Abstract
BACKGROUND: Cross-cultural studies have long suggested that the high incidence of breast cancer in developed Western countries may be linked to the high prevalence of obesity and to high total energy intake. Recent studies show that hyperinsulinemia, increased concentration of insulin-like growth factor 1 and greater abdominal fat accumulation are markers of high risk for breast cancer. Increased serum concentrations of free estradiol and free testosterone are similar risk markers and are frequent concomitants of hyperinsulinemia.
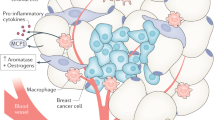
MECHANISMS: The mechanism by which such metabolic–endocrine abnormality may promote mammary carcinogenesis is uncertain, but its effect is likely to predominate in the years approaching the menopause when obesity is common among Western women. In obese subjects, enlargement of adipose deposits is known to produce an excess of free fatty acids and tumor necrosis factor alpha, both of which may be involved in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. In middle-aged women, the concomitants of hyperinsulinemia may activate invasive and proliferative activity in preneoplastic mammary lesions such as in situ duct carcinoma of the comedo type. This will enhance the risk of progression to invasive breast cancer, which is likely to manifest clinically mainly after the menopause.
CONCLUSION: Weight reduction combined with a program of regular physical exercise has been shown to reduce both estrogen and insulin concentrations in obese women and such a regimen might be tested in clinical trials for an effect on breast cancer risk in obese women. Intervention is best begun around the age of 45 y, this being the age when in situ duct carcinoma would normally begin to show evidence of spontaneous involution in women without clinical evidence of invasive breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballard-Barbash R . Anthropometry and breast cancer Cancer 1994 74: 1090–1100.
Ziegler RG . Anthropometry and breast cancer J Nutr 1997 127 (Suppl): 924–928.
Toniolo PG, Levitz M, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Banerjee S, Koenig KL. Shore RE, Strax P . Prospective study of endogenous estrogens and breast cancer in postmenopausal women J Natl Cancer Inst 1995 87: 190–197.
Dorgan JF, Longcope C, Stephenson HE Jr, Falk RT, Miller R, Franz C . Relation of prediagnostic serum estrogen and androgen levels to breast cancer risk Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1996 5: 533–539.
Berrino F, Muti P, Micheli A, Bolelli G, Krogh V, Sciajno R, Pisani P, Panico S, Secreto G . Serum sex hormone levels after menopause and subsequent breast cancer J Natl Cancer Inst 1996 88: 291–296.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Speizer FE . Plasma sex steroid hormones and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women J Natl Cancer Inst 1998 90: 1292–1299.
Cauley JA, Lucas FL, Kuller LH, Stone K, Browner W, Cummings SR . Elevated serum estradiol and testosterone concentrations are associated with a high risk for breast cancer Ann Intern Med 1999 130: 270–277.
Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Bruning PF, Bonfrer JM, Koenig KL, Shore RE, Kim MY . Relation of serum levels of testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate to risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women Am J Epidemiol 1997 145:: 1030–1038.
Thomas HV, Key TJ, Allen DS, Moore JW, Dowsett HM, Fentiman IS, Wang DY . A prospective study of endogenous serum hormone concentrations and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women on the island of Guernsey Br J Cancer 1997 76: 401–415.
Bartow SA, Pathak DR, Black WC, Key CR, Teaf SR . Prevalence of benign, atypical and malignant breast lesions in populations at different risk for breast cancer. A forensic autopsy study Cancer 1987 60: 2751–2760.
Prietto J, Filippis A, Nakhla C, Clark S . Nutrient induced insulin resistance Mol Cell Endocrine 1999 151: 143–149.
Barsky SH, Shao ZM, Bose S . Should DCIS be renamed carcinoma of the ductal system? Breast J 1999 5: 70–72.
Stoll BA . Teenage obesity in relation to breast cancer risk Int J Obes 1998 22: 1035–1040.
Sakamoto G, Sugano H . Pathology of breast cancer; present and prospects in Japan Breast Cancer Res Treatment 1991 18 (Suppl 1): 81–83.
Aaman TB, Stalsberg H, Thomas DB . Extratumoral breast tissue in breast cancer patients; a multinational study of variations with age and country of residence in low and high risk countries Int J Cancer 1997 71: 333–339.
Wazer DE, Gage J, Homer M, Krosnick SH, Schmid C . Age-related differences in patients with non-palpable breast carcinomas Cancer 1996 78: 1432–1437.
Nielsen M, Thomson JL, Primdahl S, Dyreborg U, Andersen JD . Breast cancer and atypia among young and middle aged women Br J Cancer 1987 56: 814–819.
