Abstract
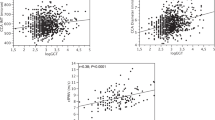
An association has been described between inflammation and the progression of hypertension (HT) and is shown with several biochemical parameters. Our aim was to examine the distribution of the serum procalcitonin (PCT), pentraxin (PTX)-3 and interleukin (IL)-33 levels and their relationship with carotid intima–media thickness (CIMT) in subjects with white coat HT (WCH), HT and normotension (NT) groups. Thirty-three patients with HT, 33 patients with WCH and 33 healthy subjects were enrolled in this study. PCT, PTX-3 and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels significantly increased in the HT group compared with the NT group. In addition, PCT and CRP levels were significantly higher in the WCH group than in the NT group. CIMT measurements were significantly higher in the WCH and HT groups than in the NT group. In the HT and WCH groups, there were significant positive correlations between PTX-3, PCT and CRP. In the WCH group, PTX-3 and PCT levels were significantly positively correlated with CIMT. PCT had area under the curve value of 0.817 which demonstrates its sufficiency to distinguish WCH from NT individuals. Our results suggest that in subjects with WCH and HT, which are characterized by increased cardiovascular risk, PTX-3 and PCT levels in the HT group and PCT levels in the WCH group are significantly and consistently higher than normotensives. Systemic inflammation moderately occurs in the WCH and HT groups. PCT monitoring may be a useful biomarker in inflammation related to atherosclerosis and early stage HT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Savoia C, Schiffrin EL . Inflammation in hypertension. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2006; 15: 152–158.
Grossman E . Does increased oxidative stress cause hypertension? Diabetes Care 2008; 31: S185–S189.
Pickering TG, James GD, Boddie C, Harshfield GA, Blank S, Laragh JH . How common is white coat hypertension? JAMA 1988; 259: 225–228.
Blake GJ, Ridker PM . Novel clinical markers of vascular wall inflammation. Circ Res 2001; 89: 763–771.
Ridker PM, Buring JE, Shih J, Matias M, Hennekens CH . Prospective study of C-reactive protein and the risk of future cardiovascular events among apparently healthy women. Circulation 1998; 98: 731–733.
Yasunaga T, Ikeda S, Koga S, Nakata T, Yoshida T, Masuda N et al. Plasma pentraxin 3 is a more potent predictor of endothelial dysfunction than high-sensitive C-reactive protein. Int Heart J 2014; 55: 160–164.
Bottazzi B, Bastone A, Doni A, Garlanda C, Valentino S, Deban L et al. The long pentraxin PTX3 as a link among innate immunity, inflamatıon and female fertility. J Leukoc Biol 2006; 79: 909–912.
Dandona P, Nix D, Wilson MF, Aljada A, Love J, Assicot M et al. Procalcitonin increase after endotoxin injection in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 79: 1605–1608.
Sinning CR, Sinning JM, Schulz A, Schnabel RB, Lubos E, Wild PS et al. AtheroGene Study Investigators. Association of serum procalcitonin with cardiovascular prognosis in coronary artery disease. Circ J 2011; 75: 1184–1191.
Mallamaci F, Leonardis D, Pizzini P, Cutrupi S, Tripepi G, Zoccali C . Procalcitonin and the inflammatory response to salt in essential hypertension: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. J Hypertens 2013; 31: 1424–1430.
Demyanets S, Konya V, Kastl SP, Kaun C, Rauscher S, Niessner A et al. Interleukin-33 induces expression of adhesion molecules and inflammatory activation in human endothelial cells and in human atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011; 31: 2080–2089.
Miller AM . Role of IL-33 in inflammation and disease. J Inflamm (Lond) 2011; 8: 22.
O'Brien E, Waeber B, Parati G, Staessen J, Myers MG . Blood pressure measuring devices: recommendations of the European Society of Hypertension. BMJ 2001; 322: 531–536.
O'Brien E, Coats A, Owens P, Petrie J, Padfield PL, Littler WA et al. Use and interpretation of Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: recommendations of the British Hypertension Society. BMJ 2000; 320: 1128–1134.
Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R . Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation 1986; 74: 1399–1406.
Pauletto P, Rattazzi M . Inflammation and hypertension: the search for a link. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21: 850–853.
