Abstract
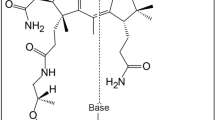
ACCORDING to Nakahara et al.1, adenylthiomethylpentose has the same effect as vitamin L2 (L1 is said to be anthranilic acid). Adenylthiomethylpentose was isolated from yeast2, from crude oryzanine3, and from impure cozymase4, and yielded adenine and thiosugar on acid hydrolysis. Falconer and Gulland5 state that the thiosugar is combined to the 9-position of the adenine. The thiosugar itself has been the subject of several studies: according to Suzuki, Ohdake and Mori3,6, the thiosugar gives the Molisch test with all other reducing sugar tests, and strong pentose reactions, but gives neither the methylpentose reaction nor Seliwanoff's. The sulphur can be detected only after fusion of the thiosugar with metallic sodium; and by estimation of the thiomethyl group, the Japanese authors assigned to the sugar the structure of 5-thiomethylpentose, and showed that the sugar could be reduced by means of sodium amalgam to the thiomethyl group containing polyalcohol (thiopentitol) (I). 
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakahara, Inugai, Ugami and Nagata, Sci. Jap. Inst. Phys. Chem. Research, 42, 153 (1945).
Mandel and Dunham, J. Biol. Chem., 11, 85 (1912).
Suzuki, Ohdake and Mori, Biochem. Z., 154, 278 (1924).
Euler and Myrbäck, Z. physiol. Chem., 177, 237 (1928).
Falconer and Gulland, J. Chem. Soc., 1912 (1937).
Suzuki and Mori, Biochem. Z., 162, 413 (1925).
Levene and Sobotka, J. Biol. Chem., 65, 551 (1925).
Wendt, Z. physiol. Chem., 272, 152 (1942).
Raymond, J. Biol. Chem., 107, 85 (1934).
Makino, Biochem. Z., 278, 161 (1935); 282, 120 (1935).
Lohmann, J. Chem. Soc., 582 (1949).
Lythgoe and Todd, Nature, 155, 695 (1945).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SATOH, K., MAKINO, K. Structure of Adenylthiomethylpentose. Nature 165, 769–770 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/165769a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/165769a0
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis of 5-Thiomethylribose
Nature (1951)
-
Structure and Synthesis of Adenine Thiomethyl Pentoside; Synthesis of 5′-Methylthio Inosine
Nature (1951)
-
Structure of Adenylthiomethylpentose
Nature (1951)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.