Visscher DW, Padiyar N, Long D, Tabaczka P . Immunohistologic analysis of estrogen receptor expression in breast carcinoma precursor lesions Breast J 1998 4: 447–451.
Schmitt FC . Multistep progression from an oestrogen-dependent growth towards an autonomous growth in breast carcinogenesis Eur J Cancer 1995 31A: 2049–2052.
Holland PA, Knox WF, Potten CS, Howell A, Anderson E, Baildam AD, Bundred NJ . Assessment of hormone dependence of comedo DCIS of the breast J Natl Cancer Inst 1997 89: 1059–1065.
Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickenham DL, Redmond CK, Kavanah P . Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer; report of the NSABF P1 study J Natl Cancer Inst 1998 90: 1371–1388.
Cummings SR, Eckert S, Krueger KA, Grady D, Powles TJ, Cauley JA, Norton L, Nickelsen T, Bjarnason NH, Morrow M, Lippman ME . The effect of raloxifene on risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women JAMA 1999 281:: 2189–2197.
James LA, Mitchell EL, Menasce L, Varley JM . Comparative genomic hybridisation of DCIS of the breast; identification of regions of DNA amplification and deletion in common with invasive carcinoma Oncogene 1997 14: 1059–1065.
Ellis MJC, Hayes DF . Improving hormonal therapy for breast cancer Breast J 1997 3 (Suppl): 57–68.
Garland CF, Friedlander NJ, Barrett-Connor E, Khaw KT . Sex hormones and post menoapsaul breast cancer; a prospective study in an adult community Am J Epidemiol 1992 135: 1220–1230.
Ballard-Barbash R, Schatzkin R, Carter CL, Kannel WB, Kreger BE, D'Agostini RB, Splansky GL, Anderson KM, Helsel WE . Body fat distribution and breast cancer in the Framingham study J Natl Cancer Inst 1990 82:: 286–290.
Folsom AR, Kaye SA, Prineas PJ, Potter JD, Gapstur SM, Wallace RB . Increased incidence of carcinoma of the beast associated with abdominal obesity in postmenopausal women Am J Epidemiol 1990 131: 794–803.
Schapira DV, Kumar NB, Lyman GH, Cox CE . Abdominal obesity and breast cancer risk Ann Intern Med 1990 112: 182–186.
Kodama M, Kodama T, Miura S, Yoshida M . Nutrition and breast cancer risk in Japan Anticancer Res 1991 11: 745–754.
Bruning PF, Bonfrer JMG, Hart AAM, Van Noord PA, Van der Hoeven PH, Collette HJ, Battemann L . Body measurements, estrogen availability and the risk of human breast cancer; a case control study Int J Cancer 1992 51:: 14–19.
Mannisto S, Pietinen P, Pyy M, Palmgren J, Eskelinen M, Uusitupa M . Body-size indicators and risk of breast cancer according to menopause and ER status Int J Cancer 1996 68: 8–13.
Den Tonkelaar I, Seidell JC, Collette HJ . Body fat distribution in relation to breast cancer in women participating in the DOM project Breast Cancer Res Treatment 1995 34: 55–61.
Ng EH, Gao F, Ji CY, Ho GH, Soo KC . Risk factors for breast cancer in Singaporean Chinese women Cancer 1997 80: 725–731.
Kaaks R, Van Noord PAH, Den Tonkelaar I, Peeters PJH, Riboli E, Grobbee DE . Breast cancer incidence in relation to height, weight and body fat distribution in the Dutch DOM cohort Int J Cancer 1998 76: 647–651.
Hall IJ, Newman B, Millikan RC, Moorman PG . Evaluating body size and breast cancer risk among black women Am J Epidemiol 1998 11 (Suppl): Abstract 359.
Petrek JA, Peters M, Cirrincione C, Rhodes D, Bajorunas D . Is body fat topography a risk factor for breast cancer? Ann Intern Med 1993 188: 357–362.
Fujimoto WY, Bergstrom RW, Boyko EJ, Leonetti DL, Newell-Morris LL, Wahl PW . Susceptibility to development of central adiposity among populations Obes Res 1995 3 (Suppl 2): 179–186.
Bruning PF, Bonfrer JMG, Van Noord PAH, Hart AAM, De Jong Bakker M, Nooijen WJ . Insulin resistance and breast cancer risk Int J Cancer 1992 52: 511–516.
Tekden N, Kahraman H, Yucel I, Adam B, Yildiz C, Tanyeri F . Insulin and C-peptide response to oral glucose in patients with breast cancer Ann Oncol 1996 7 (Suppl 5): 24 (abstract).
