Abstract
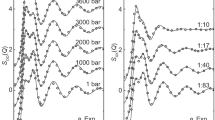
THE addition of sodium chloride has a marked effect in reducing the electrostatic interaction between deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules in solution, as is shown by the decrease in the slope of the concentration dependence of reduced viscosity (ηsp/c.) with the increase of added salt1,2. This work shows that the same information can also be obtained from the variation of the concentration dependence of sedimentation coefficient of DNA with the addition of sodium chloride. Fig. 1 is a plot of the reciprocal of the sedimentation coefficient, 1/S20,w versus DNA concentration, at sodium chloride concentrations of 0.001 M, 0.01 M, 0.1 M, 0.15 M and 0.2 M. Changes in the slope of the curves as well as a constant extrapolated value of sedimentation coefficient at zero concentration, S020,w = 22.7 × 10−13 sec, at different concentrations of salt, reveal a close similarity between the concentration dependence of reduced viscosity and that of the reciprocal of sedimentation coefficient, in the case of DNA in solution.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jordan, D. O., The Chemistry of Nucleic Acids (Butterworths, London, 1960).
Sadron, C. L., in The Nucleic Acids, edit. by Chargaff, E., and Davidson, J. N., 3, 1 (Academic Press, New York, 1960).
Coates, J. H., and Jordan, D. O., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 35, 309 (1959).
Peacocke, A. R., and Schachman, H. K., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 15, 198 (1954).
Fredericq, E., Oth, A., and Fontaine, F., J. Mol. Biol., 3, 11 (1961).
Cavalierie, L. F., Rosoff, M., and Rosenberg, B. H., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 78, 5239 (1956).
Butler, J. A. V., Pain, R. H., Robins, A. B., and Rotblat, J., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 149, 12 (1958).
Stern, K. G., and Atlas, S. M., J. Biol. Chem., 203, 795 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GANGULI, P., BHATTACHARYYA, A. Concentration Dependence of Sedimentation Coefficient of Deoxyribonucleic Acid with added Sodium Chloride. Nature 196, 1201–1203 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/1961201a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1961201a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.