Abstract
Combination therapy using two or three classes of drugs is often required to treat hypertension to prevent cardiovascular disease. In this study, we examined combination therapies administered following initial therapy with an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) in hypertensive Japanese patients. To determine which classes of antihypertensives are being prescribed as second- or third-line treatments for patients who were initially treated with a single ARB, we analyzed prescription claims data from two Japanese health-care databases for 2008 to 2015. Among the 26 998 patients who were initially treated with a single ARB (from one database), calcium channel blockers (CCBs) were the most frequently prescribed second-line antihypertensive, as these medicines were added for >20% of patients within 1 year of ARB prescription initiation. The addition rates of CCBs as a second-line therapy differed depending on the initial ARB type. In contrast, <10% of patients received a diuretic as a second-line antihypertensive. Among the 48 813 patients who were prescribed an ARB in combination with a CCB (as shown in the other database), diuretics were prescribed as third-line antihypertensives more frequently than increased doses of CCBs or ARBs. Diuretics were added for 8% of patients within 2 years of CCB addition, and the addition rates differed based on the CCB dose used for combination therapy. We also found that the addition rates of diuretics differed depending on patient clinical histories among ARB and CCB recipients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Hypertension is a serious condition associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease.1 In 2010, an estimated 43 million individuals in Japan had hypertension (defined as a systolic blood pressure ⩾140 mm Hg, a diastolic blood pressure ⩾90 mm Hg or treatment with antihypertensive drugs), including >60% of men aged ⩾50 years and women aged ⩾60 years.1, 2, 3, 4 The prevalence of hypertension, which is already high among older Japanese individuals, may increase in the future, especially in men aged ⩾50 years.4 Notably, ∼100 000 individuals die each year in Japan from complications of hypertension.1, 5
Hypertension treatment and control rates in Japan have improved over the past three decades.1, 3, 4 In 2010, >50% of Japanese men and women aged 60–69 years with hypertension received antihypertensive treatment, as did >60% of Japanese men and women aged 70–79 years. In 1980, <35% of men and 40% of women aged 60–69 years and <40% of men and 45% of women aged 70–79 years received antihypertensive treatment. Furthermore, 30% of men and 40% of women who received antihypertensive treatment achieved blood pressure control (that is, a blood pressure level <140/90 mm Hg); in 1980, ∼10% of men and <15% of women achieved blood pressure control.1, 3, 4
The primary goals of antihypertensive treatment include achieving optimal blood pressure reduction and preventing cardiovascular disease1 with a tolerability profile that promotes medication adherence.6 Guidelines pertaining to the management of hypertension, which were updated in 2014 by the Japanese Society of Hypertension (JSH 2014), recommend that hypertensive patients without compelling indications for a specific medication should initially be treated with a calcium channel blocker (CCB), angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE-I) or diuretic.1
It is often necessary to use a combination of two or three drugs to achieve target blood pressure levels.1 In fact, clinical trial data suggest that 23–52% of patients require more than three antihypertensive drugs to achieve blood pressure control and target-level blood pressure maintenance.7 ARB-based combination therapies with either CCBs or diuretics have been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure and are well tolerated.8 A study investigating trends in antihypertensive prescriptions in Japan using real-world data found that ARBs and CCBs were the two most frequently prescribed drug classes.9 The authors of this study also reported that diuretic prescription frequencies did not increase between 2005 and 2011; however, the JSH guidelines reflect a change in stance between 2004 and 2009 regarding the use of diuretics. Caution was advised when using diuretic in 2004; use was more generally promoted in 2009.9 Use of low doses of diuretics is currently recommended based on JSH 2014 for both single-drug and combination therapy with ARBs, ACE-Is or CCBs.1
To understand the current use of hypertension treatments in Japan, we focused on combination therapy regimens in which an ARB was prescribed as the initial treatment. We conducted a claims-based study to identify the drugs that are most frequently added as second- and third-line antihypertensives for Japanese patients.
