Abstract
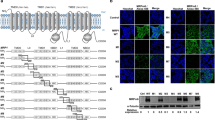
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is the major cause of failure of effective chemotherapeutic treatment of disseminated neoplasms. The “classical” MDR phenotype of human malignancies is mediated by drug extrusion by the adenosine triphosphate binding cassette (ABC)-transporter P-glycoprotein (MDR1/P-gp). For stable reversal of “classical” MDR by RNA interference (RNAi) technology, an H1-RNA gene promoter-driven expression vector encoding anti-MDR1/P-gp short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules was constructed. By introduction of anti-MDR1/P-gp shRNA expression vectors into the extremely high drug-resistant human gastric carcinoma cell line EPG85-257RDB, the MDR phenotype was completely reversed. The reversal of MDR was accompanied by a complete suppression of MDR1/P-gp expression on mRNA and protein level, and by a considerable increased intracellular anthracyline accumulation in the anti-MDR1/P-gp shRNA-treated cells. The data indicate that stable shRNA-mediated RNAi can be tremendously effective in reversing MDR1/P-gp-mediated MDR and is therefore a promising strategy for overcoming MDR by gene therapeutic applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biedler JL, Riehm H . Cellular resistance to actinomycin D in Chinese hamster cells in vitro: cross-resistance, radioautographic, and cytogenetic studies. Cancer Res. 1970;30:1174–1184.
Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE, Gottesman MM . P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene. 2003;22:7468–7485.
Lage H . ABC-transporters: implications on drug resistance from microorganisms to human cancers. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2003;22:188–199.
Kellen JA . The reversal of multidrug resistance: an update. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2003;3:5–13.
Robert J, Jarry C . Multidrug resistance reversal agents. J Med Chem. 2003;46:4805–4817.
Thomas H, Coley HM . Overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: an update on the clinical strategy of inhibiting P-glycoprotein. Cancer Control. 2003;10:159–165.
Liu C, Qureshi IA, Ding X, et al. Modulation of multidrug resistance gene (mdr-1) with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Clin Sci (Lond). 1996;91:93–98.
Stuart DD, Kao GY, Allen TM . A novel, long-circulating, and functional liposomal formulation of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeted against MDR1. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000;7:466–475.
Holm PS, Scanlon KJ, Dietel M . Reversion of multidrug resistance in the P-glycoprotein-positive human pancreatic cell line (EPP85-181RDB) by introduction of a hammerhead ribozyme. Br J Cancer. 1994;70:239–243.
Kobayashi H, Dorai T, Holland JF, Ohnuma T . Reversal of drug sensitivity in multidrug-resistant tumor cells by an MDR1(PGY1) ribozyme. Cancer Res. 1994;54:1271–1275.
Nieth C, Priebsch A, Stege A, Lage H . Modulation of the classical multidrug resistance (MDR) phenotype by RNA interference (RNAi). FEBS Lett. 2003;545:144–150.
Wu H, Hait WN, Yang JM . Small interfering RNA-induced suppression of MDR1 (P-glycoprotein) restores sensitivity to multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1515–1519.
McManus MT, Sharp PA . Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:737–747.
Hannon GJ . RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:244–251.
Nykanen A, Haley B, Zamore PD . ATP requirements and small interfering RNA structure in the RNA interference pathway. Cell. 2001;107:309–321.
Ui-Tei K, Zenno S, Miyata Y, Saigo K . Sensitive assay of RNA interference in Drosophila and Chinese hamster cultured cells using firefly luciferase gene as target. FEBS Lett. 2000;479:79–82.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T . Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–553.
Dietel M, Arps H, Lage H, Niendorf A . Membrane vesicle formation due to acquired mitoxantrone resistance in human gastric carcinoma cell line EPG85-257. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6100–6106.
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, et al. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:1107–1112.
Lage H, Perlitz C, Abele R, et al. Enhanced expression of human ABC-transporter tap is associated with cellular resistance to mitoxantrone. FEBS Lett. 2001;503:179–184.
Wichert A, Stege A, Midorikawa Y, Holm PS, Lage H . Glypican-3 is involved in cellular protection against mitoxantrone in gastric carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:945–955.
Aleman C, Annereau JP, Liang XJ, et al. P-glycoprotein, expressed in multidrug resistant cells, is not responsible for alterations in membrane fluidity or membrane potential. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3084–3091.
Lee NS, Dohjima T, Bauer G, et al. Expression of small interfering RNAs targeted against HIV-1 rev transcripts in human cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:500–505.
Miyagishi M, Taira K . U6 promoter-driven siRNAs with four uridine 3' overhangs efficiently suppress targeted gene expression in mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:497–500.
Paddison PJ, Caudy AA, Bernstein E, Hannon GJ, Conklin DS . Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) induce sequence-specific silencing in mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 2002;16:948–958.
Paul CP, Good PD, Winer I, Engelke DR . Effective expression of small interfering RNA in human cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:505–508.
Sui G, Soohoo C, el Affar B, et al. A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:5515–5520.
Yu JY, DeRuiter SL, Turner DL . RNA interference by expression of short-interfering RNAs and hairpin RNAs in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:6047–6052.
Ilves H, Barske C, Junker U, Bohnlein E, Veres G . Retroviral vectors designed for targeted expression of RNA polymerase III-driven transcripts: a comparative study. Gene. 1996;171:203–208.
Jacque JM, Triques K, Stevenson M . Modulation of HIV-1 replication by RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:435–438.
McManus MT, Petersen CP, Haines BB, Chen J, Sharp PA . Gene silencing using micro-RNA designed hairpins. RNA. 2002;8:842–850.
Harborth J, Elbashir SM, Bechert K, Tuschl T, Weber K . Identification of essential genes in cultured mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:4557–4565.
Holm PS, Dietel M, Krupp G . Similar cleavage efficiencies of an oligoribonucleotide substrate and an mdr1 mRNA segment by a hammerhead ribozyme. Gene. 1995;167:221–225.
Budworth J, Gant TW, Gescher A . Co-ordinate loss of protein kinase C and multidrug resistance gene expression in revertant MCF-7/Adr breast carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 1997;75:1330–1335.
Beaulieu E, Demeule M, Ghitescu L, Beliveau R . P-glycoprotein is strongly expressed in the luminal membranes of the endothelium of blood vessels in the brain. Biochem J. 1997;326:539–544.
Holm PS, Lage H, Bergmann S, et al. Multidrug-resistant cancer cells facilitate E1-independent adenoviral replication: impact for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res. 2004;64:322–328.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant LA 1039/2-3 of the “Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft” (DFG) and by the “RNA-network” funded by the “Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung” (BMBF) and Berlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stege, A., Priebsch, A., Nieth, C. et al. Stable and complete overcoming of MDR1/P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in human gastric carcinoma cells by RNA interference. Cancer Gene Ther 11, 699–706 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700751
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700751
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Co-delivery of Sildenafil (Viagra®) and Crizotinib for Synergistic and Improved Anti-tumoral Therapy
Pharmaceutical Research (2014)
-
Reversal of ATP-binding cassette drug transporter activity to modulate chemoresistance: why has it failed to provide clinical benefit?
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2013)
-
Thymosin beta 15A (TMSB15A) is a predictor of chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2012)
-
Argonaute2 is a potential target for siRNA-based cancer therapy for HT1080 human fibrosarcoma
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2011)
-
Inhibition of P-glycoprotein Over-expression by shRNA-mdr1b in Rat Astrocytes
Neurochemical Research (2009)