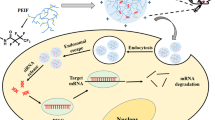
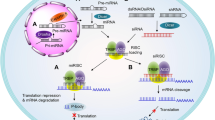
Abstract
RNA interference holds the promise to knock down expression of every cancer gene. Both academic laboratories and pharmaceutical companies have committed heavily on manpower and financial resources to develop small interfering RNA (siRNA) cancer therapeutics over the last decade. Although significant advances have been made in the design of siRNA therapeutics and mechanism of action on cancer cell killing, there are still many hurdles to overcome including effective delivery of therapeutics in vivo. Nanotechnology has had an important role in the development of delivery vectors so far. This article summarizes current nanovectors for siRNA delivery, discusses technical challenges in overcoming biological barriers, and introduces the multistage vector system for tumor-specific delivery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC . Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998; 391: 806–811.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000; 100: 57–70.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T . Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001; 411: 494–498.
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T . RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 188–200.
Fenske DB, Cullis PR . Liposomal nanomedicines. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2008; 5: 25–44.
Wu SY, McMillan NA . Lipidic systems for in vivo siRNA delivery. AAPS J 2009; 11: 639–652.
Ozpolat B, Sood AK, Lopez-Berestein G . Nanomedicine based approaches for the delivery of siRNA in cancer. J Intern Med 2010; 267: 44–53.
Santel A, Aleku M, Keil O, Endruschat J, Esche V, Fisch G et al. A novel siRNA-lipoplex technology for RNA interference in the mouse vascular endothelium. Gene Ther 2006; 13: 1222–1234.
Santel A, Aleku M, Keil O, Endruschat J, Esche V, Durieux B et al. RNA interference in the mouse vascular endothelium by systemic administration of siRNA-lipoplexes for cancer therapy. Gene Ther 2006; 13: 1360–1370.
Judge AD, Robbins M, Tavakoli I, Levi J, Hu L, Fronda A et al. Confirming the RNAi-mediated mechanism of action of siRNA-based cancer therapeutics in mice. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 661–673.
Akinc A, Zumbuehl A, Goldberg M, Leshchiner ES, Busini V, Hossain N et al. A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 561–569.
Love KT, Mahon KP, Levins CG, Whitehead KA, Querbes W, Dorkin JR et al. Lipid-like materials for low-dose, in vivo gene silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 1864–1869.
Kim HS, Han HD, Armaiz-Pena GN, Stone RL, Nam EJ, Lee JW et al. Functional roles of Src and Fgr in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 1713–1721.
Davis ME, Zuckerman JE, Choi CH, Seligson D, Tolcher A, Alabi CA et al. Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nature 2010; 464: 1067–1070.
Monteagudo S, Perez-Martinez FC, Perez-Carrion MD, Guerra J, Merino S, Sanchez-Verdu MP et al. Inhibition of p42 MAPK using a nonviral vector-delivered siRNA potentiates the antitumor effect of metformin in prostate cancer cells. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2011; 7: 493–506.
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Engle X, Scarlett UK, Martinez D, Barber A, Elgueta R et al. Polyethylenimine-based siRNA nanocomplexes reprogram tumor-associated dendritic cells via TLR5 to elicit therapeutic antitumor immunity. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 2231–2244.
Rozema DB, Lewis DL, Wakefield DH, Wong SC, Klein JJ, Roesch PL et al. Dynamic PolyConjugates for targeted in vivo delivery of siRNA to hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 12982–12987.
Braun GB, Pallaoro A, Wu G, Missirlis D, Zasadzinski JA, Tirrell M et al. Laser-Activated Gene Silencing via Gold Nanoshell-siRNA Conjugates. ACS Nano 2009; 3: 2007–2015.
Lu W, Zhang G, Zhang R, Flores 2nd LG, Huang Q, Gelovani JG et al. Tumor site-specific silencing of NF-kappaB p65 by targeted hollow gold nanosphere-mediated photothermal transfection. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3177–3188.
Soutschek J, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Charisse K, Constien R, Donoghue M et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004; 432: 173–178.
Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1002–1007.
