Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cascade surface modification of colloidal quantum dot inks enables efficient bulk homojunction photovoltaics
Cascade surface modification of colloidal quantum dot inks enables efficient bulk homojunction photovoltaics
It is challenging to realize doping and surface passivation simultaneously in colloidal quantum dot inks. Here Choi et al. employ a cascade surface modification approach to solve the problem and obtain record high efficiency of 13.3% for bulk homojunction solar cells based on these inks.
- Min-Jae Choi
- , F. Pelayo García de Arquer
- & Edward. H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional nanoframes with dual rims
Two-dimensional nanoframes with dual rims
The synthesis of anisotropic nanoparticles with structural diversity and complexity in a rational and systematic fashion is rare. Here, the authors demonstrate a rational and stepwise synthetic strategy for nanoplates with a high degree of intricacy, leading to a gallery of shapes such as rings, triangles, hexagons, and tripods, with tailorable single or double frames.
- Sungjae Yoo
- , Jeongwon Kim
- & Sungho Park
-
Article
| Open Access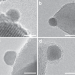 Ultrastable Au nanoparticles on titania through an encapsulation strategy under oxidative atmosphere
Ultrastable Au nanoparticles on titania through an encapsulation strategy under oxidative atmosphere
Sintering-resistant Au nanoparticles are highly desirable due to their low Tammann temperature. Here, the authors report an ultrastable titania-supported Au nanocatalyst through an encapsulation strategy under oxidative atmosphere.
- Shaofeng Liu
- , Wei Xu
- & Junhu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional flexible membranes from sponge-like porous carbon nanofibers with high conductivity
Multifunctional flexible membranes from sponge-like porous carbon nanofibers with high conductivity
Conductive porous carbons are promising for a variety of applications, but simultaneously tuning porosity and conductivity is challenging. Here, the authors develop a green method to fabricate flexible boron-nitrogen-fluorine triply doped carbon nanofibers with high porosity and conductivity.
- Jianhua Yan
- , Keqi Dong
- & Bin Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Self-organized twist-heterostructures via aligned van der Waals epitaxy and solid-state transformations
Self-organized twist-heterostructures via aligned van der Waals epitaxy and solid-state transformations
Vertically stacked twisted layers of two-dimensional materials can trigger exciting fundamental physics. Here, authors report controlled growth of 30° twisted few-layer SnS2 over SnS2 via van der Waals epitaxy of an SnS intermediate and its transformation in the presence of excess sulfur.
- Peter Sutter
- , Rina Ibragimova
- & Eli Sutter
-
Article
| Open Access In situ formation of mononuclear complexes by reaction-induced atomic dispersion of supported noble metal nanoparticles
In situ formation of mononuclear complexes by reaction-induced atomic dispersion of supported noble metal nanoparticles
Supported noble metal nanoclusters and single-metal-sites catalysts are inclined to aggregate into particles. Here, the authors report a general method with CO and CH3I to disperse the metal nanoparticles of Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Ir and Pt completely into single atoms with loading up to 5 wt%.
- Siquan Feng
- , Xiangen Song
- & Yunjie Ding
-
Article
| Open Access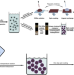 Room-temperature direct synthesis of semi-conductive PbS nanocrystal inks for optoelectronic applications
Room-temperature direct synthesis of semi-conductive PbS nanocrystal inks for optoelectronic applications
Providing large-scale iodide capped semi-conductive PbS nanocrystals inks preparation for high-throughput manufacturing remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a direct one step and scalable synthesis method enabling cost reduction and promoting its commercial viability for solar cells.
- Yongjie Wang
- , Zeke Liu
- & Wanli Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Vapour-phase-transport rearrangement technique for the synthesis of new zeolites
Vapour-phase-transport rearrangement technique for the synthesis of new zeolites
Assembly-Disassembly-Organization-Reassembly (ADOR) is a valuable method to prepare zeolites of predictable topologies, but has yet to be successfully applied on open framework zeolites. Here, the authors show that non-contact vapour-phase-transport rearrangement allows access to new zeolite topologies from open framework zeolites.
