Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic reflection self-injection-locked microcombs
Synthetic reflection self-injection-locked microcombs
Photonic crystal microring resonators with a periodic corrugation inscribed along the resonator’s circumference allow programmable synthetic reflection for self-injection-locked microcombs and their operation exclusively in the single-soliton regime.
- Alexander E. Ulanov
- , Thibault Wildi
- & Tobias Herr
-
Obituary |
 A scientist and a poet
A scientist and a poet
Vladimir Zakharov was a man of a strong passion and grand intellect, who was equally and deservedly proud of both his scientific achievements and his poetry.
- G. E. Falkovich
- , E. A. Kuznetsov
- & S. K. Turitsyn
-
Perspective |
 The bright prospects of optical solitons after 50 years
The bright prospects of optical solitons after 50 years
Since the inception of the idea of temporal solitons in optical fibres, published in 1973, the concept of optical solitons has revolutionized the fundamental science of optics and photonics technologies. This Perspective gives an outlook on the future of solitons in ultrafast lasers, frequency combs, biomedical applications, telecommunications and signal processing, as well as the emerging new science of solitons.
- Andrea Blanco-Redondo
- , C. Martijn de Sterke
- & Sergei K. Turitsyn
-
Article |
 Ultrashort dissipative Raman solitons in Kerr resonators driven with phase-coherent optical pulses
Ultrashort dissipative Raman solitons in Kerr resonators driven with phase-coherent optical pulses
By exploiting the nonlinear Raman gain inherent in fused silica, short sub-100-fs dissipative Raman soliton pulses can be formed in fused-silica fibre resonators that are driven by electro-optically generated picosecond pulses.
- Zongda Li
- , Yiqing Xu
- & Miro Erkintalo
-
Article
| Open Access Surpassing the nonlinear conversion efficiency of soliton microcombs
Surpassing the nonlinear conversion efficiency of soliton microcombs
Researchers demonstrated coherent dissipative Kerr solitons with a conversion efficiency exceeding 50% and good line spacing stability. The results may facilitate practical implementation of a scalable integrated photonic architecture for energy-efficient applications.
- Óskar B. Helgason
- , Marcello Girardi
- & Victor Torres-Company
-
Article
| Open Access Soliton pulse pairs at multiple colours in normal dispersion microresonators
Soliton pulse pairs at multiple colours in normal dispersion microresonators
Bright solitons are produced through the interaction of pulse pairs generated via a continuous-wave fibre laser, which pumps two coupled microresonators featuring normal dispersion. Multicolour pulse pairs over multiple rings can also be generated, of great promise for applications such as all-optical soliton buffers and memories, study of quantum combs and topological photonics.
- Zhiquan Yuan
- , Maodong Gao
- & Kerry Vahala
-
Article |
 Tailoring microcombs with inverse-designed, meta-dispersion microresonators
Tailoring microcombs with inverse-designed, meta-dispersion microresonators
This work reports an inverse design approach that can spectrally shape Kerr microcombs by imprinting a nanophotonic dispersion filter to a microresonator to engineer solitonic frequency-comb states in the resonator with an optimization algorithm.
- Erwan Lucas
- , Su-Peng Yu
- & Scott B. Papp
-
Article |
 Photonic snake states in two-dimensional frequency combs
Photonic snake states in two-dimensional frequency combs
By tuning the spatial width, the strength and the frequency of a pump beam in two-dimensional cylindrical microcavities supporting stable, robust photonic snake states, a set of broadband and perfectly synchronized two-dimensional frequency combs can be realized.
- Salim B. Ivars
- , Yaroslav V. Kartashov
- & Carles Milián
-
Article |
 Petabit-per-second data transmission using a chip-scale microcomb ring resonator source
Petabit-per-second data transmission using a chip-scale microcomb ring resonator source
A microcomb source based on a silicon nitride ring resonator is shown to support petabit-per-second data transmission over a multicore optical fibre.
