., and Hofer, E. 1987. Complementary DNA for human ghoblastoma-denved T-cell suppressor factor, a novel member of the transforming growth factor-β family. EMBO J. 6:3673–3677.
ten Dijke, P., Hansen, P., Iwata, K.K., Pieler, C., and Foulkes, J.G. 1988. Identification of a new member of the transforming growth factor type β gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:4715–4719.
Rosa, F., Roberts, A.B., Danielpour, D., Dart, L.L., Sporn, M.B., and Dawid, I.B. 1988. Mesoderm induction in amphibians: the role of TGF-β2-like factors. Science, 239:783–789.
Wozney, J.M., Rosen, V., Celeste, A.J., Mitsock, L.M., Whitters, M.J., Kriz, R.W., Hewick, R.M., and Wang, E.A. 1988. Novel regulations of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science 242:1528–1534.
Lobb, R.R., and Fett, J.W. 1984. Purification of 2 distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry 23:6925–6929.
Baird, A., Esch, F., Gospodarowicz, D., and Guillenium, R. 1985. Retina derived endothelial cell growth factors: partial molecular characterization identity with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochemistry 24:7855–7859.
Gospodarowicz, D., Cheng, J., Lui, G.-M., Baird, A., and Bohlen, P. 1984. Isolation by heparin sepharose affinity chromatography of brain fibroblast growth factor: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:6963–6967.
Gimenez-Gallego, G., Rodkey, J., Bennett, C., Rios-Canadelore, M., DiSalvo, J., and Thomas, K. 1985. Brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor. Complete amino acid sequence and homologies. Science 230:1385–1388.
Abraham, J.A., Mergia, A., Whang, J.L., Tumolo, A., Friedman, J., Hjerrild, K.A., Gospodarowicz, D., and Fiddes, J.C. 1986. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science 233:545–548.
Esch, F., Baird, A., Ling, N., Ueno, N., Hill, F., Deneroy, L., Klepper, R., Gospodarowizc, D., Bohlen, P., and Guillenium, R. 1985. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the ammo terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:6507–6511.
Dickson, C., and Gordon, P.E. 1987. Potential oncogene product related to growth factors. Nature 326:833–835.
Taira, M., Yoshida, T., Miyagawa, K., Sakamoto, H., Terada, M., and Sugimura, T. 1987. cDNA sequence of human transforming gene hst, and identification of the coding sequence required for transforming activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:2985–2989.
Kisiel, W., Canfield, W.M., Ericsson, L.H., and Davie, E.W. 1977. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry 16:5824–5831.
Moncada, S., Gryglewski, R., Bunting, S., and Vance, J.R. 1976. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxidoses to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature 263:663–665.
Simpson, D.M., and Ross, R. 1972. The neutrophilic leukocyte in wound repair. A study with antmeutrophil serum. J. Clin. Invest. 51:2009–2023.
Wahl, S.M., Hunt, D.A., Wakefield, L.M., McCartney-Francis, N., Wahl, L.M., Roberts, A.B., and Sporn, M.B. 1987. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:5788–5792.
Postlethwaite, A.E., Keski-Oja, J., Moses, H.L., and Kang, A.H. 1987. Stimulation of the chemotactic migration of human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta. J. Exp. Med. 165:251–256.
Van Obberghen-Schillng, E., Roche, N.S., Flanders, K.C., Sporn, M.B., and Roberts, A.B. 1988. Transforming growth factor β1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J. Biol. Chem. 263:7741–7746.
Paulsson, Y., Hammacher, A., Heldin, C-H., and Westermark, B. 1987. Possible positive autocrine feedback in the prereplicative phase of human fibroblasts. Nature 328:715–717.
Coffey, R.J., Derynck, R., Wilcox, J.N., Bringman, T.X., Goustin, S.A., Moses, H.L., and Pittelkow, M.R. 1987. Production and auto induction of transforing growth factors-α in human keratinocytes. Nature 328:817–820.
Tsunawaki, S., Sporn, M., Ding, A., and Nathan, C. 1988. Deactivation of macrophages by transforming growth factor-β. Nature 334:260–262.
Montesano, R., and Orci, L. 1988. Transforming growth factor β stimulates collagen-matrix contraction by fibroblasts Implications for wound healing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:4894–4897.
Gospodarowicz, E., Massoglia, S., Cheng, J., Lui, G-M., and Bohlen, P. 1985. Isolation of bovine pituitary fibroblast growth factor purified by fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC). Partial chemical and biological characterization. J. Cell. Physiol. 122:323–393.
Gospodarowicz, D., Neufeld, G., and Schweigerer, L. 1986. Molecular and biological characterization of fibroblast growth factor: an angiogenic factor which also controls the proliferation and differentiation of mesoderm and neuroectoderm derived cells. Cell Differ. 19:1–17.