- Valeryia Kasneryk
- , Mariya Shamzhy
- & Maksym Opanasenko
-
Article
| Open Access Microdroplet-guided intercalation and deterministic delamination towards intelligent rolling origami
Microdroplet-guided intercalation and deterministic delamination towards intelligent rolling origami
Rolling microstructures have great potential among optics and micromechanics but on-demand construction with versatile materials remains challenging. Here Xu et al. precisely construct 3D rolling microstructures by liquid-triggered delamination in predictable manner and demonstrate their applications.
- Borui Xu
- , Xinyuan Zhang
- & Yongfeng Mei
-
Article
| Open Access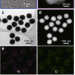 Single- and multi-component chiral supraparticles as modular enantioselective catalysts
Single- and multi-component chiral supraparticles as modular enantioselective catalysts
Nanoscale biological assemblies play crucial roles in all living systems and display a variety of chemical functionalities. Here the authors show that it is possible to replicate some of the biochemical functions in similarly-sized assemblies made from inorganic nanoparticles.
- Si Li
- , Juan Liu
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Article
| Open Access Rate-selected growth of ultrapure semiconducting carbon nanotube arrays
Rate-selected growth of ultrapure semiconducting carbon nanotube arrays
Carbon nanotubes are considered promising materials for microelectronics, but it is challenging to separate semiconducting tubes from their metallic counterparts. Here, the authors report a self-purification growth process that allows them to obtain long, highly pure semiconducting carbon nanotubes.
- Zhenxing Zhu
- , Nan Wei
- & Fei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled release of hydrogen isotope compounds and tunneling effect in the heterogeneously-catalyzed formic acid dehydrogenation
Controlled release of hydrogen isotope compounds and tunneling effect in the heterogeneously-catalyzed formic acid dehydrogenation
Hydrogen isotope compounds are useful in fine chemical production, but the natural abundance of these gases is low and the techniques used for producing D2 are expensive and energy intensive. Here, the authors develop a nanocatalyst that promotes selective production of D2 and HD from the inexpensive starting material formic acid in the presence of D2O.
- Kohsuke Mori
- , Yuya Futamura
- & Hiromi Yamashita
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating the coordination structure of single-atom Fe-NxCy catalytic sites for benzene oxidation
Regulating the coordination structure of single-atom Fe-NxCy catalytic sites for benzene oxidation
Atomically dispersed metal-N-C are efficient active site for benzene oxidation but the roles of N and C atoms are still unclear. Here the authors report a highly-active single-atom Fe-based benzene oxidation catalyst and provide deep insights into the structure-activity relationship at atomic level.
- Yuan Pan
- , Yinjuan Chen
- & Chen Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable assembly of truncated nanocubes by evaporation-driven poor-solvent enrichment
Tunable assembly of truncated nanocubes by evaporation-driven poor-solvent enrichment
Versatile methods that can predictably assemble nanocrystals into large, well-ordered superlattices are rare. Here, the authors develop such a method–evaporation-driven poor-solvent enrichment–and rigorously determine the effect of various experimental parameters on the size, morphology, and mesoscopic order of the superlattices, giving the approach high predictive power.
- Zhong-Peng Lv
- , Martin Kapuscinski
- & Lennart Bergström
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient decomposition of ammonia using high-entropy alloy catalysts
Highly efficient decomposition of ammonia using high-entropy alloy catalysts
Alloys are important materials for catalysis but are usually limited by miscibility gaps present in their phase diagrams. Here the authors break this limitation by developing high-entropy alloy catalysts made of five earth-abundant elements and demonstrate great catalytic enhancements for ammonia decomposition.
- Pengfei Xie
- , Yonggang Yao
- & Chao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-confined crystallization of organic ultrathin nanostructure arrays with programmable geometries
Nano-confined crystallization of organic ultrathin nanostructure arrays with programmable geometries
Fabrication of ultrathin organic semiconductor nanostructures with precise alignment, tuneable morphology and high crystallinity remains challenging. Here the authors use an assembly technique with dewetting process controllability for patterning organic single-crystal arrays in a sub-hundred nanometer space.