Methods
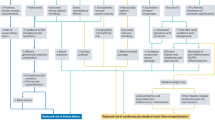
Our analyses were based on health-care insurance claims data from the following two sources: the Japan Medical Data Center (JMDC, Tokyo, Japan) and Medical Data Vision (MDV, Tokyo, Japan). Established in 2002, the JMDC provides data services to health insurance societies, pharmaceutical companies and insurance companies in Japan. The JMDC database contains standardized eligibility and claims data provided by health insurance societies for ∼2 million insured individuals (employees of general corporations and their family members). Although the JMDC database documents all medical treatments received by insured individuals at all treatment facilities, it lacks data for individuals aged ⩾65 years, as few insured individuals fall within this age range. Established in 2003, MDV provides information technology and consulting services to hospitals, as well as data services to pharmaceutical companies throughout Japan. The MDV database contains standardized health-care insurance claims data provided by hospitals using the Japanese Diagnosis and Procedure Combination (DPC) fixed-payment reimbursement system for ∼3 million individuals. Under the DPC system, treatments such as basic hospital stays, tests and diagnostic imaging are reimbursed with a comprehensive payment set for different diagnosis groups. Treatments such as surgery and anesthesia are reimbursed based on a fee-for-service system. This database covers a wide range of patient ages, but we were unable to continuously track patient treatments when a patient changed providers, as these records do not contain unique, hospital-independent patient identifiers. The JMDC and MDV both maintain large databases that can be accessed for a fee by companies (mostly within the pharmaceutical or life insurance industries). In our analysis, we noted one major difference between the two databases regarding the possibility of identifying periods during which patients did not receive medical treatment. As the JMDC database includes a comprehensive record of all treatments administered to a given patient, we were able to determine when antihypertensives were not being prescribed to particular patients. We were not able to use the MDV database for this purpose, as not all providers are included in the database; therefore, the data would be incomplete if patients received treatment from providers not reflected in the database. The comprehensive nature of the JMDC database, namely, its inclusion of data regarding specific treatment periods, allowed us to identify and define an index date for the initial ARB prescription.
We identified patients who were diagnosed with hypertension according to the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision (ICD-10, coded as I10–I15) and then extracted data from the JMDC database for all patients who were prescribed an ARB at least once between 1 January 2005 and 31 July 2015 and from the MDV database for all patients who were prescribed an ARB between 1 April 2008 and 31 October 2015. The two databases were used in separate analyses because of differences in their characteristics. The JMDC database was used to analyze which classes of antihypertensives were added as a second-line treatment for patients who were initially prescribed an ARB; however, the MDV database may have been more suitable for this study because its age composition is more similar to that of the national population of Japan. The index date for the JMDC analysis was defined as the earliest date of ARB prescription following a 6-month period during which no prescriptions were recorded in the JMDC database. In contrast, we used the MDV database to analyze which classes of antihypertensives were prescribed to patients who were already taking a CCB in addition to a single ARB. The index date for the MDV data analysis was defined as the earliest date of CCB prescription after a single prescription of an ARB. In both analyses, the date of addition was defined as the date when a subsequent antihypertensive drug was first prescribed.
We calculated an ‘addition rate’ for subsequent prescriptions of CCBs, diuretics, β-blockers or any ARBs other than those originally prescribed. Drugs were defined as additions if they were prescribed for ⩾3 consecutive months. The addition rate was calculated by dividing the number of recipients who received a prescription for a subsequent antihypertensive drug by the number of recipients who received a prescription for only an ARB on the index date. The addition rate was similarly calculated in patients for whom both an ARB and a CCB were previously prescribed.
We analyzed the addition rate of CCBs as a second-line therapy based on which of the following ARBs was initially prescribed, according to the JMDC database: 20 mg azilsartan, 8 mg candesartan, 100 mg irbesartan, 50 mg losartan, 20 mg olmesartan, 40 mg telmisartan or 80 mg valsartan. Moreover, we analyzed the addition rates of diuretics for patients who initially received both an ARB and a CCB, based on the doses of the ARB and CCB. In this study, drug combinations included both fixed-dose combination drugs and combinations of single drugs.
We also analyzed the patient groups that were prescribed diuretics and β-blockers as third-line antihypertensives to determine patient clinical histories based on the following specific ICD-10 codes: diabetes, E10–E11; dyslipidemia, E78; heart failure, I50; cerebrovascular disease, I60–I69; and chronic kidney disease, N18. The clinical histories of the hypertensive patients in each database are summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
Results
The data for 418 118 and 1 721 462 hypertensive patients were extracted from the JMDC and MDV databases, respectively (Supplementary Table S1). Of these, 26 998 patients from the JMDC database were noted as having only an ARB prescription as of the index date, and 48 813 patients from the MDV database were noted as having both an ARB and a CCB prescription. For the above data sets, the average annual observation periods (±s.d.) were 1.7±1.7 and 1.3±1.2 years, respectively (Table 1).
