Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Charged and metallic molecular monolayers through surface-induced aromatic stabilization
Charged and metallic molecular monolayers through surface-induced aromatic stabilization
When monolayers of π-conjugated organic semiconductors interact with metal surfaces, most remain semiconducting. In some cases, however, the metallic character of the substrate is seen to extend onto the molecules. A mechanism for this intriguing phenomenon is now suggested and new strategies for chemical surface engineering are proposed.
- G. Heimel
- , S. Duhm
- & N. Koch
-
News & Views |
 Oxidation goes soft
Oxidation goes soft
Creating useful feedstocks from methane is impeded by over-oxidation when O2 is used as the oxidant. Now, gaseous sulfur has been shown to be a promising 'soft' oxidant for the selective conversion of methane to ethylene.
- Frerich J. Keil
-
News & Views |
 Two sides of the acid–base story
Two sides of the acid–base story
The ability of the water surface to donate or accept protons critically influences vital processes in chemistry and biology, but intense disagreement persists regarding this property. Researchers show new evidence that the air side of the air/water interface is more basic than the aqueous one.
- Richard J. Saykally
-
Article |
 Sulfur as a selective ‘soft’ oxidant for catalytic methane conversion probed by experiment and theory
Sulfur as a selective ‘soft’ oxidant for catalytic methane conversion probed by experiment and theory
The oxidation of methane to create useful feedstocks is hampered by over-oxidation when using O2. Now a process using gaseous sulfur as a ‘soft’ oxidant for selective conversion to ethylene over metal sulfide catalysts has been developed. Simulations show that both methane activation and ethylene selectivity is linearly correlated with catalyst metal-sulfur bond strength.
- Qingjun Zhu
- , Staci L. Wegener
- & Tobin J. Marks
-
Article |
 A quantitative model for the transcription of 2D patterns into functional 3D architectures
A quantitative model for the transcription of 2D patterns into functional 3D architectures
The self-sorting of molecular building blocks should allow 2D surface patterns to be transcribed into 3D functional materials. Here, a non-empirical approach to the templated synthesis of supramolecular architectures on surfaces is reported, starting with a theoretical model and followed by comprehensive experimental validation, including direct evidence for functional relevance of the produced materials.
- Edvinas Orentas
- , Marco Lista
- & Stefan Matile
-
News & Views |
 Electronic perturbations
Electronic perturbations
Oxide materials typically used as supports for the active metal nanoparticles of heterogeneous catalysts are known to influence catalytic activity through strong metal–support interactions. Researchers have now revealed electronic interactions between platinum and ceria that go well beyond known effects and lead to excellent catalytic activity.
- Charles T. Campbell
-
-
Review Article |
 The gold–sulfur interface at the nanoscale
The gold–sulfur interface at the nanoscale
Thiolate-protected gold surfaces and interfaces are archetypal systems in various fields of current research in nanoscience, materials science, inorganic chemistry and surface science. Examples include self-assembled monolayers of organic molecules on gold, passivated gold nanoclusters and molecule–gold junctions. This Review discusses recent experimental and theoretical breakthroughs that highlight common features of gold-sulfur bonding in these systems.
- Hannu Häkkinen
-
News & Views |
 Making the right connections
Making the right connections
How do you create a molecular circuit board? Covalently coupling different molecules in a sequential manner in surface-based nanostructures opens up new possibilities and hopes for molecular electronics.
- Neil R. Champness
-
Article |
 Controlling on-surface polymerization by hierarchical and substrate-directed growth
Controlling on-surface polymerization by hierarchical and substrate-directed growth
The bottom-up construction of covalently linked molecular architectures on surfaces has recently been demonstrated, but only rather simple structures can be obtained in such one-step connection processes. A sequential approach has now been used to induce the selective connection of molecules with a programmed reactivity, enabling network formation with high selectivity.
- L. Lafferentz
- , V. Eberhardt
- & L. Grill
-
-
Article |
 Broken symmetry and the variation of critical properties in the phase behaviour of supramolecular rhombus tilings
Broken symmetry and the variation of critical properties in the phase behaviour of supramolecular rhombus tilings
Assembling random networks on a surface is an intriguing — and potentially useful — phenomenon, but partial order is difficult to control. Researchers have now altered two-dimensional tetracarboxylic acid networks through only small chemical changes. This phase behaviour reveals that entropy, alongside energy, plays a crucial role in the order–disorder balance.