Gospodarowicz, D., and Cheng, J. 1986. Heparin protects basic and acidic FGF from mactivation. J. Cell. Physiol. 128:475–484.
Savion, N., Vlodawshy, I., and Fuks, Z. 1984. Interaction of T lymphocytes and macrophages with cultured vascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 118:169–178.
Yahalom, J., Eldor, A., Fuks, Z., and Vlodavshy, I. 1984. Degradation of sulfated proteoglycans in the subendothelial basement membrane by human platelet hepantmase. J. Clin. Invest. 74:1842–1849.
Roberts, A.B., Sporn, M.B., Assoian, R.K., Smith, J.M., Roche, N.S., Wakefield, L.M., Heine, U.I., Liotta, L.A., Flalnga, V., Kehrl, J.H., and Fauci, A.S. 1986. Transforming growth factor type β: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation m vitro . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:4167–4171.
Merwin, J.R., Anderson, J., and Madri, J.A. 1988. Transforming growth factor-β1 induces angiogenesis of microvascular endothelial cells in three-dimensional culture. J. Cell. Biol. 107:48a
Bauer, E.A., Cooper, T.W., Huang, J.S., Altman, J., and Deuel, T.F. 1985. Stimulation of in vitro human skin collagenase expression by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:4132.
Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Shull, J.H., Smith, J.M., and Ward, M.M. 1983. Polypeptide transforming growth factors isolated from bovine sources and used for wound healing in vivo . Science 219:1329–1331.
Sprugel, K.H., McPherson, J.M., Clowes, A.W., and Ross, R. 1988. The effects of different growth factors in subcutaneous wound chambers. Prog. in Clin. Res 266:77–91.
Cromack, D.T., Sporn, M.B., Roberts, A.B., Merino, M.J., Dart, L.L., and Norton, J.A. 1987. Transforming growth factor p levels in rat wound chambers. J. of Surg. Res. 42:622–628.
Rappolee, D.A., Mark, D., Bandam, J., and Werloz. 1988. Wound macrophages express TGF-α and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science 241:708–712.
Brown, G.L., Curtsinger, L., Brightwell, J.R., Ackerman, D.M., Tobin, G.R., Polk, H.C., George-Nascimento, C., Valenzuela, P., and Schultz, G.S. 1986. Enhancement of epidermal regeneration by biosynthetic epidermal growth factor. J. Exp. Med. 163:1319–1324.
Mustoe, T.A., Pierce, G.F., Thomason, A., Gramates, P., Sporn, M.B., and Duel, T.F. 1987. Accelerated healing of incisional wounds in rats induced by transforming growth factor-β. Science 237:1333–1335.
Pierce, G.F., Mustoe, T.A., Senior, R.M., Reed, J., Griffin, G.L., Thomason, A., and Deuel, T.F. 1988. In vivo incisional wound healing augmented by platelet-derived growth factor and recombmant c-sis gene homodimeric proteins. J. Exp. Med. 167:974–987.
Lawrence, W.T., Sporn, M.B., Gorschboth, C., Norton, J.A., and Grotendorst, G.R. 1986. The reversal of an adriamicin induced healing impairment with chemoatractants and growth factors. Ann. Surg. 203:142–147.
Laato, M. 1988. The effect of epidermal growth factor on granulation tissue formation in the rat. Acta. Chir. Scand. Suppl. 546:1–44.
Grotendorst, G.R., Martin, G.R., Pencet, D., Sodek, J., and Harvey, A.K. 1985. Stimulation of granulation tissue formation by platelet-derived growth factor in normal and diabetic rats. J. Clin. Invest. 76:2323–2329.
Knighton, D.R., Fiegel, V.D., Austin, L.L., Ciresi, K.F., and Butler, E.L. 1986. Classification and treatment of chronic non-healing wounds. Ann. Surg. 204:322–330.
Carter, D.M., Balin, A.K., Gottlieb, A.B., Eisinger, M., Lin, A., Pratt, L., Sherbany, A., and Caldwell, D. 1988. Clinical experience with crude preparation of growth factors in healing of chronic wounds in human subjects. Prog. in Clin. Res. 266:303–319.
Brown, G.L., Curtsinger, L.J., White, M., O'Mitchell, R.O., Pictsch, J., Nordquist, R., von Fraunhofer, A., and Schultz, G. 1988. Acceleration of tensile strength of incisions treated with EGF and TGF-β. Ann. Surg. 208:788–794.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ten Dijke, P., Iwata, K. Growth Factors For Wound Healing. Nat Biotechnol 7, 793–798 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0889-793
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0889-793