- Hanfei Gao
- , Yuchen Qiu
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-non-solvent rapid-injection for preparing nanostructured materials from micelles to hydrogels
Solvent-non-solvent rapid-injection for preparing nanostructured materials from micelles to hydrogels
ABA triblock copolymer self-assembly has been focussed on equilibrium nanostructures, while little is known on the guiding principles of nanostructure formation during non-equilibrium processing conditions. Here the authors show how to control ABA triblock copolymer hierarchical structures using solvent-non-solvent rapid-injection processing.
- Chao Lang
- , Jacob A. LaNasa
- & Robert J. Hickey
-
Article
| Open Access Directly transforming copper (I) oxide bulk into isolated single-atom copper sites catalyst through gas-transport approach
Directly transforming copper (I) oxide bulk into isolated single-atom copper sites catalyst through gas-transport approach
Single-atom catalysts attract lots of attention, but direct transformation of bulk metal oxide into single atoms remains challenging. Here the authors report a gas-transport route to transform monolithic copper (I) oxide into copper single-atoms catalyst with a high activity for oxygen reduction.
- Zhengkun Yang
- , Bingxu Chen
- & Yuen Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature superionic-phase nanocrystals synthesized with a twinned lattice
Room-temperature superionic-phase nanocrystals synthesized with a twinned lattice
The ability to control the internal domain structure of a nanocrystal represents a new direction in nanomaterials design. Here, the authors develop a method to controllably introduce twin boundaries in cuprous sulfide nanocrystals, and find that twinning stabilizes these nanocrystals in the superionic phase well below room temperature.
- Jianxiao Gong
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access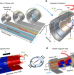 Magnetic origami creates high performance micro devices
Magnetic origami creates high performance micro devices
Despite the potential of self-assembly strategies for fabricating 3D micro-electronic devices, technological limitations prohibit widespread industrial adoption. Here, the authors report the magnetic field-assisted Origami-based assembly of high-performance devices with high yield.
- Felix Gabler
- , Dmitriy D. Karnaushenko
- & Oliver G. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access A universal approach for the synthesis of two-dimensional binary compounds
A universal approach for the synthesis of two-dimensional binary compounds
The scalable synthesis of 2D materials critically relies on finding appropriate vapour-phase metal precursors and careful fine-tuning of growth parameters. Here, the authors instead use solid elemental precursors and a single recipe to demonstrate a general approach for synthesising thin epitaxial layers of 20 different 2D binary compounds, including transition metal sulphides, selenides, tellurides, and nitrides.
- Abhay Shivayogimath
- , Joachim Dahl Thomsen
- & Timothy J. Booth
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual 4H-phase twinned noble metal nanokites
Unusual 4H-phase twinned noble metal nanokites
Twinning is a powerful approach to engineering the physicochemical properties of metallic nanomaterials. Here, the authors discover unusual non-close-packed twinning planes in 4H-phase gold nanokites and show that they can be used as templates to grow 4H-phase twinned nanostructures of other noble metals.
- Wenxin Niu
- , Jiawei Liu
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Interface-mediated Kirkendall effect and nanoscale void migration in bimetallic nanoparticles during interdiffusion
Interface-mediated Kirkendall effect and nanoscale void migration in bimetallic nanoparticles during interdiffusion
At elevated temperatures, bimetallic nanomaterials often change their composition and morphology due to the interdiffusion of atomic species, which can affect their properties. Here, the authors use in situ transmission electron microscopy to provide new insights into the Kirkendall effect and void motion in core-shell nanoparticles of Au and Pd.
- See Wee Chee
- , Zicong Marvin Wong
- & Utkur Mirsaidov
-
Article
| Open Access Embedding laser generated nanocrystals in BiVO4 photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting
Embedding laser generated nanocrystals in BiVO4 photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting
While photoelectrochemical water splitting offers a low-cost, integrated means to generate fuel from light, poor charge carrier transport limits performances. Here, authors embed laser-synthesized colloids in bismuth vanadate photoanodes to boost charge carrier mobilities and enhance photocurrents.
