Abstract
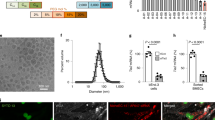
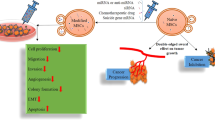
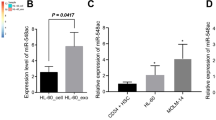
Previous studies have demonstrated functional roles for microRNAs (miRNAs) in various aspects of normal and malignant hematopoiesis, including lineage commitment, differentiation, apoptosis and maturation. In vivo delivery of naked DNA, oligonucleotides and miRNAs is complicated by their low stability, rapid degradation and inefficient delivery into target cells. In our experiments, we used a new type of polymer carriers to monitor the effects of miR-155 and antago-miR-155 on the morphology and genetics of Kasumi-1 cells. We obtained platelet-like cells from leukemic cells, and detected the expression of platelet marker genes after transfection with antago-miR-155. Our findings suggest that administration of miR mimics or antago-miRs as therapeutic agents is a desirable goal for future treatment of hematologic malignancies and that polymer-based carriers for the delivery of miR mimics or antago-miRs may provide a solution to the challenges of standard miR delivery approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edelstein LC, Bray PF . MicroRNAs in platelet production and activation. Blood 2011; 117: 5289–5296.
Connelly CM, Uprety R, Hemphill J, Deiters A . Spatiotemporal control of microRNA function using light-activated antagomirs. Mol BioSyst 2012; 8: 2987–2993.
Blenkiron C, Miska EA . MiRNAs in cancer: approaches, aetiology, diagnostics and therapy. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: R106–R113.
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T . MiRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol 2011; 223: 102–115.
Liu C, Tang DG . MicroRNA regulation of cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 5950.
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature 2005; 438: 685–689.
Shcherbo D, Merzlyak EM, Chepurnykh TV, Fradkov AF, Ermakova GV et al. Bright far-red fluorescent protein for whole body imaging. Nat Methods 2007; 4: 741–746.
Rizos AK, Tashmukhamedov RI, Tsatsakis AM, Klyagina MV, Goryachaya AV et al. The aggregation of amino acid derivatives of poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone in water solution. Plasticheskie Massy 2007; 5: 19–21 in Russian.
Artykova ZB, Goryachaya AV, Gritskova IA, Shtilman MI . The interaction of poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone with chloroacetamide in alcohol medium. Plasticheskie Massy 2010; 7: 15–19 in Russian.
Kuskov AN, Voskresenskaya AA, Goryachaya AV, Shtilman MI, Spandidos DA et al. Aggregates of amphiphilic Poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone with Mn=3500 and one end n-dodecyl group. Int J Mol Med 2010; 26: 85–94.
Torchilin VP, Shtilman MI, Trubetskoy VS, Whiteman K, Milshtein AM . Amphyphylic vinyl polymers effectively prolong liposome circulation time in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta 1994; 1195: 181–184.
Huret JL . t(8;21)(q22;q22) in treatment related leukemia. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. October 2003. URL: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Anomalies/t0821q22q22TreatRelID1293.html.
Siatecka M, Bieker JJ . The multifunctional role of EKLF/KLF1 during erythropoiesis. Blood 2011; 118: 2044–2054.
Covello KL, Kehler J, Yu H, Gordan JD, Arsham AM et al. HIF-2α regulates Oct-4: effects of hypoxia on stem cell function, embryonic development, and tumor growth. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 557–570.
Lightfoot HL, Bugaut A, Armisen J, Lehrbach NJ, Miska EA et al. A LIN28-dependent structural change in pre-let-7g directly inhibits Dicer processing. Biochemistry 2011; 50: 7514–7521.
Chung SS, Hu W, Park CY . The role of microRNAs in hematopoietic stem cell and leukemic stem cell function. Ther Adv Hematol 2011; 2: 317–334.
Faraoni I, Laterza S, Ardidri D, Ciardi C, Fazi F, Lo-Coco F . MiR-424 and miR-155 deregulated expression in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia: correlation with NPM1 and FLT3 mutation status. J Hematol Oncol 2012; 5: 26.
Chuang YS, Huang WH, Park SW, Persaud SD, Hung CH, Ho PC et al. Promyelocytic leukemia protein in retinoic acid-induced chromatin remodeling of Oct4 gene promoter. Stem Cells 2011; 29: 660–669.
Norton LJ, Funnell APW, Pearson RCM, Crossley M . Cellular reprogramming toward the erythroid lineage. Int J Cell Biol 2011; 2011: 501464.
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, Mi S, Zhang H . Distinct microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 15535–15540.
Pelosi E, Labbaye C, Test U . MicroRNAs in normal and malignant myelopoiesis. Leuk Res 2009; 33: 1584–1593.
Gazzar ME, McCall CE . MicroRNAs regulatory networks in myeloid lineage development and differentiation: regulators of the regulators. Immunol Cell Biol 2012; 90: 587–593.
O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, Boldin MP, Taganov KD, Nicoll J et al. Sustained expression of microRNA-155 in hematopoietic stem cells causes a myeloproliferative disorder. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 585–594.
O'Connell RM, Chaudhuri AA, Rao DS, Baltimore D . Inositol phosphatase SHIP1 is a primary target of miR-155. PNAS 2009; 106: 7113–7118.
Marcucci G, Mrozek K, Radmacher MD, Garzon R, Bloomfield CD . The prognostic and functional role of microRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 117: 1121–1129.
Opalinska JB, Bersenev A, Zhang Z, Schmaier AA, Choi J, Yao Y et al. MicroRNA expression in maturing murine megakaryocytes. Blood 2010; 116: e128–e138.
Volinia S, Galasso M, Costinean S, Tagliavini L, Camberoni G, Drusco A et al. Reprogramming of miRNA networks in cancer and leukemia. Genome Res 2010; 20: 589–599.
Rhyasen GW, Starczynowski DT . Deregulation of microRNAs in myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2012; 26: 13–22.
Lepage A, Uzan G, Touche N, Morales M, Cazenave J-P, Lanza F . Functional characterization of the human platelet glycoprotein V gene promoter: a specific marker of late megakaryocytic differentiation. Blood 1999; 94: 3366–3380.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klimenko, O., Shtilman, M. Transfection of Kasumi-1 cells with a new type of polymer carriers loaded with miR-155 and antago-miR-155. Cancer Gene Ther 20, 237–241 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2013.11
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2013.11
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Soliton Dynamics and DDMC/sncRNAs Complex for Epigenetic Change to Normal Cells in TME
BioNanoScience (2023)
-
New amphiphilic terpolymers of N-vinylpyrrolidone with poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate and triethylene glycol dimethacrylate as carriers of the hydrophobic fluorescent dye
Polymer Bulletin (2022)
-
miR-155 drives oncogenesis by promoting and cooperating with mutations in the c-Kit oncogene
Oncogene (2019)
-
Preparation of the amphiphilic copolymer of N-vinylpyrrolidone with triethylene glycol dimethacrylate nanoparticles and the study of their properties in vitro
Russian Chemical Bulletin (2016)