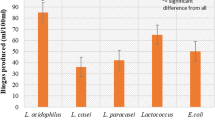
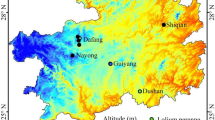
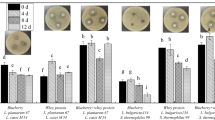
Abstract
DURING the course of investigations on the utilization of cheese whey by micro-organisms, a strain of Aerobacter aerogenes was found capable of growing in whey and increasing the total protein of the whey without requiring the addition of a fixed form of nitrogen. Various attempts to convert cheese whey into useful substances by microbiological means have been covered in the review by Wix and Woodbine1. Cheese whey is a waste product with a high potential energy source in the form of lactose which has been studied in this laboratory as a substrate for members of the genus Azotobacter 2. This was concerned with increasing the protein content of whey by the production of bacterial cell material. Azotobacter will not use lactose. Since we found that hydrolysis of the lactose must be followed by the removal of salts and other toxic ingredients in order to support growth of Azotobacter, attention was directed to other microorganisms. An economic advantage of the genus Azotobacter is its nitrogen-fixing ability. Hence, interest was turned to a nitrogen-fixing strain of Aerobacter aerogenes which was recently discovered in this laboratory3. Pirt4 has shown that the efficiency of conversion of substrate carbon to cell carbon and carbon dioxide by Aerobacter is directly proportional to the degree of oxygenation of the culture. This indicated that fermentation of whey could be accomplished under aerobic conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wix, P., and Woodbine, M., Dairy Sci. Abst., 20, 539 (1958).
Pfeffer, M., M.S. thesis, University of Vermont (1958).
Blanchard, G. C., M.S. thesis, University of Vermont (1958).
Pirt, S. J., J. Gen. Microbiol., 16, 59 (1957).
Pengra, R. M., and Wilson, P. W., J. Bact., 75, 21 (1958).
Jensen, V., Physiol. Plantarum., 9, 130 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JOHNSTONE, D., PFEFFER, M. Aerobic Fermentation of Whey by a Nitrogen-fixing Strain of Aerobacter aerogenes . Nature 183, 992–993 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1038/183992a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/183992a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.