- Andrew Stannard
- , James C. Russell
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article |
 Ultrafast vibrational energy transfer at the water/air interface revealed by two-dimensional surface vibrational spectroscopy
Ultrafast vibrational energy transfer at the water/air interface revealed by two-dimensional surface vibrational spectroscopy
At water's surface, its network of hydrogen-bonds is abruptly interrupted, conferring distinct properties on interfacial water from bulk water. Understanding aqueous interfaces is essential for many environmental, technological and biophysical systems, and now the pathways and rates of energy transfer at the water/air interface are elucidated using a surface-specific ultrafast spectroscopic technique.
- Zhen Zhang
- , Lukasz Piatkowski
- & Mischa Bonn
-
News & Views |
 Feeling the strain
Feeling the strain
Characterizing electrochemical behaviour on the nanometre scale is fundamental to gaining complete insight into the working mechanisms of fuel cells. The application of a new scanning probe microscopy technique can now relate local surface structure to electrochemical activity at a resolution below 10 nm.
- Johannes A. A. W. Elemans
-
News & Views |
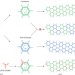 Intelligent design
Intelligent design
Achiral molecules have now been assembled into a homochiral porous network at a solid–liquid interface. This has implications for practical processes such as separations, but also for understanding how homochirality — crucial in biological systems — arose from achiral or racemic species.
- Leila M. Foroughi
- & Adam J. Matzger
-
Article |
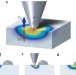 Measuring oxygen reduction/evolution reactions on the nanoscale
Measuring oxygen reduction/evolution reactions on the nanoscale
Optimizing oxygen-reduction and -evolution reactions is crucial for improving fuel cell efficiency, but the reaction is poorly understood at the nanoscopic level. Now, the oxygen activity of a platinum-functionalized surface has been mapped at below 10-nm resolution using electrochemical strain microscopy.
- Amit Kumar
- , Francesco Ciucci
- & Stephen Jesse
-
Article |
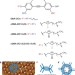 Control and induction of surface-confined homochiral porous molecular networks
Control and induction of surface-confined homochiral porous molecular networks
The generation of two-dimensional homochiral porous molecular networks at the liquid–solid interface is described. Using scanning tunnelling microscopy, the formation of homochiral porous networks was observed both from solutions of homochiral molecules and from solutions of achiral molecules in the presence of a small amount of a chiral modifier.
- Kazukuni Tahara
- , Hiroyuki Yamaga
- & Yoshito Tobe
-
Perspective |
 Exploring and exploiting chemistry at the cell surface
Exploring and exploiting chemistry at the cell surface
When cells interact with an artificial surface, the result is a rapidly evolving and complex interface. This Perspective discusses how expressing the properties of both the cell and the substrate in chemical terms can aid in future material design. We also explore the importance of using multifunctional surfaces with quantitative, dynamic capabilities.
- Morgan D. Mager
- , Vanessa LaPointe
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Perspective |
 Blueprinting macromolecular electronics
Blueprinting macromolecular electronics
The efficient engineering of nanostructures with semiconducting properties is vital to the development of organic electronics. This Perspective discusses a variety of techniques for fabricating such macromolecules, including graphene carving, the stimulus-induced synthesis of conjugated polymers and surface-assisted synthesis, and considers their potential for reproducing chemically and spatially precise molecular arrangements, that is 'molecular blueprints'.
- Carlos-Andres Palma
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article |
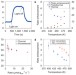 Visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation reactions on plasmonic silver nanostructures
Visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation reactions on plasmonic silver nanostructures
High operating temperatures in heterogeneous catalytic processes compromise energy efficiency, catalyst lifetime and product selectivity. Plasmonic silver nanoparticles are shown to couple thermal energy and a low-intensity photon flux to drive commercially important oxidation reactions at lower temperatures than conventional thermal processes.
- Phillip Christopher
- , Hongliang Xin
- & Suljo Linic
-
News & Views |
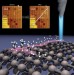 Molecular cart-wheeling
Molecular cart-wheeling
Energetic adsorption of molecules on surfaces is known to either trigger local chemical reactions or initiate the recoil of adsorbates away from the surface. Now, another possible outcome has been observed — the long-range 'cart-wheeling' of energetic molecules across a surface.
- Joseph W. Lyding
-
Article |
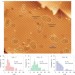 Directed long-range molecular migration energized by surface reaction
Directed long-range molecular migration energized by surface reaction
The recoil of adsorbates away from and towards surfaces is well-known. Here, long-range recoil in the plane of the surface, which leads to reaction at a distance, is described. Surface reactions are shown to propel their physisorbed ethylenic products across the rough surface of Si(100) by up to 200 Å before re-attachment.
