Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Phase-separation behaviour of RNAs
Phase-separation behaviour of RNAs
Ribonucleoprotein granules are ubiquitous in living organisms with the protein and RNA components having distinct roles. In the absence of proteins, RNAs are shown to undergo phase separation upon heating. This transition is driven by desolvation entropy and ion-mediated crosslinking and is tuned by the chemical specificity of the RNA nucleobases.
-
Article |
 RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
The physicochemical driving forces of protein-free, RNA-driven phase transitions were previously unclear, but it is now shown that RNAs undergo entropically driven liquid–liquid phase separation upon heating in the presence of magnesium ions. In the condensed phase, RNAs can undergo an enthalpically favourable percolation transition that leads to arrested condensates.
- Gable M. Wadsworth
- , Walter J. Zahurancik
- & Priya R. Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Optical control of ultrafast structural dynamics in a fluorescent protein
Optical control of ultrafast structural dynamics in a fluorescent protein
Pump–probe measurements conventionally achieve femtosecond time resolution for X-ray crystallography of reactive processes, but the measured structural dynamics are complex. Using coherent control techniques, we show that the ultrafast crystallographic differences of a fluorescent protein are dominated by ground-state vibrational processes that are unconnected to the photoisomerization reaction of the chromophore.
- Christopher D. M. Hutchison
- , James M. Baxter
- & Jasper J. van Thor
-
Article |
 Kinetic control of shape deformations and membrane phase separation inside giant vesicles
Kinetic control of shape deformations and membrane phase separation inside giant vesicles
The kinetics of liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) in cell-like confinements remains poorly understood. Now it has been shown that it involves complex interplay between the incipient phases and the membrane boundary, which arrests phase coarsening, deforms the membrane and couples LLPS with lipid phase separation.
- Wan-Chih Su
- , James C. S. Ho
- & Atul N. Parikh
-
Article |
 Insights from an information thermodynamics analysis of a synthetic molecular motor
Insights from an information thermodynamics analysis of a synthetic molecular motor
Information is physical, but the flow between information, energy and mechanics in chemical systems remains largely unexplored. Now, an autonomous molecular motor has been analysed with information thermodynamics, which relates information to other thermodynamic parameters. This treatment provides a general thermodynamic understanding of molecular motors, with practical implications for machine design.
- Shuntaro Amano
- , Massimiliano Esposito
- & Benjamin M. W. Roberts
-
-
News & Views |
 Sticky when dry
Sticky when dry
Is a nanoscale hydrophobic bowl wet or dry when dissolved in water? It turns out that the answer depends on the architecture of its rim. A molecular host decorated with four methyl groups around its rim pointing inward, rather than up, has now been shown to expel water from the bowl, making it dry and sticky.
- Shekhar Garde
-
Article |
 Spontaneous drying of non-polar deep-cavity cavitand pockets in aqueous solution
Spontaneous drying of non-polar deep-cavity cavitand pockets in aqueous solution
Water plays an active role in modulating guest recognition by both artificial and biological hosts, but how this role can be controlled is unclear. Now, the de-wetting of the non-polar pockets of cavitands is shown to be affected by the orientation of methyl groups encircling the portal, which moderate the enthalpic and entropic contributions driving recognition.
- J. Wesley Barnett
- , Matthew R. Sullivan
- & Henry S. Ashbaugh
-
Article |
 Overcoming chemical equilibrium limitations using a thermodynamically reversible chemical reactor
Overcoming chemical equilibrium limitations using a thermodynamically reversible chemical reactor
Conventional chemical reactors are subject to the equilibrium limitations imposed by the overall reaction. It has now been shown that this limitation can be overcome if reactants are fed separately to a reactor and a non-stoichiometric oxygen carrier is used to transfer both oxygen and key chemical information across a reaction cycle.
- Ian S. Metcalfe
- , Brian Ray
- & John S. O. Evans
-
Article |
 Control over phase separation and nucleation using a laser-tweezing potential
Control over phase separation and nucleation using a laser-tweezing potential
A low-power laser can cause phase separation or trigger the nucleation of a new phase in the proximity of a liquid–liquid critical point, or binodal, using a laser tweezing potential. This effect explains the physics behind non-photochemical laser-induced nucleation and suggests new ways of manipulating matter.
- Finlay Walton
- & Klaas Wynne
-
Article |
 Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water
Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water
Aggregation usually prevents dissolution of graphene in water. Now, hydroxide ion adsorption has been shown to allow the stabilization of true single-layer graphene in water — with no surfactant required — so long as the liquid is degassed beforehand. The resulting aqueous dispersions can contain high concentrations of exfoliated graphene that are stable for several months.
