Abstract
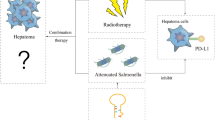
The development of RNA interference-based cancer gene therapies has been delayed due to the lack of effective tumor-targeting delivery systems. Attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) has a natural tropism for solid tumors. We report here the use of attenuated S. Typhimurium as a vector to deliver shRNA directly into tumor cells. Constitutively activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) is a key transcription factor involved in both hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) growth and metastasis. In this study, attenuated S. Typhimurium was capable of delivering shRNA-expressing vectors to the targeted cancer cells and inducing RNA interference in vivo. More importantly, a single oral dose of attenuated S. Typhimurium carrying shRNA-expressing vectors targeting Stat3 induced remarkably delayed and reduced HCC (in 70% of mice). Cancer in these cured mice did not recur over 2 years following treatment. These data demonstrated that RNA interference combined with Salmonella as a delivery system may offer a novel clinical approach for cancer gene therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF . Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 2137–2150.
Zender L, Kubicka S . Molecular pathogenesis and targeted therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Onkologie 2008; 31: 550–555.
Thomas M . Molecular targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 2009; 44 (Suppl 19): 136–141.
Alexia C, Bras M, Fallot G, Vadrot N, Daniel F, Lasfer M et al. Pleiotropic effects of PI-3′ kinase/Akt signaling in human hepatoma cell proliferation and drug-induced apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1090: 1–17.
Saxena NK, Sharma D, Ding X, Lin S, Marra F, Merlin D et al. Concomitant activation of the JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling is involved in leptin-mediated promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2497–2507.
Li WC, Ye SL, Sun RX, Liu YK, Tang ZY, Kim Y et al. Inhibition of growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by antisense oligonucleotide targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 7140–7148.
Gartel AL, Kandel ES . RNA interference in cancer. Biomol Eng 2006; 23: 17–34.
Gondi CS, Rao JS . Concepts in in vivo siRNA delivery for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol 2009; 220: 285–291.
Pawelek JM, Low KB, Bermudes D . Tumor-targeted Salmonella as a novel anticancer vector. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 4537–4544.
Zhang L, Gao L, Zhao L, Guo B, Ji K, Tian Y et al. Intratumoral delivery and suppression of prostate tumor growth by attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium carrying plasmid-based small interfering RNAs. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5859–5864.
Ren Z, Gay R, Thomas A, Pae M, Wu D, Logsdon L et al. Effect of age on susceptibility to Salmonella typhimurium infection in C57BL/6 mice. J Med Microbiol 2009; 58 (Pt 12): 1559–1567.
Hohmann EL, Oletta CA, Killeen KP, Miller SI . phoP/phoQ-deleted Salmonella typhi (Ty800) is a safe and immunogenic single-dose typhoid fever vaccine in volunteers. J Infect Dis 1996; 173: 1408–1414.
Gao L, Zhang L, Hu J, Li F, Shao Y, Zhao D et al. Down-regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expression using vector-based small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human prostate tumor in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 6333–6341.
Zhang L, Gao L, Li Y, Lin G, Shao Y, Ji K et al. Effects of plasmid-based Stat3-specific short hairpin RNA and GRIM-19 on PC-3M tumor cell growth. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 559–568.
Leong OK, Muhammad TS, Sulaiman SF . Cytotoxic activities of physalis minima L. chloroform extract on human lung adenocarcinoma NCI-H23 cell lines by induction of apoptosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2009.
Cuevas EP, Escribano O, Monserrat J, Martínez-Botas J, Sánchez MG, Chiloeches A et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of insulin receptor substrate-4 enhances actinomycin D- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death in hepatocarcinoma cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem 2009; 108: 1292–1301.
Dykxhoorn DM . RNA interference as an anticancer therapy: a patent perspective. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2009; 19: 475–491.
Lee SK, Kumar P . Conditional RNAi: towards a silent gene therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2009; 61: 650–664.
Williams BR . Targeting specific cell types with silencing RNA. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1410–1411.
Numnum TM, Makhija S, Lu B, Wang M, Rivera A, Stoff-Khalili M et al. Improved anti-tumor therapy based upon infectivity-enhanced adenoviral delivery of RNA interference in ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Gynecol Oncol 2008; 108: 34–41.
Nishikawa H, Sato E, Briones G, Chen LM, Matsuo M, Nagata Y et al. In vivo antigen delivery by a Salmonella typhimurium type III secretion system for therapeutic cancer vaccines. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 1946–1954.