- Jie Jian
- , Youxun Xu
- & Hongqiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High gas barrier coating using non-toxic nanosheet dispersions for flexible food packaging film
High gas barrier coating using non-toxic nanosheet dispersions for flexible food packaging film
Food packaging industry is in search of non-toxic, stable, and recyclable coatings acting as gas-barriers. Here the authors synthesise transparent films meeting these requirements, based on high aspect ratio layered double hydroxide nanosheets obtained by exfoliation in aqueous amino acid solution.
- Jingfang Yu
- , Kanittika Ruengkajorn
- & Dermot O’Hare
-
Article
| Open Access Layer-by-layer self-assembly of pillared two-dimensional multilayers
Layer-by-layer self-assembly of pillared two-dimensional multilayers
Layer-by-layer self-assembly method using small molecules holds promise to precisely combine atomically thin materials and enable fabrication of pillared structures with superior device performance. Here, the authors report controlled synthesis of supercapacitor electrodes based on 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene multilayers with a volumetric capacitance of 583 F/cm3.
- Weiqian Tian
- , Armin VahidMohammadi
- & Mahiar M. Hamedi
-
Article
| Open Access Scaling growth rates for perovskite oxide virtual substrates on silicon
Scaling growth rates for perovskite oxide virtual substrates on silicon
A scalable method for the growth of perovskite oxides thin films on silicon is desirable for integration of buffer layers in devices. Here the authors demonstrate the stoichiometric growth of thin SrTiO3 layers on silicon at high growth rates by hybrid molecular beam epitaxy.
- Jason Lapano
- , Matthew Brahlek
- & Roman Engel-Herbert
-
Comment
| Open Access Paving the path to the future of carbogenic nanodots
Paving the path to the future of carbogenic nanodots
Insufficient purification and incomplete characterization pose a serious problem for attributing photoluminescence properties to carbogenic nanodots, especially those synthesized by bottom-up approaches. Here, we provide a roadmap for the successful future of these nanodots.
- Navneet C. Verma
- , Aditya Yadav
- & Chayan K. Nandi
-
Article
| Open Access Covalent organic framework membranes through a mixed-dimensional assembly for molecular separations
Covalent organic framework membranes through a mixed-dimensional assembly for molecular separations
The fabrication of defect-free covalent organic framework (COF) membranes for the separation of small molecules is challenging. Here, the authors report robust COF membranes with precise molecular sieving through a mixed-dimensional assembly, exhibiting high performance for alcohol dehydration and salt rejection.
- Hao Yang
- , Leixin Yang
- & Zhongyi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-metal electrohydrodynamic redox 3D printing at the submicron scale
Multi-metal electrohydrodynamic redox 3D printing at the submicron scale
Inkfree multi-material printing is a common challenge in 3D printing. Here, the authors introduce electrohydrodynamic redox printing, a method that enables the deposition of multiple metals and their alloys with nanoscale resolution and thus the synthesis of materials with locally tuned properties.
- Alain Reiser
- , Marcus Lindén
- & Ralph Spolenak
-
Article
| Open Access Additive-free MXene inks and direct printing of micro-supercapacitors
Additive-free MXene inks and direct printing of micro-supercapacitors
Printing functional inks is attractive for applications in electrochemical energy storage and smart electronics, among others. Here the authors report highly concentrated, additive-free, aqueous and organic MXene-based inks that can be used for high-resolution extrusion and inkjet printing.
- Chuanfang (John) Zhang
- , Lorcan McKeon
- & Valeria Nicolosi
-
Article
| Open Access On demand synthesis of hollow fullerene nanostructures
On demand synthesis of hollow fullerene nanostructures
At nanoscale, it is synthetically very difficult to increase the structural complexity of hollow structures. Here, the authors use a stepwise liquid templating strategy to build, assemble, and interconnect fullerene hollow nanostructures, just like the synthetic freedom one could have with pottery.
- Fei Han
- , Ruoxu Wang
- & Hongyu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct electronetting of high-performance membranes based on self-assembled 2D nanoarchitectured networks
Direct electronetting of high-performance membranes based on self-assembled 2D nanoarchitectured networks
Nanofibrous networks are applied in environmental protection and electrical or bioengineering and experience a great demand, but the design of these functional materials is challenging. Here the authors demonstrate an electronetting technology for fabricating self-assembled nanonets from various materials.