- K. R. Harikumar
- , John C. Polanyi
- & Werner A. Hofer
-
News & Views |
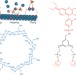 A hop, skip and jump
A hop, skip and jump
A model based on the well-known β-cyclodextrin–adamantane receptor–ligand pair has been used to obtain important insight into the kinetics of gradient-driven motion across a surface.
- W. Bruce Turnbull
-
News & Views |
 Closing the gap
Closing the gap
Photocatalysts such as titanium dioxide that use sunlight to split water and produce hydrogen would be a clean and sustainable solution to many problems, but their efficiency is currently too low to be widely used. Two approaches to engineer the surface properties of titanium dioxide offer hope that its efficiency can be increased.
- Ulrike Diebold
-
Perspective |
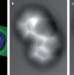 Recent advances in submolecular resolution with scanning probe microscopy
Recent advances in submolecular resolution with scanning probe microscopy
Recently, individual organic molecules have been imaged with atomic resolution using non-contact atomic force microscopy with functionalized tips and scanning tunnelling hydrogen microscopy. The resulting applications of these techniques and further improvements of ultra-high spatially resolved molecular investigations are discussed in this Perspective.
- Leo Gross
-
Article |
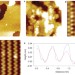 A two-dimensional phase of TiO2 with a reduced bandgap
A two-dimensional phase of TiO2 with a reduced bandgap
The ability of TiO2 photocatalysts to absorb solar light has so far been limited to the UV because of their large bandgap. Now, a surface phase of TiO2 that possess a narrower bandgap closely matching the visible light energy has been synthesized at the surface of pure rutile TiO2(011) faces.
- Junguang Tao
- , Tim Luttrell
- & Matthias Batzill
-
Article |
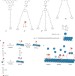 Gradient-driven motion of multivalent ligand molecules along a surface functionalized with multiple receptors
Gradient-driven motion of multivalent ligand molecules along a surface functionalized with multiple receptors
The kinetics of multivalent interactions at interfaces is poorly understood despite its fundamental importance for (bio)molecular motion and molecular recognition events at biological interfaces. Here, directional spreading of multivalent molecules has been observed, and multiple surface diffusion mechanisms have been identified and dubbed walking, hopping and flying.
- András Perl
- , Alberto Gomez-Casado
- & Jurriaan Huskens
-
News & Views |
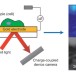 Waves in microscopy
Waves in microscopy
Advances in transduction of electrochemical activity through surface plasmon resonance afford new opportunities for spatially and temporally resolved studies of interfaces.
- Lane A. Baker
- & Chiao-Chen Chen
-
News & Views |
 From 2D to 3D
From 2D to 3D
The self-assembly of molecules into porous two-dimensional networks on surfaces has been well studied in recent years, but now the concept has been extended to three dimensions with a little help from fullerene molecules.
- Steven De Feyter
-
Article |
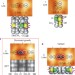 Surface-mediated chain reaction through dissociative attachment
Surface-mediated chain reaction through dissociative attachment
Chain-reactions could provide an alternative method for surface patterning. Now the chain reaction of CH3Cl molecules on a silicon surface has been observed to create lines that are made up of alternating CH3 groups and Cl atoms. The reactions are propagated through surface-mediated charge-transfer and have been studied using microscopy and ab initio theory.
- Tingbin Lim
- , John C. Polanyi
- & Wei Ji
-
Article |
 Guest-induced growth of a surface-based supramolecular bilayer
Guest-induced growth of a surface-based supramolecular bilayer
The self-assembly of planar molecules at interfaces can produce porous nanostructured surfaces that allow the selective trapping of guest molecules. By careful choice of both network and guest molecule it is possible to promote controlled, reversible growth perpendicular to the surface in the form of a molecular bilayer.
- Matthew O. Blunt
- , James C. Russell
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article |
 Surface-assisted cyclodehydrogenation provides a synthetic route towards easily processable and chemically tailored nanographenes
Surface-assisted cyclodehydrogenation provides a synthetic route towards easily processable and chemically tailored nanographenes
Large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons or nanographenes have huge potential for organic electronics applications, but it is challenging to synthesize them in a controlled way. Now, a surface chemical route has been used to produce tailored nanographenes with atomically precise control over the final structure.
- Matthias Treier
- , Carlo Antonio Pignedoli
- & Roman Fasel
-
Research Highlights |
Matters of size
Differences in nanoparticle surface energies account for varying phase stabilities on the nanoscale compared with bulk.
- Neil Withers
-
-
News & Views |
 Molecules under the microscope
Molecules under the microscope
A series of scanning probe microscopy experiments combined with density functional theory calculations have now been used to unambiguously determine the structure of a marine natural product. Can this method become generally useful for the determination of the structure of natural products?
