Abstract
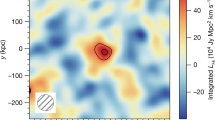
Observations of 21-cm radio emission by neutral hydrogen at redshifts z ≈ 0.5 to ∼2.5 are expected to provide a sensitive probe of cosmic dark energy1,2. This is particularly true around the onset of acceleration at z ≈ 1, where traditional optical cosmology becomes very difficult because of the infrared opacity of the atmosphere. Hitherto, 21-cm emission has been detected3 only to z = 0.24. More distant galaxies generally are too faint for individual detections but it is possible to measure the aggregate emission from many unresolved galaxies in the ‘cosmic web’. Here we report a three-dimensional 21-cm intensity field at z = 0.53 to 1.12. We then co-add neutral-hydrogen (H i) emission from the volumes surrounding about 10,000 galaxies (from the DEEP2 optical galaxy redshift survey4). We detect the aggregate 21-cm glow at a significance of ∼4σ.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, T.-C., Pen, U.-L., Peterson, J. B. & McDonald, P. Baryon acoustic oscillation intensity mapping of dark energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 091303 (2008)
Loeb, A. & Wyithe, J. S. B. Possibility of precise measurement of the cosmological power spectrum with a dedicated survey of 21cm emission after reionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 161301 (2008)
Lah, P. et al. The HI content of star-forming galaxies at z = 0.24. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 376, 1357–1366 (2007)
Davis, M., Newman, J. A., Faber, S. M. & Phillips, A. C. in Deep Fields (eds Cristiani, S. Renzini, A. & Williams, R. E.) 241 (Springer, 2001)
Komatsu, E. et al. Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe observations: cosmological interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 180, 330–376 (2009)
Pen, U. et al. The GMRT EoR experiment: limits on polarized sky brightness at 150 MHz. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399, 181–194 (2009)
Coil, A. L. et al. The DEEP2 Galaxy Redshift Survey: clustering of galaxies in early data. Astrophys. J. 609, 525–538 (2004)
Madgwick, D. S. et al. The 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey: galaxy clustering per spectral type. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 847–856 (2003)
Rao, S. M., Turnshek, D. A. & Nestor, D. B. Damped Lyα systems at z<1.65: the expanded Sloan Digital Sky Survey Hubble Space Telescope sample. Astrophys. J. 636, 610–630 (2006)
Prochaska, J. X. & Wolfe, A. M. On the (non)evolution of H I gas in galaxies over cosmic time. Astrophys. J. 696, 1543–1547 (2009)
Zwaan, M. A., Meyer, M. J., Staveley-Smith, L. & Webster, R. L. The HIPASS catalogue: Ω HI and environmental effects on the HI mass function of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 359, L30–L34 (2005)
Masui, K. W., McDonald, P. & Pen, U. Near term measurements with 21 cm intensity mapping: neutral hydrogen fraction and BAO at z<2. Preprint at 〈http://arXiv.org/abs/1001.4811〉 (2010)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the GBT support staff, in particular T. Minter and P. Ruffle, for their help with the observation. We thank K. Blagrave, O. Doré, P. McDonald, J. Sievers, K. Sigurdson and R. Yen for discussions. We acknowledge financial support by NSERC, NSF and NRAO. The NRAO is a facility of the NSF operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.-C.C. and U.-L.P. analysed and interpreted the data. K.B. conducted the remote observations. J.B.P. was in charge of manuscript preparation. All authors were present at the telescope for the on-site observations and contributed to the writing of the manuscript and Supplementary Information.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Information comprising Observation details, Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) Removal, Calibration, Foreground (Continuum) Removal, Cross Correlation, Auto Correlation, Error Estimation and Null Tests, Adjustment for 21-cm signal loss, Volume and Mass Scales and Supplementary References. (PDF 221 kb)
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, TC., Pen, UL., Bandura, K. et al. An intensity map of hydrogen 21-cm emission at redshift z ≈ 0.8. Nature 466, 463–465 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09187
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09187
This article is cited by
-
Prospects for measuring dark energy with 21 cm intensity mapping experiments: A joint survey strategy
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
A joint survey strategy helps 21 cm intensity mapping become a powerful cosmological probe
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
Cosmology with fast radio bursts in the era of SKA
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
Detecting galaxies in a large H i spectral cube
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2022)
-
Unveiling the Universe with emerging cosmological probes
Living Reviews in Relativity (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.