Abstract
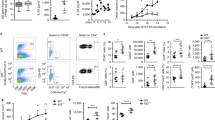
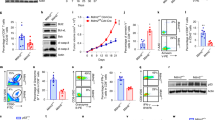
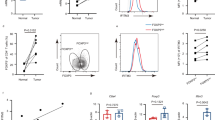
STAT1 and STAT3 are the main mediators of the signaling of interferons (IFNs) and of gp130 cytokines, respectively. Neoplastic T lymphocytes frequently become resistant to the IFN-γ/STAT1 apoptotic pathway, often because of the downregulation of the IFN-γR2 receptor chain. Many studies suggest that cross-regulation between different STATs, in particular between STAT1 and STAT3, may profoundly affect cytokine/growth factor signaling. Here, the function of STAT3 in the negative regulation of STAT1 apoptotic pathway was investigated by RNA interference-mediated STAT3 silencing in human malignant T lymphocytes. In STAT3-depleted cells, interleukin (IL)-6 acquired the capacity to induce apoptosis, correlating with prolonged STAT1 activation and the induction of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression. In contrast, in the absence of STAT3, IFN-γ could slightly enhance apoptosis but its ability to induce MHC class I expression was unchanged. Accordingly, IL-6, but not IFN-γ, could significantly impair the in vivo growth of STAT3-depleted human neoplastic T lymphocytes transplanted into severe combined immunodeficient mice. Therefore, treatment with IL-6 and simultaneous STAT3 silencing may represent a potential therapeutic approach to control the expansion of IFN-γ-unresponsive neoplastic T cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy DE, Darnell Jr JE . Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002; 3: 651–662.
Wormald S, Hilton DJ . Inhibitors of cytokine signal transduction. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 821–824.
Costa-Pereira AP, Tininini S, Strobl B, Alonzi T, Schlaak JF, Is'harc H et al. Mutational switch of an IL-6 response to an interferon-gamma-like response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 8043–8047.
Qing Y, Stark GR . Alternative activation of STAT1 and STAT3 in response to interferon-gamma. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 41679–41685.
Tanabe Y, Nishibori T, Su L, Arduini RM, Baker DP, David M . Cutting edge: role of STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 in IFN-alpha beta responses in T lymphocytes. J Immunol 2005; 174: 609–613.
Gimeno R, Lee CK, Schindler C, Levy DE . Stat1 and Stat2 but not Stat3 arbitrate contradictory growth signals elicited by alpha/beta interferon in T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 5456–5465.
Stephanou A, Latchman DS . Opposing actions of STAT-1 and STAT-3. Growth Factors 2005; 23: 177–182.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999; 98: 295–303.
Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD . The roles of IFN gamma in protection against tumor development and cancer immunoediting. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2002; 13: 95–109.
Pestka S, Kotenko SV, Muthukumaran G, Izotova LS, Cook JR, Garotta G . The interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) receptor: a paradigm for the multichain cytokine receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 1997; 8: 189–206.
Kaplan DH, Shankaran V, Dighe AS, Stockert E, Aguet M, Old LJ et al. Demonstration of an interferon gamma-dependent tumor surveillance system in immunocompetent mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 7556–7561.
Dunn GP, Sheehan KC, Old LJ, Schreiber RD . IFN unresponsiveness in LNCaP cells due to the lack of JAK1 gene expression. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3447–3453.
Regis G, Conti L, Boselli D, Novelli F . IFNgammaR2 trafficking tunes IFNgamma-STAT1 signaling in T lymphocytes. Trends Immunol 2006; 27: 96–101.
Novelli F, Di Pierro F, Francia di Celle P, Bertini S, Affaticati P, Garotta G et al. Environmental signals influencing expression of the IFN-gamma receptor on human T cells control whether IFN-gamma promotes proliferation or apoptosis. J Immunol 1994; 152: 496–504.
Conti L, Regis G, Longo A, Bernabei P, Chiarle R, Giovarelli M et al. In the absence of IGF-1 signaling, IFN-gamma suppresses human malignant T-cell growth. Blood 2007; 109: 2496–2504.
Durelli L, Conti L, Clerico M, Boselli D, Contessa G, Ripellino P et al. T Helper 17 cells expand in multiple sclerosis and are inhibited by interferon-BETA. Ann Neurol 2009; 65: 499–509.
Novelli F, D'Elios MM, Bernabei P, Ozmen L, Rigamonti L, Almerigogna F et al. Expression and role in apoptosis of the alpha- and beta-chains of the IFN-gamma receptor on human Th1 and Th2 clones. J Immunol 1997; 159: 206–213.
Regis G, Bosticardo M, Conti L, De Angelis S, Boselli D, Tomaino B et al. Iron regulates T-lymphocyte sensitivity to the IFN-gamma/STAT1 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2005; 105: 3214–3221.
Fleisher TA, Dorman SE, Anderson JA, Vail M, Brown MR, Holland SM . Detection of intracellular phosphorylated STAT-1 by flow cytometry. Clin Immunol 1999; 90: 425–430.
Friedman RL, Stark GR . alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature 1985; 314: 637–639.
Bernabei P, Coccia EM, Rigamonti L, Bosticardo M, Forni G, Pestka S et al. Interferon-gamma receptor 2 expression as the deciding factor in human T, B, and myeloid cell proliferation or death. J Leukoc Biol 2001; 70: 950–960.
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA . Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol 2004; 75: 163–189.
Novelli F, Bernabei P, Ozmen L, Rigamonti L, Allione A, Pestka S et al. Switching on of the proliferation or apoptosis of activated human T lymphocytes by IFN-gamma is correlated with the differential expression of the alpha- and beta-chains of its receptor. J Immunol 1996; 157: 1935–1943.
Bernabei P, Bosticardo M, Losana G, Regis G, Di Paola F, De Angelis S et al. IGF-1 down-regulates IFN-gamma R2 chain surface expression and desensitizes IFN-gamma/STAT-1 signaling in human T lymphocytes. Blood 2003; 102: 2933–2939.
Xi S, Gooding WE, Grandis JR . In vivo antitumor efficacy of STAT3 blockade using a transcription factor decoy approach: Implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene 2005; 24: 970–979.
Gao L, Zhang L, Hu J, Li F, Shao Y, Zhao D et al. Down-regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expression using vector-based small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human prostate tumor in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 6333–6341.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Compagnia di San Paolo (special project Oncology), Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca (MIUR), ex 40% and Fondo per gli Investimenti della Ricerca di Base (FIRB), Ministero della Salute, Progetto integrato Oncologia; Regione Piemonte: Ricerca Industriale e Sviluppo Precompetitivo (ONCOPROT), Ricerca Industriale ‘Converging Technologies’ (BIOTHER), Ricerca Sanitaria Finalizzata, by a fellowship from FIRB (GR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Regis, G., Icardi, L., Conti, L. et al. IL-6, but not IFN-γ, triggers apoptosis and inhibits in vivo growth of human malignant T cells on STAT3 silencing. Leukemia 23, 2102–2108 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.139
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.139
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Betulin and Its Derivatives Reduce Inflammation and COX-2 Activity in Macrophages
Inflammation (2023)
-
Senescence and cancer — role and therapeutic opportunities
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2022)
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 promotes radiosensitivity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via positive feedback on NF-κB/IL-6/ROS signaling
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
NTRK2 activation cooperates with PTEN deficiency in T-ALL through activation of both the PI3K–AKT and JAK–STAT3 pathways
Cell Discovery (2016)
-
Elucidating the crosstalk mechanism between IFN-gamma and IL-6 via mathematical modelling
BMC Bioinformatics (2013)