In patients who initially received only an ARB, CCBs were prescribed more often as a second-line antihypertensive therapy than diuretics or β-blockers or increased doses of an ARB (Figure 1a). CCBs were added for >20% of patients within 1 year of initiation of ARB treatment; in contrast, <10% of patients received a diuretic as a second-line antihypertensive therapy during the 5-year period following ARB prescription initiation.
(a) Addition rates of each drug class as a second-line treatment after initial therapy with an ARB only and (b) the percentages of patients, stratified by age and sex, who initially received an ARB only. ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; BETA, β-blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; DIU, diuretic. Age was based on the index date of initial ARB prescription.
Patients who received an ARB in combination with a CCB were prescribed a diuretic more frequently as a third-line antihypertensive therapy than a β-blocker or increased CCB or ARB doses (Figure 2a). Diuretics were added for ∼8% of patients within 2 years of CCB addition.
(a) Addition rates of each drug class as a third-line treatment after initial therapy with an ARB in combination with a CCB and (b) the percentages of each patient, stratified by age and sex, who received an ARB in combination with a CCB. ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; BETA, β-blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; DIU, diuretic. Age was based on the date of CCB addition.
Patients who had initially been prescribed only an ARB were younger than those who received an initial ARB prescription in combination with a CCB (Figures 1b and 2b), a consequence of our source data. The data used to analyze the former group were extracted from the JMDC database that contains data provided by health insurance societies and therefore has little data pertaining to individuals aged ⩾65 years. In contrast, the data used for the latter group were extracted from the MDV database that contains DPC data pertaining to patients of all ages, including those aged ⩾65 years.
We analyzed the number of antihypertensive drug prescriptions received by each patient within the most recent 1-year period using the MDV database. We found that ∼80% of patients who were prescribed ARBs were also prescribed other antihypertensive drugs (that is, CCBs, diuretics, β-blockers or vasodilators) and that CCBs were the second-line agents most frequently combined with ARBs (Figure 3a). To confirm that the two databases were not significantly different from each other with respect to prescription patterns, the analysis shown in Figure 3a was also performed on the JMDC database. As shown in Figure 3b, the top three combinations of antihypertensive drugs listed in the JMDC database were consistent with those listed in the MDV database. Regarding individual classes of medication, ARBs and CCBs were prescribed more frequently than other classes, according to both databases (Supplementary Figure S1). Although the percentages in each class and the orders of diuretic and β-blocker prescription were different between the databases, the prescription tendencies were similar in both.
Most frequently prescribed combinations of ARBs and other antihypertensives in 2014 from the (a) MDV and (b) JMDC databases. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; BETA, β-blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; DIU, diuretic; JMDC, Japan Medical Data Center; MDV, Medical Data Vision; VAS, vasodilator.
Before analysis of the CCB addition rates for patients who initially received only an ARB, which differed based on the type of ARB, we calculated the percentage of each type of CCB that was added to an ARB. The percentages were 73.3% for amlodipine, 12.3% for azelnidipine, 5.5% for nifedipine, 4.7% for cilnidipine, 3.5% for benidipine and 0.8% for other CCBs. Consequently, we did not calculate an addition rate based on the type of CCB. We found that the addition rate differed based on the type of ARB, as shown in Table 2.
For patients who received a combination of ARBs and CCBs, the addition rates of diuretics differed based on ARB and CCB doses. The addition rate for patients receiving a combination of a middle-dose ARB and low-dose CCB was particularly low (4% within 1 year) compared with that of patients receiving a combination of a middle-dose ARB and middle-dose CCB (7% within 1 year). The addition rate of diuretics was lower than the addition rate of CCBs (20% within 1 year) in patients receiving a middle-dose ARB and low-dose CCB.
