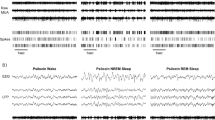
Abstract
WE have previously noted what seemed to be marked discrepancies between human and other mammalian species in the association of serotonin and sleep1–3. Furthermore, L-dopa, the immediate precursor of dopamine and noradrenaline, by producing a decrease in human rapid eye movement (REM) sleep4 (an opposite effect from the predictions based on animal studies5), indicated that there might also be differences between human and other mammalian species in the adrenergic system. To further determine the role of the adrenergic nervous system in human sleep we studied the effect of depleting brain Catecholamines by administration of alpha-methyl-d 1-paratyrosine (AMPT) and alpha-methyl-P-phenylalanine (AMPHe), which are potent and specific inhibitors of catecholamine synthesis6,7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wyatt, R. J., Engelman, K., Kupfer, D. J., Scott, J., Sjoerdsma, A., and Snyder, F., Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol., 27, 529 (1969).
Wyatt, R. J., Chase, T. N., Engelman, K., Kupfer, D. J., Scott, J., Sjoerdsma, A., and Snyder, F., Psychophysiology (in the press).
Lovenberg, W., Engelman, K., Carpenter, jun., W. T., Wyatt, R. J., and Gessa, G. L., Ann. Internal. Med., 607 (1970).
Wyatt, R. J., Chase, T. N., Engelman, K., Scott, J., and Snyder, F., Nature (in the press).
Jouvet, M., Science, 162, 32 (1969).
Engelman, K., Horowitz, D., Jequier, E., Sjoerdsma, A., J. Clin. Invest., 47, 577 (1968).
Torcliana, M. L., Porter, C. C., Stone, C. A., and Hanson, A. M., Biochem. Pharmacol. (in the press).
A Manual of Standardized Terminology, Techniques and Scoring System for Sleep Stages of Human Subjects (edit. by Rechtschaffen, A., and Kales, A.) (US Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1968).
Chase, T. N., Schnur, J., and Gordon, E. K., Neuropharmacol. (in the press).
Cerbode, F., and Bowers, M. B., J. Neurochem., 15, 1053 (1968).
Ashcroft, G. W., and Sharman, D. F., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 19, 153 (1962).
Guldberg, H. C., and Yates, C. M., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 36, 535 (1969).
Marantz, R., and Rechtschaffen, A., Perception Motor Skills, 25, 805 (1967).
Hartmann, E., Bridwell, I., and Shildkraut, J., Psychophysiology (in the press).
King, C. K., and Jewett, R. E., Psychophysiology, 6, 220 (1969).
Iskander, T., and Kailbling, R., Psychophysiology, 6, 219 (1970).
Crowley, J. T., Pegram, G. V., Smith, E., and Lewis, D. F., Primate Electrophysiology Particularly Related to Sleep (Rep. ARL-TR-69-5) (Holloman Air Force Base, New Mexico, 1969).
Weitzman, E. D., McGregor, P., Moore, C., and Jacoby, J., Life Sci., 8, 751 (1969).
Wyatt, R. J., Engelman, K., Sjoerdsma, A., and Snyder, F., Psychophysiology (in the press).
Weitzman, E. D., Rapport, M. S., McGregor, P., and Jacoby, J., Science, 160, 1361 (1968).
Koella, W. P., Feldstein, A., and Czicman, J. S., Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol., 25, 481 (1968).
Torda, C., Brain Res., 6, 375 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WYATT, R., CHASE, T., KUPFER, D. et al. Brain Catecholamines and Human Sleep. Nature 233, 63–65 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/233063a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/233063a0
This article is cited by
-
REM sleep suppression induced by selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Psychopharmacology (1982)
-
Suppression of REM and delta sleep by apomorphine in man: A dopamine mimetic effect
Psychopharmacology (1980)
-
Hypersomnia with simultaneous waking and sleep patterns in the electroencephalogram
Journal of Neurology (1979)
-
Effects of central dopaminergic blockade with pimozide upon the EEG stages of sleep in man
Psychopharmacologia (1975)
-
The effects of amoxapine on electroencephalographic stages of sleep in normal human subjects
Psychopharmacologia (1975)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.