- Shichao Zhang
- , Hui Liu
- & Bin Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable synthesis of ant-nest-like bulk porous silicon for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes
Scalable synthesis of ant-nest-like bulk porous silicon for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes
Silicon is a promising anode material for lithium-ion batteries but experiences large volume changes during cycling. Here the authors report a scalable method to synthesize porous ant-nest-like silicons. The unique structure of this anode solves the swelling problem and enables impressive performance.
- Weili An
- , Biao Gao
- & Kaifu Huo
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning infrared plasmon resonances in doped metal-oxide nanocrystals through cation-exchange reactions
Tuning infrared plasmon resonances in doped metal-oxide nanocrystals through cation-exchange reactions
Doping semiconductor nanocrystals with impurity atoms is a key pathway for tuning their plasmonic properties. Here, the authors use a cation exchange strategy to dope p-type or n-type metal ions into n-type metal-oxide nanocrystals, post-synthetically tailoring their localized surface plasmon resonances in the infrared region.
- Zeke Liu
- , Yaxu Zhong
- & Xingchen Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Conformal hexagonal-boron nitride dielectric interface for tungsten diselenide devices with improved mobility and thermal dissipation
Conformal hexagonal-boron nitride dielectric interface for tungsten diselenide devices with improved mobility and thermal dissipation
Plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD) is an industrially compatible microelectronics technology. Here, the authors use PECVD to obtain low-temperature, catalyst-free growth of poly-crystalline two-dimensional hexagonal-boron nitride, thus enabling superior thermal dissipation in WSe2 field-effect transistors with mobility up to 121 cm2 V−1 s−1.
- Donghua Liu
- , Xiaosong Chen
- & Dacheng Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Low temperature self-densification of high strength bulk hexagonal boron nitride
Low temperature self-densification of high strength bulk hexagonal boron nitride
Sintering hexagonal boron nitride until it is more than 96% dense remains a challenge. Here, the authors mix cubic boron nitride particles into hexagonal boron nitride flakes and sinter the combined powders to obtain dense hexagonal boron nitride ceramics with significantly increased strength.
- Haotian Yang
- , Hailiang Fang
- & Jianlin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental aspects to localize self-catalyzed III-V nanowires on silicon
Fundamental aspects to localize self-catalyzed III-V nanowires on silicon
The ability to place perfectly aligned vertical nanowires at chosen positions on a silicon substrate is an important challenge in device fabrication. Here, the authors propose a mechanism to explain self-catalyzed III-V nanowire growth on silicon, providing valuable insights for growing high yield nanowire arrays.
- J. Vukajlovic-Plestina
- , W. Kim
- & A. Fontcuberta i Morral
-
Article
| Open Access Composition change-driven texturing and doping in solution-processed SnSe thermoelectric thin films
Composition change-driven texturing and doping in solution-processed SnSe thermoelectric thin films
Despite significant efforts to improve the thermoelectric properties of polycrystalline SnSe, precise control of texturing and doping is a challenge. Here, the authors report hole doped and highly textured SnSe thin films prepared by low cost, scalable solution processing.
- Seung Hwae Heo
- , Seungki Jo
- & Jae Sung Son
-
Article
| Open Access Size-dependent stability of ultra-small α-/β-phase tin nanocrystals synthesized by microplasma
Size-dependent stability of ultra-small α-/β-phase tin nanocrystals synthesized by microplasma
Key features of tin, including electronic band structure and opto-electronic properties, are influenced by the crystal structure. Here the authors report a microplasma process for the synthesis of ultra-small tin nanocrystals in which the crystal structure is dependent on crystallite size.
- Atta Ul Haq
- , Sadegh Askari
- & Davide Mariotti
-
Article
| Open Access Transition metal dichalcogenides bilayer single crystals by reverse-flow chemical vapor epitaxy
Transition metal dichalcogenides bilayer single crystals by reverse-flow chemical vapor epitaxy
Epitaxial growth of the two-dimensionally thin material flakes with effective layer number and shape calls for precise control over temperature and carrier gas. Here, authors report controlled epitaxial growth of the second layer vertically for MoS2, WS2, MoWS and MoWSSe compounds by reverse hydrogen gas flow chemical vapor epitaxy.