Panthel K, Meinel KM, Sevil Domenech VE, Trulzsch K, Russmann H . Salmonella type III-mediated heterologous antigen delivery: a versatile oral vaccination strategy to induce cellular immunity against infectious agents and tumors. Int J Med Microbiol 2008; 298: 99–103.
Domínguez-Bernal G, Tierrez A, Bartolomé A, Martínez-Pulgarín S, Salguero FJ, Antonio Orden J et al. Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis derivatives harbouring deletions in rpoS and phoP regulatory genes are attenuated in pigs, and survive and multiply in porcine intestinal macrophages and fibroblasts, respectively. Vet Microbiol 2008; 130: 298–311.
Sirard JC, Niedergang F, Kraehenbuhl JP . Live attenuated Salmonella: a paradigm of mucosal vaccines. Immunol Rev 1999; 171: 5–26.
Bermudes D, Low B, Pawelek J . Tumor-targeted Salmonella. Highly selective delivery vectors. Adv Exp Med Biol 2000; 465: 57–63.
Darji A, Guzmán CA, Gerstel B, Wachholz P, Timmis KN, Wehland J et al. Oral somatic transgene vaccination using attenuated S. typhimurium. Cell 1997; 91: 765–775.
Eo SK, Yoon HA, Aleyas AG, Park SO, Han YW, Chae JS et al. Systemic and mucosal immunity induced by oral somatic transgene vaccination against glycoprotein B of pseudorabies virus using live attenuated Salmonella typhimurium. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2006; 47: 451–461.
Kuboki S, Shimizu H, Mitsuhashi N, Kusashio K, Kimura F, Yoshidome H et al. Angiopoietin-2 levels in the hepatic vein as a useful predictor of tumor invasiveness and prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 23: e157–e164.
Nakamura K, Zen Y, Sato Y, Kozaka K, Matsui O, Harada K et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor, its receptor Flk-1, and hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha are involved in malignant transformation in dysplastic nodules of the liver. Hum Pathol 2007; 38: 1532–1546.
Tanaka H, Yamamoto M, Hashimoto N, Miyakoshi M, Tamakawa S, Yoshie M et al. Hypoxia-independent overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha as an early change in mouse hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11263–11270.
Yao DF, Jiang H, Yao M, Li YM, Gu WJ, Shen YC et al. Quantitative analysis of hepatic hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and its abnormal gene expression during the formation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2009; 8: 407–413.
Wang M, Tan J, Coffey A, Fehrenbacher J, Weil BR, Meldrum DR . Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-stimulated hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha mediates estrogen receptor-alpha-induced mesenchymal stem cell vascular endothelial growth factor production. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009; 138: 163–171, 171 e161.
Tannapfel A, Anhalt K, Häusermann P, Sommerer F, Benicke M, Uhlmann D et al. Identification of novel proteins associated with hepatocellular carcinomas using protein microarrays. J Pathol 2003; 201: 238–249.
Lau CK, Yang ZF, Lam SP, Lam CT, Ngai P, Tam KH et al. Inhibition of Stat3 activity by YC-1 enhances chemo-sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 2007; 6: 1900–1907.
Yang SF, Wang SN, Wu CF, Yeh YT, Chai CY, Chunag SC et al. Altered p-STAT3 (tyr705) expression is associated with histological grading and intratumour microvessel density in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 2007; 60: 642–648.
Xie TX, Wei D, Liu M, Gao AC, Ali-Osman F, Sawaya R et al. Stat3 activation regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 2004; 23: 3550–3560.
Sun BS, Dong QZ, Ye QH, Sun HJ, Jia HL, Zhu XQ et al. Lentiviral-mediated miRNA against osteopontin suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008; 48: 1834–1842.
Wang T, Niu G, Kortylewski M, Burdelya L, Shain K, Zhang S et al. Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat Med 2004; 10: 48–54.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr EL Hohmann (Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA) for supplying the S. Typhimurium strain LH430. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30801354, no. 30970791), Jilin Provincial Science & Technology Department (no. 20080154), PhD Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (no. 200801831077) and National Cancer Institute Grants CA105005 and CA78282 (DV Kalvakolanu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Guo, B., Jia, H. et al. Targeted therapy via oral administration of attenuated Salmonella expression plasmid-vectored Stat3-shRNA cures orthotopically transplanted mouse HCC. Cancer Gene Ther 19, 393–401 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Promising dawn in tumor microenvironment therapy: engineering oral bacteria
International Journal of Oral Science (2024)
-
Salmonella Typhimurium as an Anticancer Therapy: Recent Advances and Perspectives
Current Clinical Microbiology Reports (2019)
-
Delivery of the co-expression plasmid pEndo-Si-Stat3 by attenuated Salmonella serovar typhimurium for prostate cancer treatment
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2013)