- George Bepete
- , Eric Anglaret
- & Carlos Drummond
-
Article |
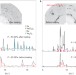 Synthesis and stability of xenon oxides Xe2O5 and Xe3O2 under pressure
Synthesis and stability of xenon oxides Xe2O5 and Xe3O2 under pressure
The reactivity of the noble gases—a notoriously inert group—at high pressures is intriguing. Now, two xenon oxides with unusual stoichiometries, Xe2O5 and Xe3O2, have been synthesized above 78 GPa and predicted to be stable above 50 GPa, indicating that xenon is more reactive than previously thought.
- Agnès Dewaele
- , Nicholas Worth
- & Tetsuo Irifune
-
Correspondence |
Entropic factors also contribute to the high melting points of polyhedral alkanes
- Andrew D. Bond
-
Commentary |
 Beyond Hofmeister
Beyond Hofmeister
Research efforts related to the Hofmeister series of salt ions have waxed and waned during its long and storied history. The past few decades have, however, witnessed a renaissance in its study, and the importance of the related solvation science is becoming ever more apparent.
- Pavel Jungwirth
- & Paul S. Cremer
-
Article |
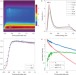 The energy barrier in singlet fission can be overcome through coherent coupling and entropic gain
The energy barrier in singlet fission can be overcome through coherent coupling and entropic gain
Better understanding of the mechanisms of singlet fission may facilitate its implementation in solar cells, improving their efficiency. Although singlet fission in tetracene is endothermic, it is now observed not to be thermally activated; rather a quantum coherent process allows access to the higher-energy multi-exciton state, which then forms two triplet excitons through an entropic driving force.
- Wai-Lun Chan
- , Manuel Ligges
- & X-Y. Zhu
-
News & Views |
 Robust sequence discrimination
Robust sequence discrimination
Careful consideration of thermodynamics has allowed the design of nucleic acid probes that are highly specific and virtually unaffected by changes in reaction conditions.
- Grégoire Altan-Bonnet
- & Fred Russell Kramer
-
News & Views |
 Are native proteins metastable?
Are native proteins metastable?
Thermodynamic measurements show that the most stable structural form of a number of proteins under cellular conditions is fibrillar, implying that their functional states may only be metastable.
- D. Thirumalai
- & G. Reddy
-
-
News & Views |
 Under water's influence
Under water's influence
Hydration is known to affect molecular-recognition processes, such as those between proteins and ligands. Now, theoretical simulations provide thermodynamic insight into cavity–ligand binding, revealing how it is predominantly driven by the behaviour of the few surrounding water molecules.
- Gerhard Hummer
-
Research Highlights |
 Jumping crystals
Jumping crystals
Energetic phase transitions that cause whole crystals to move have been studied at the molecular level.
- Neil Withers
-
Article |
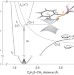 Experimental probing of conical intersection dynamics in the photodissociation of thioanisole
Experimental probing of conical intersection dynamics in the photodissociation of thioanisole
Direct experimental probing of conical intersections is rare but here, in studies of the photodissociation of thioanisole, a striking dependence of the non-adiabatic transition probability on photoexcitation energy has been observed, revealing the nuclear configuration of the conical intersection and its dynamic role in such transitions.
- Jeong Sik Lim
- & Sang Kyu Kim
-
Article |
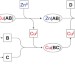 Cascading transformations within a dynamic self-assembled system
Cascading transformations within a dynamic self-assembled system
The addition of a single chemical signal can trigger multiple disassembly–reassembly events in a dynamic self-assembling system that is based on the formation and exchange of both imine and metal–ligand bonds. Different metal-helicate superstructures are either created or destroyed in response to the signal as the system seeks thermodynamic equilibrium following perturbation.
- Victoria E. Campbell
- , Xavier de Hatten
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article |
 Binding energies, lifetimes and implications of bulk and interface solvated electrons in water
Binding energies, lifetimes and implications of bulk and interface solvated electrons in water
The existence of solvated electrons bound at the liquid/water surface has not, until now, been proved experimentally. Here, using ultrafast photoelectron spectroscopy, the existence, vertical binding energies and lifetimes of solvated electrons bound at the water-surface/vacuum interface, and in bulk solution, have been revealed.
- Katrin R. Siefermann
- , Yaxing Liu
- & Bernd Abel

 Expanding the molecular language of protein liquid–liquid phase separation
Expanding the molecular language of protein liquid–liquid phase separation Deconvoluting double layers
Deconvoluting double layers