Zimmermann TS, Lee AC, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Bumcrot D, Fedoruk MN et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2006; 441: 111–114.
Akinc A, Goldberg M, Qin J, Dorkin JR, Gamba-Vitalo C, Maier M et al. Development of lipidoid-siRNA formulations for systemic delivery to the liver. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 872–879.
Heidel JD, Yu Z, Liu JY, Rele SM, Liang Y, Zeidan RK et al. Administration in non-human primates of escalating intravenous doses of targeted nanoparticles containing ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 siRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5715–5721.
Bartlett DW, Su H, Hildebrandt IJ, Weber WA, Davis ME . Impact of tumor-specific targeting on the biodistribution and efficacy of siRNA nanoparticles measured by multimodality in vivo imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 15549–15554.
Xue HY, Wong HL . Solid lipid-PEI hybrid nanocarrier: an integrated approach to provide extended, targeted, and safer siRNA therapy of prostate cancer in an all-in-one manner. ACS Nano 2011; 5: 7034–7047.
Huh MS, Lee SY, Park S, Lee S, Chung H, Choi Y et al. Tumor-homing glycol chitosan/polyethylenimine nanoparticles for the systemic delivery of siRNA in tumor-bearing mice. J Control Release 2010; 144: 134–143.
von Maltzahn G, Park JH, Lin KY, Singh N, Schwoppe C, Mesters R et al. Nanoparticles that communicate in vivo to amplify tumour targeting. Nat Mater 2011; 10: 545–552.
Bos JL . ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res 1989; 49: 4682–4689.
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, Miller VA, Pan Q, Ladanyi M et al. KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med 2005; 2: e17.
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J, Sjoblom T, Leary RJ et al. The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2007; 318: 1108–1113.
Kariko K, Buckstein M, Ni H, Weissman D . Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 2005; 23: 165–175.
Matsumura Y, Maeda H . A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res 1986; 46 (12 Pt 1): 6387–6392.
Maeda H . Tumor-selective delivery of macromolecular drugs via the EPR effect: background and future prospects. Bioconjug Chem 2010; 21: 797–802.
Yuan F, Leunig M, Huang SK, Berk DA, Papahadjopoulos D, Jain RK . Microvascular permeability and interstitial penetration of sterically stabilized (stealth) liposomes in a human tumor xenograft. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 3352–3356.
Yuan F, Dellian M, Fukumura D, Leunig M, Berk DA, Torchilin VP et al. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 3752–3756.
Ferrari M . Frontiers in cancer nanomedicine: directing mass transport through biological barriers. Trends Biotechnol 2010; 28: 181–188.
Hornung V, Guenthner-Biller M, Bourquin C, Ablasser A, Schlee M, Uematsu S et al. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-alpha by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nat Med 2005; 11: 263–270.
Judge AD, Sood V, Shaw JR, Fang D, McClintock K, MacLachlan I . Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 457–462.
Amarzguioui M, Lundberg P, Cantin E, Hagstrom J, Behlke MA, Rossi JJ . Rational design and in vitro and in vivo delivery of Dicer substrate siRNA. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 508–517.
Foster DJ, Barros S, Duncan R, Shaikh S, Cantley W, Dell A et al. Comprehensive evaluation of canonical versus Dicer-substrate siRNA in vitro and in vivo. RNA 2012; 18: 557–568.
Kleinman ME, Yamada K, Takeda A, Chandrasekaran V, Nozaki M, Baffi JZ et al. Sequence- and target-independent angiogenesis suppression by siRNA via TLR3. Nature 2008; 452: 591–597.
Stohrer M, Boucher Y, Stangassinger M, Jain RK . Oncotic pressure in solid tumors is elevated. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 4251–4255.
Netti PA, Berk DA, Swartz MA, Grodzinsky AJ, Jain RK . Role of extracellular matrix assembly in interstitial transport in solid tumors. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 2497–2503.
Cabral H, Matsumoto Y, Mizuno K, Chen Q, Murakami M, Kimura M et al. Accumulation of sub-100 nm polymeric micelles in poorly permeable tumours depends on size. Nat Nanotechnol 2011; 6: 815–823.
