Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of mitoribosomal small subunit biogenesis and preinitiation
Mechanism of mitoribosomal small subunit biogenesis and preinitiation
Structural analysis of several small mitoribosomal subunit intermediates reveals a sequential mechanism of biogenesis, and how assembly links to initiation to form active mitoribosomes.
- Yuzuru Itoh
- , Anas Khawaja
- & Alexey Amunts
-
Article |
 AKIRIN2 controls the nuclear import of proteasomes in vertebrates
AKIRIN2 controls the nuclear import of proteasomes in vertebrates
Using time-controlled CRISPR screens, the authors identify AKIRIN2 as a factor involved in the nuclear import of the proteasome.
- Melanie de Almeida
- , Matthias Hinterndorfer
- & Johannes Zuber
-
Article
| Open Access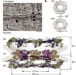 The cellular environment shapes the nuclear pore complex architecture
The cellular environment shapes the nuclear pore complex architecture
Structure of human nuclear pore complex in its cellular environment reveals a substantially dilated central channel and shows that its nucleoplasmic and cytoplasmic rings restrict channel dimensions and create membrane asymmetry at the inner ring.
- Anthony P. Schuller
- , Matthias Wojtynek
- & Thomas U. Schwartz
-
Article |
 Atomic-resolution protein structure determination by cryo-EM
Atomic-resolution protein structure determination by cryo-EM
Advances in electron cryo-microscopy allow the structure of apoferritin to be determined at a resolution that enables the visualization of individual atoms.
- Ka Man Yip
- , Niels Fischer
- & Holger Stark
-
Article |
 Structural basis for dimerization quality control
Structural basis for dimerization quality control
Structural studies of the dimerization quality control E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF–FBXL17 indicate that its selectivity for aberrant complex formation is based on recognizing both shape and complementarity of interacting domains.
- Elijah L. Mena
- , Predrag Jevtić
- & Michael Rape
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of the Frizzled 4 receptor in a ligand-free state
Crystal structure of the Frizzled 4 receptor in a ligand-free state
The crystal structure of the Frizzled 4 receptor transmembrane domain is reported to a resolution of 2.4 Å in a ligand-free state.
- Shifan Yang
- , Yiran Wu
- & Fei Xu
-
Article |
 Integrative structure and functional anatomy of a nuclear pore complex
Integrative structure and functional anatomy of a nuclear pore complex
The structure of the yeast nuclear pore complex, determined at sub-nanometre precision using an integrative approach that combines a wide range of data, reveals details of its architecture, transport mechanism and evolutionary origins.
- Seung Joong Kim
- , Javier Fernandez-Martinez
- & Michael P. Rout
-
Article |
 De novo phasing with X-ray laser reveals mosquito larvicide BinAB structure
De novo phasing with X-ray laser reveals mosquito larvicide BinAB structure
The structure of the bacterial toxin BinAB, which is used to combat mosquito-borne diseases, reveals pH-sensitive switches and carbohydrate-binding modules that may contribute to the larvicidal function of the toxin.
- Jacques-Philippe Colletier
- , Michael R. Sawaya
- & David S. Eisenberg
-
Letter |
 X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase
X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase
The crystal structure of mouse SCD1 bound to fatty acid stearoyl-CoA is solved at 2.6 Å resolution; the structure reveals a novel geometry for the dimetal centre, and the acyl chain of the bound fatty acid is shown to be shielded and shaped to a particular conformation by the enzyme, providing a structural basis for the selectivity of fatty acid metabolism.
- Yonghong Bai
- , Jason G. McCoy
- & Ming Zhou
-
Letter |
 hiCLIP reveals the in vivo atlas of mRNA secondary structures recognized by Staufen 1
hiCLIP reveals the in vivo atlas of mRNA secondary structures recognized by Staufen 1
A method, termed hiCLIP, has been developed to determine the RNA duplexes bound by RNA-binding proteins, revealing an unforeseen prevalence of long-range duplexes in 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), and a decreased incidence of SNPs in duplex-forming regions; the results also show that RNA structure is able to regulate gene expression.
- Yoichiro Sugimoto
- , Alessandra Vigilante
- & Jernej Ule
-
Letter |
 Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 Å resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses
Native structure of photosystem II at 1.95 Å resolution viewed by femtosecond X-ray pulses
The radiation-damage-free structure of the photosystem II membrane protein complex, which oxidizes water into dioxygen in an oxygen evolving complex, has been determined by an X-ray free electron laser at a resolution of 1.95 Å; one of the substrate oxygen atoms in this reaction is now identified.
- Michihiro Suga
- , Fusamichi Akita
- & Jian-Ren Shen
-
Obituary |
 David Sayre (1924–2012)
David Sayre (1924–2012)
Crystallographer who pioneered methods of X-ray imaging and modern computing.
- Janos Kirz
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Article |
 Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure
Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure
Microscopy reveals the dynamics of the type VI secretion system of Vibrio cholerae and its structural and functional resemblance to the contractile tail sheath of bacteriophages.
- M. Basler
- , M. Pilhofer
- & J. J. Mekalanos
-
Letter |
 Improved molecular replacement by density- and energy-guided protein structure optimization
Improved molecular replacement by density- and energy-guided protein structure optimization
- Frank DiMaio
- , Thomas C. Terwilliger
- & David Baker
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of the α6β6 holoenzyme of propionyl-coenzyme A carboxylase
Crystal structure of the α6β6 holoenzyme of propionyl-coenzyme A carboxylase
Propionyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (PCC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that is essential for the catabolism of several amino acids, cholesterol and some fatty acids. Here, the crystal structure of a bacterial PCC is presented, along with a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction showing a similar structure for human PCC. The structural information establishes a molecular basis for understanding the known disease-causing mutations in PCC, and is relevant to the holoenzymes of other biotin-dependent carboxylases.
- Christine S. Huang
- , Kianoush Sadre-Bazzaz
- & Liang Tong
-
Letter |
 Atom-by-atom structural and chemical analysis by annular dark-field electron microscopy
Atom-by-atom structural and chemical analysis by annular dark-field electron microscopy
An imaging technique that could identify all the individual atoms, including defects, in a material would be a useful tool. Here an electron-microscopy approach to the problem, based on annular dark-field imaging, is described. A monolayer of boron nitride was studied, and three types of atomic substitution were identified. Careful analysis of the data enabled the construction of a detailed map of the atomic structure.
- Ondrej L. Krivanek
- , Matthew F. Chisholm
- & Stephen J. Pennycook

 Structure of dynein–dynactin on microtubules shows tandem adaptor binding
Structure of dynein–dynactin on microtubules shows tandem adaptor binding