Abstract
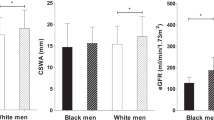
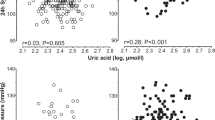
Plasma gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) was suggested to reflect the level of systemic oxidative stress. Oxidative stress induces changes in arterial structure and function and contributes to the development of hypertension. Therefore, GGT may be associated with arterial remodeling and blood pressure (BP) increment, even in absence of disease. To test this hypothesis, we evaluated, in 825 healthy subjects at low cardiometabolic risk, the associations of plasma GGT with carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT), luminal diameter and prehypertension; in 154 subjects was evaluated also the association with aortic stiffness (cfPWV). Associations were controlled for insulin sensitivity, C-reactive protein, and life-style habits. In the main population, BP was remeasured after 3 years. Carotid diameter and cfPWV, but not IMT, were directly and independently related to plasma GGT. Subjects with prehypertension (N = 330) had higher GGT as compared with subjects with normal BP (22 [14] vs 17 [11] IU/L; adjusted P = 0.001), and within prehypertensive subjects, those who developed hypertension during 3 years had higher GGT than those without incident hypertension (27 [16] vs 21 [14] IU/L; adjusted P < 0.05). Within subjects with arterial stiffness measurement, those with prehypertension (N = 79) had higher both GGT and arterial stiffness (25 [14] vs 16 [20] IU/L and 9.11 ± 1.24 vs 7.90 ± 0.94 m/s; adjusted P < 0.01 and <0.05). In the view of previous evidence linking plasma GGT concentration to the level of systemic oxidative stress, our findings suggest a role of oxidative stress in subclinical arterial damage and in prehypertension, even in healthy subjects free of cardiometabolic risk. Arterial organ damage may represent the link between GGT and hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunutsor SK, Apekey TA, Cheung BM. Gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of hypertension: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective evidence. J Hypertens. 2015;33:2373–81.
Strasak AM, Kelleher CC, Klenk J, Brant LJ, Ruttmann E, Rapp K, Vorarlberg Health Monitoring and Promotion Program Study Group. et al. Longitudinal change in serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and cardiovascular disease mortality: a prospective population-based study in 76,113 Austrian adults. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:1857–65.
Liu J, Au Yeung SL, Lin SL, Leung GM, Schooling CM. Liver enzymes and risk of ischemic heart disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Mendelian randomization study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38813.
Lim J-S, Yang J-H, Chun B-Y, Kam S, Jacobs DR Jr, Lee D-H. Is serum γ-glutamyltransferase inversely associated with serum antioxidants as a marker of oxidative stress? Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:1018–23.
Koenig G, Seneff S. Gamma-glutamyltransferase: a predictive biomarker of cellular antioxidant inadequacy and disease risk. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:818570.
Lee DH, Gross MD, Jacobs DR Jr, Cardiovascular Risk Development in Young Adults Study. Association of serum carotenoids and tocopherols with gamma-glutamyltransferase: the Cardiovascular Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Clin Chem. 2004;50:582–8.
Lee DH, Blomhoff R, Jacobs DR Jr. Is serum gamma glutamyltransferase a marker of oxidative stress? Free Radic Res. 2004;38:535–9.
Ide T, Tsutsui H, Ohashi N, et al. Greater oxidative stress in healthy young men compared with premenopausal women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:438–42.
Carraro E, Schilirò E, Biorci F, et al. Physical activity, lifestyle factors and oxidative stress in middle-aged healthy subjects. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:1152.
Shimokawa H. Reactive oxygen species promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circ Res 2013;113:1040–2.
Nelson KK, Melendez JA. Mitochondrial redox control of matrix metalloproteinases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:768–84.
Raffetto JD, Khalil RA. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 2008;75:346–59.
Mitchell GF, Hwang SJ, Vasan RS, Larson MG, Pencina MJ, Hamburg NM, et al. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2010;121:505–11.