Muti P, Liu J, Trevisan A, Menotti A . Insulin resistance as a risk factor for colon and breast cancer Am J Epidemiol 1997 145 (Suppl 11): 25 (abstract).
Gamayunova VB, Bobrov YF, Tsyrlina EV, Evtushento TP, Berstein LM . Comparative study of blood/insulin levels in breast and endometrial cancer Neoplasma 1997 44: 123.
Del Giudice ME, Fantus IG, Ezzat S, McKeown-Eyssen G, Page D, Goodwin PJ . Insulin and related factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk Breast Cancer Res Treatment 1998 47: 111–120.
Byrne C, Hankinson SE, Cohen RM, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Speizer FE . Plasma insulin level and subsequent risk of breast cancer Am J Epidemiol 1998 147 (Suppl 11): 355 (abstract).
Peyrat JP, Bonneterre J, Hecquet B, Vennin P, Louchez MM, Fournier C, Lefebvre J, Demaille A . Plasma IGF1 concentrations in human breast cancer Eur J Cancer 1993 29A:: 492–497.
Barni S, Lissoni P, Brivio F, Fumagalli L, Merlini D, Cataldo M, Rovelli F, Tancini G . Serum levels of IGF1 in operable breast cancer in relation to their main prognostic variables Tumori 1994 80: 212–215 (English abstract).
Bruning PF, Van Doorn J, Bonfrer JMG . IGFBP3 is reduced in early stage operable breast cancer Int J Cancer 1995 62: 266–270.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Pollak M . Circulating concentrations of IGF1 and risk of breast cancer Lancet 1998 351: 1393–1396.
Ng EH, Ji CY, Tan PH, Lin V, Soo KC, Lee KP . Altered levels of IGF binding proteins in breast cancer patients Ann Surg Oncol 1998 5: 194–201.
Peyrat JP, Revillion F, Bonneterre J . Plasma IGF in primary breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy Br J Cancer 1998 77: 1669–1671.
Vadgama JV, Wu Y, Datta G, Khan H, Chillar R . Plasma IGF1 and IGFBP3 can be associated with progression of breast cancer and predict risk of recurrence in African American ad Hispanic women Oncology 1999 57: 330–340.
Favoni RE, de Cupis A, Perrotta A, Sforzini S, Amoroso D, Pensa F, Miglietta L . IGF1 and IGFBP3 blood serum levels in women with early and late stage breast cancer J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1995 121: 674–682.
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovanucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P . Plasma IGF1 and prostate cancer risk; a prospective study Science 1998 279: 563–566.
Yu H, Spitz MR, Mistry J, Gu J, Hong WK, Wu X . Plasma levels of IGF1 and lung cancer risk; a case-control analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999 91: 151–156.
Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovanucci E, Chan JM, Tao Y, Hennekens CH, Stampfer MJ . Prospective study of colorectal cancer in men and plasma levels IGF1 and IGF binding proteins J Natl Cancer Inst 1999 91: 620–625.
Foekens JA, Portengen H, Janssen M, Klijn JG . IGF1 receptors and IGF-like activity in human primary breast cancer Cancer 1989 63: 2139–2147.
Lee AV, Weng CN, Jackson JG, Yee D . Activation of the estrogen receptor mediated gene transcription by IGF1 in human breast cancer cells J Endocrinol 1997 152:: 39–47.
Westley BR, Clayton SJ, Daws MR, Molloy CA, May FC . Interactions between the oestrogen and IGF signalling pathways in the control of breast epithelial cell proliferation Biochem Soc Symp 1998 63: 35–44.
Macaulay VM . Insulin-like growth factors and cancer Br J Cancer 1992 65: 311–320.
Surmacz E, Burgaud JL . Overexpression of IRS-1 in the human breast cancer cell line MCF7 induces loss of estrogen requirements for growth and transformation Clin Cancer Res 1995 1: 1429–1436.
Gordge PC, Hulme MJ, Clegg RA, Miller WR . Elevation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C activities in malignant as compared with normal human breast tissue Eur J Cancer 1996 32A: 2120–2126.
Powis G, Alberts DS . Inhibiting intracellular signalling as a strategy for cancer chemoprevention Eur J Cancer 1994 30A: 1138–1144.
Hahnel R, Geschwendt M . The interaction between PKC and estrogens Int J Oncol 1995 7: 11–16.
Lamson M, Besson P, Bougnoux P . Supplementation of MCF-7 cells with essential fatty acids induces the activation of PKC in response to IGF1 J Lipid Mediated Cell Signalling 1997 16: 189–197.
Johnson MD, Torri JA, Lippman ME, Dickson RB . Regulation of motility and protease expression in PKC-mediated induction of MCF-7 breast cancer cell invasiveness Exp Cell Res 1999 247: 105–113.