The addition rates of specific diuretics and β-blockers as third-line agents were determined based on patient clinical histories (Figure 4). Regarding diuretics, addition rates were higher for patients with chronic kidney disease and lower for patients with diabetes, dyslipidemia or cerebrovascular disease than for patients with heart failure. Regarding β-blockers, addition rates were higher for patients with chronic kidney disease or heart failure than for those with diabetes, dyslipidemia or cerebrovascular disease.
Discussion
We found that CCBs were the most frequently prescribed second-line antihypertensive among patients receiving ARBs, and this is consistent with the results obtained via snapshot analysis. Diuretics were the most frequently prescribed third-line antihypertensive in patients receiving an ARB in combination with a CCB. In addition, we found that the decision to add other antihypertensive drugs was made within the first 1 or 2 years of initiation of ARB therapy.
Based on our snapshot analysis of ARBs and other antihypertensive combinations, we found that combinations of an ARB and a CCB accounted for the majority of antihypertensive drug combination therapy regimens (Figure 3). Once a CCB was combined with an ARB, this combination was typically maintained even when a third-line antihypertensive was added. ARB–CCB combinations were likely frequently used for the following reasons: (1) many fixed-dose combinations of ARBs and CCBs are available, as they were developed by many pharmaceutical companies for antihypertensive treatment in Japan; (2) CCBs have been the most popular antihypertensives, and ARBs have become one of the most popular antihypertensives, likely because of their organ-protective effects and side-effect profile;10 and (3) combination therapy with ARBs and CCBs has become the most popular antihypertensive therapy regimen in Japan, as the enhanced blood pressure-lowering effects of this regimen have been shown to decrease the likelihood of cardiovascular events1, 11, 12, 13 and to reduce the incidence of edema and that of potential side effects caused by CCBs.1, 12 JSH 2014 notes that it is reasonable to use small doses of diuretics because the salt content of the Japanese diet is considered relatively high.1 However, physicians may avoid using diuretics in lieu of CCBs, likely because of their high level of confidence in CCBs and their hesitation to overuse diuretics owing to their metabolic side effects.
Through the above snapshot analysis of ARBs and other antihypertensive combinations, we observed several antihypertensive combinations that were not included on the recommended list published in JSH 2014, such as ARBs and ACE-Is, and ARBs and β-blockers. First, according to JSH 2014, careful administration is required for the combination of an ARB and ACE-I that appeared as one of the top 10 combination prescriptions in the JMDC database (Figure 3b). As our analysis was performed by grouping antihypertensive drugs that were prescribed in the most recent year for each patient, one possible reason for the appearance of ARB/ACE-I combinations is that counts may have included data pertaining to patients who switched from one antihypertensive drug to another. For example, even when a patient was switched from an ACE-I to ARB, this was counted as a combination of an ARB and ACE-I. Second, the combination of an ARB and a β-blocker, which is not classified as a recommended combination, also appeared among the top 10 combination prescriptions in both databases (Figure 3). Because β-blockers had been listed as a first-line treatment in the JSH guidelines published in 2009, it is possible this combination continues to appear in the database, as the database contains claims data collected before JSH 2014 publication. In addition, the combination of an ARB and a β-blocker (administered at lower than standard doses) can be prescribed to patients with hypertension and heart failure.
The addition rates of β-blockers as both second- and third-line drugs were lower than those of diuretics (Figures 1a and 2a). These results may be attributed to the weakened recommendations for β-blockers in JSH 2014; β-blockers are mentioned as an option only for patients who are already receiving either an ACE-I or an ARB or a CCB and diuretic who still require additional treatment to achieve their target blood pressure level.1
We found that the CCB addition rate among patients who initially received only an ARB differed based on the type of ARB that was initially prescribed. In clinical practice, differences in ARB prescription patterns are likely linked to the availability of combination tablets and the doses of each individual medication within these tablets, as well as the particular characteristics of each type of ARB.