Jain RK . Transport of molecules, particles, and cells in solid tumors. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 1999; 1: 241–263.
Pluen A, Boucher Y, Ramanujan S, McKee TD, Gohongi T, di Tomaso E et al. Role of tumor-host interactions in interstitial diffusion of macromolecules: cranial vs. subcutaneous tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 4628–4633.
Tasciotti E, Liu X, Bhavane R, Plant K, Leonard AD, Price BK et al. Mesoporous silicon particles as a multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications. Nat Nanotechnol 2008; 3: 151–157.
Tanaka T, Mangala LS, Vivas-Mejia PE, Nieves-Alicea R, Mann AP, Mora E et al. Sustained small interfering RNA delivery by mesoporous silicon particles. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3687–3696.
Shen H, You J, Zhang G, Ziemys A, Li Q, Bai L et al. Cooperative, nanoparticle-enabled thermal therapy of breast cancer. Adv Healthcare Mater 2012; 1: 84–89.
Ananta JS, Godin B, Sethi R, Moriggi L, Liu X, Serda RE et al. Geometrical confinement of gadolinium-based contrast agents in nanoporous particles enhances T1 contrast. Nat Nanotechnol 2010; 5: 815–821.
Decuzzi P, Ferrari M . Design maps for nanoparticles targeting the diseased microvasculature. Biomaterials 2008; 29: 377–384.
Lee SY, Ferrari M, Decuzzi P . Shaping nano-/micro-particles for enhanced vascular interaction in laminar flows. Nanotechnology 2009; 20: 495101.
Decuzzi P, Godin B, Tanaka T, Lee SY, Chiappini C, Liu X et al. Size and shape effects in the biodistribution of intravascularly injected particles. J Control Release 2010; 141: 320–327.
van de Ven AL, Kim P, Haley O, Fakhoury JR, Adriani G, Schmulen J et al. Rapid tumoritropic accumulation of systemically injected plateloid particles and their biodistribution. J Control Release 2011; 158: 148–155.
Godin B, Tasciotti E, Liu X, Serda RE, Ferrari M . Multistage nanovectors: from concept to novel imaging contrast agents and therapeutics. Acc Chem Res 2011; 44: 979–989.
Serda RE, Gu J, Bhavane RC, Liu X, Chiappini C, Decuzzi P et al. The association of silicon microparticles with endothelial cells in drug delivery to the vasculature. Biomaterials 2009; 30: 2440–2448.
Serda RE, Mack A, van de Ven AL, Ferrati S, Dunner Jr K, Godin B et al. Logic-embedded vectors for intracellular partitioning, endosomal escape, and exocytosis of nanoparticles. Small 2010; 6: 2691–2700.
Landen Jr CN, Chavez-Reyes A, Bucana C, Schmandt R, Deavers MT, Lopez-Berestein G et al. Therapeutic EphA2 gene targeting in vivo using neutral liposomal small interfering RNA delivery. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 6910–6918.
Baluk P, Hashizume H, McDonald DM . Cellular abnormalities of blood vessels as targets in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2005; 15: 102–111.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the following sources: Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program W81XWH-09-1-0212 and NIH R01CA128797, R33CA122864, U54CA143837, U54CA151668, and the Ernest Cockrell Jr Distinguished Endowed Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
M Ferrari is the founding scientist and a member of the Board of Directors of Leonardo Biosystems, a member of Board of Directors of ArrowHead Research Corporation, and hereby discloses potential financial interests in the companies. The other authors disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Sun, T. & Ferrari, M. Nanovector delivery of siRNA for cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 19, 367–373 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.22
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.22
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nanoengineered strategies for siRNA delivery: from target assessment to cancer therapeutic efficacy
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2017)
-
Emerging Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Tauopathies
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2017)
-
NANOMEDICINE: will it offer possibilities to overcome multiple drug resistance in cancer?
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2016)
-
RNA interference mediated downregulation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) in LN18 cells
Cytotechnology (2016)
-
Recent Advances in Immunoliposome-Based Cancer Therapy
Current Pharmacology Reports (2016)