Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of prone and supine positioning on the cardiorespiratory stability of preterm infants with apnea and bradycardia.
METHODS:
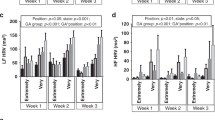
A total of 22 preterm infants with symptomatic apnea and bradycardia (gestational age of 26.9 ± 1.8 weeks and birth weight of 865 ± 235 gm) were monitored for 24 hours (in four sequential 6-hour blocks) for apnea, bradycardia, and oxygen desaturation in alternating positions (prone or supine) following randomization. Postconceptional age at the time of study was 31.9 ± 3.0 weeks. Respiratory rate, heart rate, and transcutaneous oxygen saturation were continuously monitored. All episodes of apnea (≥10 seconds), bradycardia (<100 beats per minute), and oxygen desaturation (<90%) were recorded on an event monitor. Episodes of apnea, bradycardia, and oxygen desaturation were defined as clinically significant if the following criteria were met: apnea, ≥15 seconds; bradycardia, <90 beats per minute; and oxygen desaturation, <80%. All other recorded episodes were considered mild. The episodes were analyzed for statistical significance using the paired t-test.
RESULTS:
No significant differences (p > 0.05) in the incidence of clinically significant apnea, bradycardia, or desaturation between supine and prone positions were seen in these preterm infants.
CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that the cardiorespiratory stability of preterm infants is not significantly compromised by supine positioning.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keene, D., Wimmer, J. & Mathew, O. Does Supine Positioning Increase Apnea, Bradycardia, and Desaturation in Preterm Infants?. J Perinatol 20, 17–20 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200301
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200301
This article is cited by
-
Early and consistent safe sleep practices in the neonatal intensive care unit: a sustained regional quality improvement initiative
Journal of Perinatology (2024)
-
Combined effects of body position and sleep status on the cardiorespiratory stability of near-term infants
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Proposal for mechanisms of protection of supine sleep against sudden infant death syndrome: an integrated mechanism review
Pediatric Research (2015)