Laurent S, Cunha PG. Arterial stiffness in early phases of prehypertension. In: Zimlichman R, Julius S, Mancia G (eds). Prehypertension and metabolic syndrome. 1st edn. Springer Nature; 2019 pp. 101–26.
Kaess BM, Rong J, Larson MG, Hamburg NM, Vita JA, Levy D, et al. Aortic stiffness, blood pressure progression, and incident hypertension. JAMA. 2012;308:875–81.
Kozakova M, Palombo C, Eng MP, Dekker J, Flyvbjerg A, Mitrakou A, RISC Investigators. et al. Fatty liver index, gamma-glutamyltransferase, and early carotid plaques. Hepatology. 2012;55:1406–15.
Bonnet F, Gastaldelli A, Piha-Le bars F, Natali A, Rousell R, Petrie J, et al. Gamma-glutamyltransferase, fatty liver index and hepatic insulin resistance are associated with incident hypertension in two longitudinal studies. J Hypertens. 2017;35:493–500.
Hills SA, Balkau B, Coppack SW, Dekker JM, Mari A, Natali A, EGIR-RISC Study groups. et al. The EGIR-RISC Study (The European group for the study of insulin resistance; relationship between insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk): I. Methodology and objectives. Diabetologia. 2004;47:566–70.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–72.
Ruhl CE, Everhart JE. Upper limits of normal for alanine aminotransferase activity in the United States population. Hepatology. 2012;55:447–54.
Ferrannini E, Iervasi G, Cobb J, Ndreu R, Nannipieri M. Insulin resistance and normal thyroid hormone levels: prospective study and metabolomic analysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017;312:E429–436.
Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J. Calibration of the computer science and applications, Inc. accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30:777–81.
Stranges S, Trevisan M, Dorn JM, Dmochowski J, Donahue RP. Body fat distribution, liver enzymes, and risk of hypertension: evidence from the Western New York Study. Hypertension. 2005;46:1186–93.
Parfenova H, Basuroy S, Bhattacharya S, Tcheranova D, Qu Y, Regan RF, Leffler CW. Glutamate induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in cerebral vascular endothelial cells: contributions of HO-1 and HO-2 to cytoprotection. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;290:C1399–1410.
Zhou X, He L, Wu C, Zhang Y, Wu X, Yin Y. Serine alleviates oxidative stress via supporting glutathione synthesis and methionine cycle in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017;61:11.
Hurrle S, Hsu WH. The etiology of oxidative stress in insulin resistance. Biochem J. 2017;40:257–62.
Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Roles of adiponectin and oxidative stress in obesity-associated metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014;15:1–10.
Patel R, Cardneau JD, Colles SM, Graham LM. Synthetic smooth muscle cell phenotype is associated with increased nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphateoxidase activity: effect on collagen secretion. J Vasc Surg. 2006;43:364–71.
Kozakova M, Palombo C, Paterni M, Anderwald CH, Konrad T, Colgan MP, et al. Body composition and common carotid artery remodeling in a healthy population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3325–32.
Vaziri ND, Wang XQ, Oveisi F, Rad B. Induction of oxidative stress by glutathione depletion causes severe hypertension in normal rats. Hypertension. 2000;36:142–6.
Sathiyapriya V, Nandeesha H, Bobby Z, Selvaraj N, Pavithran P. Perturbation of oxidant-antioxidant status in non-obese prehypertensive male subjects. J Hum Hypertens. 2007;21:176–8.
Chinta SJ, Kumar JM, Zhang H, Forman HJ, Andersen JK. Up-regulation of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity following glutathione depletion has a compensatory rather than an inhibitory effect on mitochondrial complex I activity: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:1557–63.
Block G, Jensen CD, Norkus EP, Hudes M, Crawford PB. Vitamin C in plasma is inversely related to blood pressure and change in blood pressure during the previous year in young Black and White women. Nutr J. 2008;7:35.