- John W. Blunt
-
Research Highlights |
 Under a graphene cover
Under a graphene cover
Layers of water adsorbed on a mica surface have been trapped under a graphene sheet and their structure determined by atomic force microscopy.
- Anne Pichon
-
News & Views |
 Interface influence
Interface influence
The aggregation of proteins into fibrils plays a crucial role in neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease. Further insight into fibril formation has now been gained that reveals the effect of hydrophobic surfaces, including air.
- Ian W. Hamley
-
Research Highlights |
 Imaging interactions
Imaging interactions
The interactions between molecules on a surface have been directly imaged using scanning tunnelling microscopy.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Enhanced electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction based on patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide
Enhanced electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction based on patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide
The phosphoric acid fuel cell is limited by its slow rate of oxygen reduction at the cathode, but now an approach to the rational design of improved catalysts for this process has been developed. Molecular patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide adsorbates is used to block the adsorption of spectator anions without hindering oxygen reduction, thus improving catalytic activity.
- Dusan Strmcnik
- , María Escudero-Escribano
- & Nenad M. Marković
-
Article |
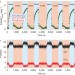 The role of steps in surface catalysis and reaction oscillations
The role of steps in surface catalysis and reaction oscillations
Steps are known to be important sites on the surface of heterogeneous catalysts. Now it is shown that the density of steps on a palladium surface can alter its stability, and thus reactivity, and is key to understanding the oscillatory behaviour of the CO oxidation reaction at atmospheric pressure.
- Bas L. M. Hendriksen
- , Marcelo D. Ackermann
- & Joost W. M. Frenken
-
Article |
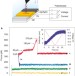 Electrically induced bonding of DNA to gold
Electrically induced bonding of DNA to gold
The assembly and evaluation of molecular structures on surfaces has been boosted by advances in single-molecule techniques. The development of such methods are continued here, showing that double-stranded DNA, bound to the tip of an atomic force microscope, can be deposited on the surface of a gold electrode using an electrical trigger.
- Matthias Erdmann
- , Ralf David
- & Hermann E. Gaub
-
Research Highlights |
 Petite patterns
Petite patterns
A heated AFM tip has been used to create nanoscale patterns of reduced graphene oxide.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Research Highlights |
 Disruptive influences
Disruptive influences
The structure of the interfacial water network near a hydrophobic surface is disrupted more by hydrophilic cations than hydrophobic ones.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
News & Views |
 Seeing both sides
Seeing both sides
To improve organic electronic devices, the principles underlying organic-film/metal-electrode interfaces must be understood. A comprehensive study of the organic electron acceptor TCNQ on a copper surface reveals a structural rearrangement of both the organic molecule and the metal surface atoms after charge transfer across the interface.
- Clara Santato
- & Federico Rosei
-
Article |
 Using first principles to predict bimetallic catalysts for the ammonia decomposition reaction
Using first principles to predict bimetallic catalysts for the ammonia decomposition reaction
The decomposition of ammonia is an important process if ammonia is to be used as a hydrogen storage medium. The most active catalyst for this is ruthenium, but its expense has provoked the search for alternatives. Now, using theory to guide the investigation, researchers have identified a bimetallic nickel–platinum surface as an active catalyst for this process.
- Danielle A. Hansgen
- , Dionisios G. Vlachos
- & Jingguang G. Chen
-
-
Article |
 Charge-transfer-induced structural rearrangements at both sides of organic/metal interfaces
Charge-transfer-induced structural rearrangements at both sides of organic/metal interfaces
Interfaces between organic molecules and metal surfaces have a key role in determining the performance of many emerging technologies. Now an intensive experimental study — supported by calculations — of tetracyano-p-quinodimethane molecules on a copper surface, reveals structural rearrangement of both the organic molecules and the surface atoms after charge transfer across the interface.
- Tzu-Chun Tseng
- , Christian Urban
- & Rodolfo Miranda
-
Research Highlights |
 Hot to trot
Hot to trot
The motion of a molecule on a hot surface is investigated using molecular dynamics, revealing a regime of fast rolling and vibrational excitation.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Research Highlights |
 Surface conversion
Surface conversion
The reversible conversion between guanine-based extended ribbons and macrocyclic G-quartets has been directly observed at a liquid–solid interface by scanning tunnelling microscopy.
- Anne Pichon

 Snub square tiling
Snub square tiling Panning for gold
Panning for gold One-way traffic
One-way traffic Imaging interactions
Imaging interactions Ice ice maybe
Ice ice maybe