Compared with the addition rates of CCBs, the addition rates of diuretics were lower for patients receiving a middle-dose ARB and low-dose CCB. These results suggest that physicians tend to prescribe middle-dose CCBs rather than adding diuretics for patients receiving a combination of a middle-dose ARB and low-dose CCB. In contrast, the addition rates of diuretics for patients receiving a combination of a middle-dose ARB and middle-dose CCB were higher than the addition rates of CCBs. According to JSH 2014, adding other classes of antihypertensives is preferred to increasing the doses of drugs that have already been prescribed.1
The addition rates of diuretics differed based on patient clinical histories (Figure 4a). Relatively low rates were observed in patients with diabetes and dyslipidemia, indicating that physicians may avoid using diuretics because of their metabolic side effects.1 Regarding β-blockers, addition rates were high for patients with heart failure or chronic kidney disease. This may be attributed to the fact that β-blockers are used specifically for heart failure1 and chronic kidney disease complicated by heart failure;14 however, the addition rates of β-blockers were lower than those of diuretics for all diseases.
Our study was the first to investigate antihypertensive prescription patterns in Japanese patients who initially received ARB therapy; thus, our findings cannot be directly compared with those of other previously conducted studies. Nonetheless, it is important to cite the results of a large study (N=66 223) that analyzed trends in antihypertensive drug prescriptions in Japan using claims data.9 In that study, ARBs and CCBs were found to be the two most frequently prescribed classes of antihypertensives in patients who were prescribed more than one antihypertensive drug at least once between January 2005 and October 2011. In addition, the prescription rates of diuretics remained constant at ∼4% in 2005 and 2006 but increased during the next 4 years, reaching ∼11% in 2011.
There were several limitations to this study. The two databases are inherently biased because of differences in their underlying data sources. Given that the prevalence of hypertension increases with increasing age, performing both analyses using the MDV database may have been preferable; however, identifying the starting dates of the initial prescriptions and analyzing the data pertaining to patients for whom only an ARB was initially prescribed required claims data collected before ARB prescription. The MDV database does not contain this information, and hence the JMDC data were used. We used the MDV database for our analysis regarding subsequent prescriptions in patients who initially received both an ARB and a CCB. Therefore, a discontinuity exists between the two analyses. In addition, patients may have received treatments from multiple providers or from providers not listed in the MDV database; thus, we were unable to use the MDV database to conclusively determine whether any periods of time passed during which treatments were not prescribed. Furthermore, because patient chart data are not included in either database, we could not attain a comprehensive understanding of the history of each patient and could not evaluate the accuracies of their diagnoses.
In conclusion, several classes of antihypertensive drugs are recommended, and combination therapy with these drugs is often required for hypertension treatment. In this study, we examined the combination therapy regimens that are currently used among Japanese hypertension patients who were initially prescribed an ARB. Using prescription claims information from Japanese medical databases, we found that CCBs were the most frequently prescribed second-line antihypertensive for patients who had received initial therapy with an ARB only. The addition rates of second-line CCBs differed based on the type of ARB that was initially administered. We also found that diuretics were the most frequently prescribed third-line antihypertensive for patients receiving combination therapy with an ARB and a CCB. The addition rates of diuretics differed based on the doses of CCBs used in combination therapy. Moreover, we also found that the addition rates of diuretics differed depending on patient clinical histories. To better understand the hypertensive treatment regimens that are currently used in Japan, we must conduct additional analyses of combination treatment regimens using CCBs, the other class of antihypertensives that is frequently prescribed as an initial treatment.
References
Shimamoto K, Ando K, Fujita T, Hasebe N, Higaki J, Horiuchi M, Imai Y, Imaizumi T, Ishimitsu T, Ito M, Ito S, Itoh H, Iwao H, Kai H, Kario K, Kashihara N, Kawano Y, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Kimura G, Kohara K, Komuro I, Kumagai H, Matsuura H, Miura K, Morishita R, Naruse M, Node K, Ohya Y, Rakugi H, Saito I, Saitoh S, Shimada K, Shimosawa T, Suzuki H, Tamura K, Tanahashi N, Tsuchihashi T, Uchiyama M, Ueda S, Umemura S . The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2014). Hypertens Res 2014; 37: 253–390.
The 2010 National Health and Nutrition Survey in Japan. The Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. Tokyo, Japan, 2012. In Japanese http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/eiyou/h22-houkoku.html. Accessed 15 March 2016.
Miura K . (chief investigator) Comprehensive research business on strategies to prevent/treat cardiovascular disease/lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes mellitus by a scientific grants/subsidy from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, ‘Research on the start of follow-up of the subjects of the 2010 National Health and Nutrition Survey (NIPPON DATA2010) and continuation of NIPPON DATA80/90 follow-up’, Comprehensive/project study reports in 2012. 2013. Japanese.
