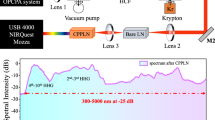
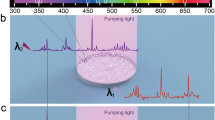
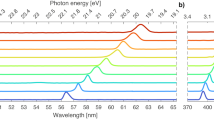
Abstract
Many systems, such as atoms and molecules in gas mixtures, dye solutions and some solid-state materials, can exhibit simultaneous laser action at several wavelengths as a result of the excitation of several optical transitions1. But semiconductor lasers are usually monochromatic because the electronic levels are distributed in continuous energy bands2. In order to achieve simultaneous lasing at several well-separated wavelengths, researchers have proposed3 combining different semiconductors with distinct bandgap energies in the active material. However, the difficulty of pumping different regions and of absorption of the shorter-wavelength light could be resolved only by using separated multiple resonators or by multisection injection devices4,5,6,7. Here we report the realization of a single artificial semiconductor material with distinct optical transitions, which permits simultaneous multiwavelength laser action at mid-infrared wavelengths (6.6, 7.3 and 7.9 µm). This is achieved by tailoring the electronic states and electron relaxation times in the material, which is a superlattice layered structure. The laser has potential applications in sensors for trace-gas analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silfvast, W. T. Laser Fundamentals (Cambridge Univ. Press, (1996).
Yariv, A. Optical Electronics (Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia, 1991).
Ikeda, S., Shimizu, A. & Hara, T. Asymmetric dual quantum well laser-wavelength switching controlled by injection current. Appl. Phys. Lett. 55, 1155–1157 (1989).
Beernik, K. J., Thornton, R. L. & Chung, H. F. Low threshold current dual wavelength planar buried heterostructure lasers with close spatial and large spectral separation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 64, 1082–1084 (1994).
Garcia, J. Ch. et al. Epitaxially stacked lasers with Esaki junctions: a bipolar cascade laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 3752–3754 (1997).
Dutta, N. K. et al. InGaAsP closely spaced dual wavelength laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 48, 1725–1726 (1986).
Pellandini, P. et al. Dual-wavelength laser emission from a coupled semiconductor microcavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 864–866 (1997).
Sirtori, C., Capasso, F., Faist, J. & Scandolo, S. Nonparabolicity and a sum rule associated with bound-to-bound and bound-to-continuum intersubband transitions in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 50, 8663–8674 (1994).
Faist, J. et al. Quantum cascade laser. Science 264, 553–556 (1994).
Faist, J. et al. Short wavelength (λ ∼ 3.4 µm) quantum cascade laser based on strained compensated InGaAs/AlInAs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 680–682 (1998).
Gmachl, C. et al. Long wavelength (λ ≃ 13µm) quantum cascade lasers. Electron. Lett. 34, 1103–1104 (1998).
Capasso, F., Faist, J., Sirtori, C. & Cho, A. Y. Infrared (4–11 µm) quantum cascade lasers. Solid State Commun. 102, 231–236 (1997).
Gmachl, C. et al. Continuous-wave and high-power pulsed operation of index-coupled distributed feedback quantum cascade lasers at λ ≈ 8.5 µm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1430–1432 (1998).
Namjou, K. et al. Sensitive absorption spectroscopy with a room-temperature distributed-feedback quantum-cascade laser. Opt. Lett. 23, 219–221 (1998).
Sharpe, S. W. et al. High-resolution (Doppler-limited) spectroscopy using quantum-cascade distributed-feedback lasers. Opt. Lett. 23, 1396–1398 (1998).
Sigrist, M. W. Air Monitoring by Spectroscopic Techniques (Wiley, New York, (1994).
Faist, J. et al. Laser action by tuning the oscillator strength. Nature 387, 777–782 (1997).
Scamarcio, G. et al. High-power infrared (8-micrometer wavelength) superlattice lasers. Science 276, 773–776 (1997).
Dingle, R., Gossard, A. C. & Wiegmann, W. Direct observation of superlattice formation in a semiconductor heterostructure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 34, 1327–1330 (1975).
Tredicucci, A. et al. High-power inter-miniband lasing in intrinsic superlattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 2388–2390 (1998).
Ferreira, R. & Bastard, G. Evaluation of some scattering times for electrons in unbiased and biased single- and multiple-quantum-well structures. Phys. Rev. B 40, 1074–1086 (1989).
Sirtori, C. et al. Continuous wave operation of midinfrared (7.4–8.6 µm) quantum cascade lasers up to 110 K temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 1745–1747 (1996).
Hakki, B. W. & Paoli, T. L. Gain spectra in GaAs double-heterostructure injection lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 1299–1306 (1975).
Mendez, E. E., Agullo-Rueda, F. & Hong, J. M. Stark localization in GaAs-GaAlAs superlattices under an electric field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2426–2429 (1988).
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Office of Naval Research and by DARPA/US Army Research Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tredicucci, A., Gmachl, C., Capasso, F. et al. A multiwavelength semiconductor laser. Nature 396, 350–353 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/24585
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/24585
This article is cited by
-
Mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers
Nature Photonics (2012)
-
Quasi-periodic distributed feedback laser
Nature Photonics (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.