Lu HH, Guo ZR, Hu XS, Wu M, Zhou MH, Zhou ZY . The prospective study of association between C-reactive protein and hypertension in community population. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2013; 47: 1026–1030.
Zhang M, Wang G, Wang A, Tong W, Zhang Y . Association of hypertension with coexistence of abnormal metabolism and inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Blood Press 2013; 22: 151–157.
Melander O, Newton-Cheh C, Almgren P, Hedblad B, Berglund G, Engström G et al. Novel and conventional biomarkers for prediction of incident cardiovascular events in the community. JAMA 2009; 302: 49–57.
Sung KC, Suh JY, Kim BS, Kang JH, Kim H, Lee MH et al. High sensitivity C-reactive protein as an independent risk factor for essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2003; 16: 429–433.
Bautista LE, López-Jaramillo P, Vera LM, Casas JP, Otero AP, Guaracao AI . Is C-reactive protein an independent risk factor for essential hypertension? J Hypertens 2001; 19: 857–861.
Ozdogan M, Bozcuk H, Coban E . Low-grade inflammation in white-coat hypertension. Med Sci Monit 2007; 13: CR570–CR573.
Sesso HD, Buring JE, Rifai N, Blake GJ, Gaziano JM, Ridker PM . C-reactive protein and the risk of developing hypertension. JAMA 2003; 290: 2945–2951.
Niskanen L, Laaksonen DE, Nyyssönen K, Punnonen K, Valkonen VP, Fuentes R et al. Inflammation, abdominal obesity, and smoking as predictors of hypertension. Hypertension 2004; 44: 859–865.
Peer M, Boaz M, Zipora M, Shargorodsky M . Determinants of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients: identification of high-risk patients by metabolic, vascular, and inflammatory risk factors. Int J Angiol 2013; 22: 223–228.
Turak O, Özcan F, Canpolat U, Işleyen A, Cebeci M, Öksüz F et al. Increased echocardiographic epicardial fat thickness and high-sensitivity CRP level indicate diastolic dysfunction in patients with newly diagnosed essential hypertension. Blood Press Monit 2013; 18: 259–264.
Amer MS, Elawam AE, Khater MS, Omar OH, Mabrouk RA, Taha HM . Association of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein with carotid artery intima-media thickness in hypertensive older adults. J Am Soc Hypertens 2011; 5: 395–400.
Gupta V, Sachdeva S, Khan AS, Haque SF . Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in different stages of essential hypertension. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2011; 22: 97–103.
Parlak A, Aydoğan U, Iyisoy A, Dikililer MA, Kut A, Cakır E et al. Elevated pentraxin-3 levels are related to blood pressure levels in hypertensive patients: an observational study. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 2012; 12: 298–304.
Büyükkaya E, Karakaş MF, Kurt M, Motor S, Akçay AB, Büyükkaya S et al. The serum pentraxin-3 is elevated in patients with cardiac syndrome X. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars 2013; 41: 290–295.
Yano Y, Matsuda S, Hatakeyama K, Sato Y, Imamura T, Shimada K et al. Plasma Pentraxin 3, but not high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, is a useful inflammatory biomarker for predicting cognitive impairment in elderly hypertensive patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2010; 65: 547–552.
Ataoglu HE, Yilmaz F, Uzunhasan I, Cetin F, Temiz L, Döventaş YE et al. Procalcitonin: a novel cardiac marker with prognostic value in acute coronary syndrome. J Int Med Res 2010; 38: 52–61.
Schiopu A, Hedblad B, Engström G, Struck J, Morgenthaler NG, Melander O . Plasma procalcitonin and the risk of cardiovascular events and death: a prospective population-based study. J Intern Med 2012; 272: 484–491.
Miller AM, Xu D, Asquith DL, Denby L, Li Y, Sattar N et al. IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 339–346.
Choi YS, Choi HJ, Min JK, Pyun BJ, Maeng YS, Park H et al. Interleukin-33 induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production. Blood 2009; 114: 3117–3126.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Research Fund of Istanbul University (Project Number: 29559).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuzer, H., Cengiz, M., Yavuzer, S. et al. Procalcitonin and Pentraxin-3: Current biomarkers in inflammation in white coat hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 30, 424–429 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.59
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.59
This article is cited by
-
Association of circulating miR-155 expression level and inflammatory markers with white coat hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2020)