Miura K, Nagai M, Ohkubo T . Epidemiology of hypertension in Japan: where are we now? Circ J 2013; 77: 2226–2231.
Ikeda N, Saito E, Kondo N, Inoue M, Ikeda S, Satoh T, Wada K, Stickley A, Katanoda K, Mizoue T, Noda M, Iso H, Fujino Y, Sobue T, Tsugane S, Naghavi M, Ezzati M, Shibuya K . What has made the population of Japan healthy? Lancet 2011; 378: 1094–1105.
Gradman AH . Rationale for triple-combination therapy for management of high blood pressure. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2010; 12: 869–878.
Bhushan B, Gupta S, Khajuria V, Kumar D, Lal M, Kumar D, Bhat S, Sharma A . Comparative efficacy and safety of triple therapy (Ramipril, telmisartan, hydrochlorothiazide) vs dual antihypertensive therapy (Ramipril or telmisartan, hydrochlorothiazide) in stage 2 hypertensive patients. J Clin Diagn Res 2014; 8: HC25–HC28.
Sato N, Hasebe N . Fixed-drug combinations for hypertension. Nihon Rinsho 2014; 72: 1477–1484 (in Japanese).
Kohro T, Yamazaki T, Sato H, Ohe K, Nagari R . The impact of a change in hypertension management guidelines on diuretic use in Japan: trends in antihypertensive drug prescriptions from 2005 to 2011. Hypertens Res 2013; 36: 559–563.
Law MR, Wald NJ, Morris JK, Jordan RE . Value of low dose combination treatment with blood pressure lowering drugs: analysis of 354 randomised trials. BMJ 2003; 326: 1427.
Ogihara T, Saruta T, Rakugi H, Saito I, Shimamoto K, Matsuoka H, Teramukai S, Higaki J, Ito S, Shimada K COLM Investigators. Combination therapy of hypertension in the elderly: a subgroup analysis of the Combination of OLMesartan and a calcium channel blocker or diuretic in Japanese elderly hypertensive patients trial. Hypertens Res 2015; 38: 89–96.
Saruta T, Ogihara T, Saito I, Rakugi H, Shimamoto K, Matsuoka H, Teramukai S, Higaki J, Ito S, Shimada K . Comparison of olmesartan combined with a calcium channel blocker or a diuretic in elderly hypertensive patients (COLM Study): safety and tolerability. Hypertens Res 2015; 38: 132–136.
Kim-Mitsuyama S, Ogawa H, Matsui K, Jinnouchi T, Jinnouchi H, Arakawa K, OSCAR Study Group. Differential effectiveness of ARB plus CCB therapy and high-dose ARB therapy in high-risk elderly hypertensive patients: subanalysis of the OSCAR study. Hypertens Res 2015; 38: 199–207.
Badve SV, Roberts MA, Hawley CM, Cass A, Garg AX, Krum H, Tonkin A, Perkovic V . Effects of beta-adrenergic antagonists in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 58: 1152–1161.
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. We thank Dr Tomomi Takeshima at Milliman for providing writing and editorial support. Writing and editorial support was also funded by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
SH, YS and TK are current employees of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. YO and KI are current employees of Milliman. MO has received financial support for research from Daiichi Sankyo Company, Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, MSD KK, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Kowa Pharmaceutical Company, Teijin Home Healthcare, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Pfizer Japan, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Mochida Pharmaceutical, Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Teijin Pharma and Genzyme Japan KK.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Hypertension Research website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Hiroi, S., Shimasaki, Y., Kikuchi, T. et al. Analysis of second- and third-line antihypertensive treatments after initial therapy with an angiotensin II receptor blocker using real-world Japanese data. Hypertens Res 39, 907–912 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2016.96
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2016.96
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Management of Hypertension in the Asia-Pacific Region: A Structured Review
American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs (2024)
-
Prescription of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in Japan during the COVID-19 pandemic: interrupted time series study
Hypertension Research (2023)
-
Analysis of antihypertensive treatment using real-world Japanese data—the retrospective study of antihypertensives for lowering blood pressure (REAL) study
Hypertension Research (2019)
-
Treatment patterns and adherence to antihypertensive combination therapies in Japan using a claims database
Hypertension Research (2019)