Abstract
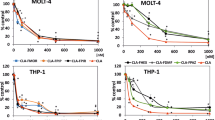
The inhibitory effects of (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2′-deoxyuridine (BVDU) and its arabinosyl derivative (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-1-β-D-arabinofuranosyluracil (BVaraU) on the growth of both MDA-MB-435 human breast carcinoma and 9L rat gliosarcoma cells expressing the thymidine kinase (tk)-encoding gene of the Varicella zoster virus (VZV) or the Herpes simplex virus (HSV) were evaluated. In vitro, BVDU and BVaraU effectively killed both cell types expressing VZVtk, with 50% inhibitory concentration values ranging from 0.06 to 0.4 μM, whereas ganciclovir (GCV) lacked activity. On HSVtk+ cells, BVDU had high cytotoxic activity, with 50% inhibitory concentration values that were similar to those of GCV, whereas BVaraU was inactive. In vivo, BVDU applied intraperitoneally caused a 50% tumor growth inhibition in nude mice inoculated subcutaneously with VZVtk+ as well as HSVtk+ mammary tumor cells. In mice and at variance with the in vitro results, BVaraU had very little activity against the VZVtk+ mammary cells; GCV had the highest activity on the HSVtk+ cells, resulting in a 50% eradication of the tumors. With the 9L rat gliosarcoma model, the VZVtk/BVDU system completely failed to inhibit the development of VZVtk+ glioma tumors induced subcutaneously in syngeneic rats, although BVDU had a similar 45-minute half-life in both rats and mice. Factors other than degradation of the prodrug and related to the mode of action of these analogs are possibly involved in the observed discrepancies between the in vitro and in vivo results.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grignet-Debrus, C., Cool, V., Baudson, N. et al. Comparative in vitro and in vivo cytotoxic activity of (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2′-deoxyuridine (BVDU) and its arabinosyl derivative, (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-1-β-D-arabinofuranosyluracil (BVaraU), against tumor cells expressing either the Varicella zoster or the Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 215–223 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700108
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700108
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cell Fate Control Gene Therapy Based on Engineered Variants of Human Deoxycytidine Kinase
Molecular Therapy (2012)
-
Dexamethasone inhibits the HSV-tk/ ganciclovir bystander effect in malignant glioma cells
BMC Cancer (2005)
-
Functional expression of thymidine kinase in human leukaemic and colorectal cells, delivered as EGFP fusion protein by herpesvirus saimiri-based vector
Cancer Gene Therapy (2004)
-
(E)-5-(2-Bromovinyl)-2′-deoxyuridine potentiates ganciclovir-mediated cytotoxicity on herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase–expressing cells
Cancer Gene Therapy (2001)