- Xiumei Zhang
- , Haiyan Nan
- & Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov
-
Article
| Open Access Unwinding a spiral of cellulose nanocrystals for stimuli-responsive stretchable optics
Unwinding a spiral of cellulose nanocrystals for stimuli-responsive stretchable optics
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) spontaneously organize into a helical arrangement but flexible CNC elastomer composite materials with this structure were so far not realized. Here the authors demonstrate the fabrication of a CNC based elastomer composite and its application as a photonic strain sensor.
- Osamu Kose
- , Andy Tran
- & Mark J. MacLachlan
-
Article
| Open Access Non defect-stabilized thermally stable single-atom catalyst
Non defect-stabilized thermally stable single-atom catalyst
Developing stable single-atom catalysts (SACs) with a high metal loading remains a challenge due to the difficulty of creating high densities of defects on support materials. Here the authors prepare Pt SACs with high Pt loadings by virtue of strong covalent metal-support interaction, rather than support defects.
- Rui Lang
- , Wei Xi
- & Tao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access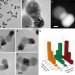 A welding phenomenon of dissimilar nanoparticles in dispersion
A welding phenomenon of dissimilar nanoparticles in dispersion
Solution-phase welding of nanoparticles to form larger structures typically requires that the particles are the same type, limiting the diversity of possible products. Here, the authors report a welding process between gold and chalcogenide nanoparticles in dispersion that leads to asymmetric hybrid nanoparticles with two distinct domains.
- Zhiqi Huang
- , Zhi-Jian Zhao
- & Zhihong Nie
-
Article
| Open Access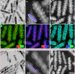 Strain-controlled shell morphology on quantum rods
Strain-controlled shell morphology on quantum rods
Core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals have advantageous optoelectronic properties, which depend on the shell architecture. Here the authors show that by reducing the growth rate of ZnS shells on ZnSe nanorods the shell morphology can be tuned from flat to islands-like to helical
- Botao Ji
- , Yossef E. Panfil
- & Uri Banin
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible and selective ion intercalation through the top surface of few-layer MoS2
Reversible and selective ion intercalation through the top surface of few-layer MoS2
Electrochemical ion intercalation in 2D layered materials is known to occur through the material’s edges, accompanied by frequent structural deformations. Here the authors show that in MoS2 flakes where the edges have been sealed, a reversible and ion-selective intercalation occurs through the top surface via the intrinsic defects.
- Jinsong Zhang
- , Ankun Yang
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic assembly of two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanostructures
Hydrodynamic assembly of two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanostructures
While liquid-phase synthesis of 2D materials presents opportunities for large-scale production, achieving precise control over product quality, size and morphology remains challenging. Here, the authors show that hydrodynamic manipulation of nanoparticle assembly enables control over crystallinity, size and aspect ratio.
- Nicholas A. Jose
- , Hua Chun Zeng
- & Alexei A. Lapkin
-
Article
| Open Access Water assisted biomimetic synergistic process and its application in water-jet rewritable paper
Water assisted biomimetic synergistic process and its application in water-jet rewritable paper
Water based inks used for water-jet rewritable paper (WJRP) are an environmental friendly alternative to conventional printing, but black colour in WJRP could not be realized so far. Here the authors demonstrate black as well as other colour WJRP based on binary systems containing less-sensitive acidochromic dyes and mild proton donors.
- Guan Xi
- , Lan Sheng
- & Sean Xiao-An Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Dehydrative π-extension to nanographenes with zig-zag edges
Dehydrative π-extension to nanographenes with zig-zag edges
Nanographenes with zig-zag peripheries are expected to have unique electronic properties, but their application in organic electronics has been curbed by their difficult synthesis. Here, the authors develop a facile route to zig-zag nanographenes based on a key dehydrative π-extension reaction.
- Dominik Lungerich
- , Olena Papaianina
- & Konstantin Amsharov

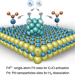 Titania supported synergistic palladium single atoms and nanoparticles for room temperature ketone and aldehydes hydrogenation
Titania supported synergistic palladium single atoms and nanoparticles for room temperature ketone and aldehydes hydrogenation