Jung CH, Yu JH, Bae SJ, Koh EH, Kim MS, Park JY, et al. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase is associated with arterial stiffness in healthy individuals. Clin Endocrinol. 2011;75:328–34.
Maritz M, Fourie CM, Van Rooyen JM, Moss SJ, Schutte AE. Large artery stiffness is associated with gamma-glutamyltransferase in young, healthy adults: The African-PREDICT study. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016;10:772–8.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to prof Aldo Paolicchi for critical revision of the manuscript.
RISC Investigators
R. J. Heine6, J Dekker6, S. de Rooij6, G. Nijpels6, W. Boorsma6, A. Kok6, A. Mitrakou7, S. Tournis7, K. Kyriakopoulou7, P. Thomakos7, N. Lalic8, K. Lalic8, A. Jotic8, L. Lukic8, M. Civcic8, J. Nolan9, T. P. Yeow9, M. Murphy9, C. DeLong9, G. Neary9, M. P. Colgan9, M. Hatunic9, P. Gaffney9, G. Boran9, T. Konrad10, H. Böhles10, S. Fuellert10, F. Baer10, H. Zuchhold10, A. Golay11, E. Harsch Bobbioni11, V. Barthassat11, V. Makoundou11, T. N. O. Lehmann11, T. Merminod11, J. R. Petrie (now Dundee)12, C. Perry12, F. Neary12, C. MacDougall12, K. Shields12, L. Malcolm12, M. Laakso13, U. Salmenniemi13, A. Aura13, R. Raisanen13, U. Ruotsalainen13, T. Sistonen13, M. Laitinen13, H. Saloranta13, S. W. Coppack14, N. McIntosh14, J. Ross14, L. Pettersson14, P. Khadobaksh14, B. Balkau15, L. Mhamdi15, M. T. Guillanneuf15, M. Laville16, F. Bonnet16, A. Brac de la Perriere16, C. Louche-Pelissier16, C. Maitrepierre16, J. Peyrat16, S. Beltran16, A. Serusclat16, R. Gabriel17, E. M. Sánchez17, R. Carraro17, A. Friera17, B. Novella17, P. Nilssone5, M. Persson5, G. Östling5, O. Melander5, P. Burri5, P. M. Piatti18, L. D. Monti18, E. Setola18, E. Galluccio18, F. Minicucci18, A. Colleluori18, M. Walker19, I. M. Ibrahim19, M. Jayapaul19, D. Carman19, C. Ryan19, K. Short19, Y. McGrady19, D. Richardson19, S. Patel19, H. Beck-Nielsen20, P. Staehr20, K. Hojlundd20, V. Vestergaard20, C. Olsen20, L. Hansen20, G. B. Bolli21, F. Porcellati21, C. Fanelli21, P. Lucidi21, F. Calcinaro21, A. Saturni21, E. Ferranninia22, A. Natali22, E. Muscelli22, S. Pinnola22, M. Kozakovaa22, S. A. Hills22, L. Landucci22, L. Mota22, A. Gastaldelli23, D. Ciociaro23, A. Mari24, G. Pacini24, C. Cavaggion24, G. Mingrone25, C. Guidone25, A. Favuzzi25, P. Di Rocco25, C. Anderwald26, M. Bischof26, M. Promintzer26, M. Krebs26, M. Mandl26, A. Hofer26, A. Luger26, W. Waldhäusl26, M. Roden26
Funding
The European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR) RISC study was partly supported by EU grant QLG1-CT-2001-01252.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Further information on the RISC Study can be found on www.egir.org.
Members of the RISC Investigators are listed below Acknowledgements.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozakova, M., Gastaldelli, A., Morizzo, C. et al. Gamma-glutamyltransferase, arterial remodeling and prehypertension in a healthy population at low cardiometabolic risk. J Hum Hypertens 35, 334–342 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0337-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-0337-1