Morse-Gaudio M, Connolly JM, Rose DP . PKC and its isoforms in human breast cancer cells; relationship to invasive phenotype Int J Oncol 1998 12: 1349–1354.
Greenwald P . NCI cancer prevention and control research Prev Med 1993 11: 642–660.
Woods MW, Gorbach SL, Longcope C, Goldin BR, Dwyer JT, Morrill-Labrode A . Low fat, high fiber diet and serum estrone sulfate in premenopausal women Am J Clin Nutr 1989 49: 1179–1183.
Prentice R, Thompson D, Clifford C, Gorbach S, Goldin B, Byar D . Dietary fat reduction and plasma estradiol concentration in healthy postmenopausal women J Natl Cancer Inst 1990 82: 129–134.
Goldin BR, Adlercreutz H, Gorbach SL . Estrogen excretion patterns and plasma levels in vegetarian and omniverous women N Engl J Med 1982 307: 1542–1547.
Barbosa JC, Schultz TD, Filley SJ, Nieman DC . Relationship among adiposity, diet and hormone concentrations in vegetarian and non-vegetarian postmenopausal women Am J Clin Nutr 1990 51: 798–803.
Rose DP, Goldman M, Connolly JM, Strong LE . High fiber diet reduces serum estrogen concentrations in premenopausal women Am J Clin Nutr 1991 54: 520–525.
Thissen JP, Ketelslegers JM, Underwood LE . Nutritional regulation of the insulin-like growth factors Endocr Rev 1994 15: 80–101.
Lovejoy J, Girolamo M . Habitual dietary intake and insulin sensitivity in lean and obese adults Am J Clin Nutr 1992 55: 1174–1179.
Barnard RJ, Ugionskis EJ, Martin DA, Inkeles SB . Role of diet and exercise in the management of hyperinsulinemia and associated atherosclerotic risk factors Am J Cardiol 1992 69: 440–444.
De Waard F, Poortman J, De Pedro AFM, Baanders van Halewijn EA . Weight reduction and oestrogen excretion in obese postmenopausal women Maturitas 1982 4: 155–162.
Huang Z, Hankinson SE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Hunter DJ, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Willett WC . Dual effects of weight and weight gain on breast cancer risk JAMA 1997 278: 1407–1411.
Trentham-Dietz A, Newcomb PA, Storer BE, Longnecker MP, Baron J, Greenberg ER, Willett WC . Body size and risk of breast cancer Am J Epidemiol 1997 145: 1011–1019.
De Ridder CM, De Boer RW, Seidell JC, Nieuwenhoff CM, Jeneson JA, Bakker CJ, Zonderland ML, Erich WB . Body fat distribution in pubertal girls quantified by magnetic resonance imaging Int J Obes 1992 16: 443–449.
Thune L, Brenn T, Lunk E, Gaard M . Physical activity and the risk of breast cancer N Engl J Med 1997 336: 1269–1275.
Gammon MD, John EM, Britton JA . Recreational and occupational physical activities and risk of breast cancer J Natl Cancer Inst 1998 90: 100–117.
Pratley RE, Hagberg JM, Rogus EM, Goldberg AP . Enhanced insulin sensitivity and lower waist-to-hip ratio in master athletes Am J Physiol 1995 268 (Endocrinol Metab 31): E484–490.
Despres JP, Pouliot MC, Moorjani S, Nadeau A, Tremblay A, Lupien PJ, Theriault G, Bouchard C . Loss of abdominal fat and metabolic response to exercise training in obese women Am J Physiol 1991 261 (Endocrinol Metab 24): E159–E167.
Cauley JA, Gutai JP, Kuller LH, Le Donne D, Powell JG . The epidemiology of sex hormones in postmenopausal women Am J Epidemiol 1989 129: 1120–1131.
Stoll BA . Western diet, early puberty and breast cancer risk Breast Cancer Res Treatment 1998 49: 187–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoll, B. Adiposity as a risk determinant for postmenopausal breast cancer. Int J Obes 24, 527–533 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801247
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801247
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Reduced Basal Nitric Oxide Production Induces Precancerous Mammary Lesions via ERBB2 and TGFβ
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Adult weight change and the risk of pre- and postmenopausal breast cancer in the Chinese Wuxi Exposure and Breast Cancer Study
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2019)
-
The role of SRC-3 in human breast cancer
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2010)
-
Risk factors for breast carcinoma in situ versus invasive breast cancer in a prospective study of pre- and post-menopausal women
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2007)
-
The Nurses' Health Study: lifestyle and health among women
Nature Reviews Cancer (2005)