Abstract
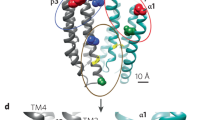
Inhibitory neurotransmission mediated by GABAA receptors can be modulated by the endogenous neurosteroids, allopregnanolone and tetrahydro-deoxycorticosterone1. Neurosteroids are synthesized de novo in the brain during stress2, pregnancy3and after ethanol consumption4, and disrupted steroid regulation of GABAergic transmission is strongly implicated in several debilitating conditions such as panic disorder, major depression, schizophrenia, alcohol dependence and catamenial epilepsy3,5,6,7,8. Determining how neurosteroids interact with the GABAA receptor is a prerequisite for understanding their physiological and pathophysiological roles in the brain. Here we identify two discrete binding sites in the receptor’s transmembrane domains that mediate the potentiating and direct activation effects of neurosteroids. They potentiate GABA responses from a cavity formed by the α-subunit transmembrane domains, whereas direct receptor activation is initiated by interfacial residues between α and β subunits and is enhanced by steroid binding to the potentiation site. Thus, significant receptor activation by neurosteroids relies on occupancy of both the activation and potentiation sites. These sites are highly conserved throughout the GABAA receptor family, and their identification provides a unique opportunity for the development of new therapeutic, neurosteroid-based ligands and transgenic disease models of neurosteroid dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belelli, D. & Lambert, J. J. Neurosteroids: endogenous regulators of the GABAA receptor. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6, 565–575 (2005)
Reddy, D. S. Is there a physiological role for the neurosteroid THDOC in stress-sensitive conditions?. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 103–106 (2003)
Stoffel-Wagner, B. Neurosteroid biosynthesis in the human brain and its clinical implications. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1007, 64–78 (2003)
Kumar, S., Fleming, R. L. & Morrow, A. L. Ethanol regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors: genomic and nongenomic mechanisms. Pharmacol. Ther. 101, 211–226 (2004)
Backstrom, T. et al. Pathogenesis in menstrual cycle-linked CNS disorders. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1007, 42–53 (2003)
Finn, D. A., Ford, M. M., Wiren, K. M., Roselli, C. E. & Crabbe, J. C. The role of pregnane neurosteroids in ethanol withdrawal: behavioral genetic approaches. Pharmacol. Ther. 101, 91–112 (2004)
Eser, D. et al. Neuroactive steroids as modulators of depression and anxiety. Neuroscience 138, 1041–1048 (2006)
Marx, C. E. et al. Neuroactive steroids are altered in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: relevance to pathophysiology and therapeutics. Neuropsychopharmacology 31, 1249–1263 (2006)
Fritschy, J. M. & Brunig, I. Formation and plasticity of GABAergic synapses: physiological mechanisms and pathophysiological implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 98, 299–323 (2003)
Purdy, R. H., Morrow, A. L., Moore, P. H. & Paul, S. M. Stress-induced elevations of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-active steroids in the rat brain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 4553–4557 (1991)
Barbaccia, M. L. et al. The effects of inhibitors of GABAergic transmission and stress on brain and plasma allopregnanolone concentrations. Br. J. Pharmacol. 120, 1582–1588 (1997)
Zhu, W. J. & Vicini, S. Neurosteroid prolongs GABAA channel deactivation by altering kinetics of desensitized states. J. Neurosci. 17, 4022–4031 (1997)
Stell, B. M., Brickley, S. G., Tang, C. Y., Farrant, M. & Mody, I. Neuroactive steroids reduce neuronal excitability by selectively enhancing tonic inhibition mediated by δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 14439–14444 (2003)
Belelli, D. & Herd, M. B. The contraceptive agent Provera enhances GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission in the rat hippocampus: evidence for endogenous neurosteroids? J. Neurosci. 23, 10013–10020 (2003)
Majewska, M. D., Harrison, N. L., Schwartz, R. D., Barker, J. L. & Paul, S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science 232, 1004–1007 (1986)
Rick, C. E., Ye, Q., Finn, S. E. & Harrison, N. L. Neurosteroids act on the GABAA receptor at sites on the N-terminal side of the middle of TM2. Neuroreport 9, 379–383 (1998)
Akk, G. et al. Neurosteroid access to the GABAA receptor. J. Neurosci. 25, 11605–11613 (2005)
Ueno, S., Tsutsui, M., Toyohira, Y., Minami, K. & Yanagihara, N. Sites of positive allosteric modulation by neurosteroids on ionotropic gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunits. FEBS Lett. 566, 213–217 (2004)
Chen, R. et al. Cloning and functional expression of a Drosophila γ-aminobutyric acid receptor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 6069–6073 (1994)
Harrison, N. L., Majewska, M. D., Harrington, J. W. & Barker, J. L. Structure-activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptor complex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241, 346–353 (1987)
Grishkovskaya, I. et al. Crystal structure of human sex hormone-binding globulin: steroid transport by a laminin G-like domain. EMBO J. 19, 504–512 (2000)
Brzozowski, A. M. et al. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 389, 753–758 (1997)
Miyazawa, A., Fujiyoshi, Y. & Unwin, N. Structure and gating mechanism of the acetylcholine receptor pore. Nature 423, 949–955 (2003)
Williams, D. B. & Akabas, M. H. γ-Aminobutyric acid increases the water accessibility of M3 membrane-spanning segment residues in γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Biophys. J. 77, 2563–2574 (1999)
Lobo, I. A., Mascia, M. P., Trudell, J. R. & Harris, R. A. Channel gating of the glycine receptor changes accessibility to residues implicated in receptor potentiation by alcohols and anesthetics. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 33919–33927 (2004)
Jung, S., Akabas, M. H. & Harris, R. A. Functional and structural analysis of the GABAA receptor α1 subunit during channel gating and alcohol modulation. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 308–316 (2005)
Schwede, T., Kopp, J., Guex, N. & Peitsch, M. C. SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3381–3385 (2003)
Trudell, J. R. & Bertaccini, E. Comparative modeling of a GABAA α1 receptor using three crystal structures as templates. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 23, 39–49 (2004)
Acknowledgements
We thank I. Duguid, P. Miller and P. Thomas for comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by the Medical Research Council and The Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Notes
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1–4, Supplementary Tables, and Supplementary Methods. (PDF 1017 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosie, A., Wilkins, M., da Silva, H. et al. Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 444, 486–489 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05324
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05324
This article is cited by
-
Neurosteroids: mechanistic considerations and clinical prospects
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Neurosteroids and their potential as a safer class of general anesthetics
Journal of Anesthesia (2024)
-
Roles of bile acids signaling in neuromodulation under physiological and pathological conditions
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
The hypothalamic steroidogenic pathway mediates susceptibility to inflammation-evoked depression in female mice
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Understanding the mechanism of action and clinical effects of neuroactive steroids and GABAergic compounds in major depressive disorder
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.