- A. A. Jørgensen
- , D. Kong
- & L. K. Oxenløwe
-
Article |
 Interaction and co-assembly of optical and topological solitons
Interaction and co-assembly of optical and topological solitons
Researchers demonstrate systems in which optical solitons coexist and interact with topological solitonic structures localized in the molecular alignment field of a soft birefringent medium. The findings could lead to solitonic tractor beams and new light–matter self-patterning phenomena.
- Guilhem Poy
- , Andrew J. Hess
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article |
 Temporal walk-off induced dissipative quadratic solitons
Temporal walk-off induced dissipative quadratic solitons
The formation of ultra-short dissipative quadratic solitons is realized using optical parametric amplification at low pump energies and in the presence of substantial temporal walk-off between the pump and signal.
- Arkadev Roy
- , Rajveer Nehra
- & Alireza Marandi
-
Article |
 Dissipative Kerr solitons in semiconductor ring lasers
Dissipative Kerr solitons in semiconductor ring lasers
A ring-cavity quantum cascade laser is demonstrated to generate soliton microcombs in the mid-infrared regime.
- Bo Meng
- , Matthew Singleton
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Article |
 Quantum optics of soliton microcombs
Quantum optics of soliton microcombs
The quantum aspect of soliton microcomb from an integrated silicon carbide microresonator is studied in several regimes — below threshold, above threshold and in the soliton regime — using a single-photon optical spectrum analyser for second-order photon correlation measurement.
- Melissa A. Guidry
- , Daniil M. Lukin
- & Jelena Vučković
-
Article |
 Parametrically driven Kerr cavity solitons
Parametrically driven Kerr cavity solitons
Parametric driving of Kerr solitons – cavity soliton excitation around twice the carrier frequency of solitons – in an optical parametric oscillator with competing nonlinearities look prone to extend the applications of Kerr resonators to random number generators and Ising machines.
- Nicolas Englebert
- , Francesco De Lucia
- & François Leo
-
Article |
 Temporal solitons in a coherently driven active resonator
Temporal solitons in a coherently driven active resonator
By adding a carefully designed amplification section in a passive resonator, but pumping it below the lasing threshold, ultra-stable high-power cavity solitons can be formed, effectively removing the important barrier of having to work in low-loss environments.
- Nicolas Englebert
- , Carlos Mas Arabí
- & François Leo
-
Article |
 Spontaneous pulse formation in edgeless photonic crystal resonators
Spontaneous pulse formation in edgeless photonic crystal resonators
Researchers have demonstrated spontaneous soliton formation in an edgeless photonic crystal resonator.
- Su-Peng Yu
- , Daniel C. Cole
- & Scott B. Papp
-
Article |
 Dissipative solitons in photonic molecules
Dissipative solitons in photonic molecules
When a laser is tuned across a split energy level, photonic diatomic molecules in two linearly coupled microresonators support the formation of self-enforcing solitary waves, featuring coherent, tunable and reproducible microcombs with up to ten times higher net conversion efficiency than the state of the art.
- Óskar B. Helgason
- , Francisco R. Arteaga-Sierra
- & Victor Torres-Company
-
News & Views |
 Exotic waves in multimode hollow-core fibres
Exotic waves in multimode hollow-core fibres
Unexpected multimode solitary waves can be formed spontaneously in hollow-core fibres, hinting at a vast world of exciting nonlinear optics, with applications for generating few-cycle, ultra-intense pulses.
- Logan G. Wright
- & Frank W. Wise
-
Article |
 High-energy multidimensional solitary states in hollow-core fibres
High-energy multidimensional solitary states in hollow-core fibres
The formation of multidimensional solitary states through the nonlinear propagation of high-energy pulses in a molecular gas-filled large-core hollow-core fibre is demonstrated, offering new opportunities for studying multimodal spatiotemporal dynamics in the high-energy regime.
- Reza Safaei
- , Guangyu Fan
- & François Légaré
-
Article |
 Pockels soliton microcomb
Pockels soliton microcomb
Photonic-chip-based microcomb solitons driven by Pockels nonlinearity—the quadratic χ(2) effect—instead of the Kerr soliton are demonstrated in an aluminium nitride microring resonator with a conversion efficiency of 17%.
- Alexander W. Bruch
- , Xianwen Liu
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Letter |
 Optical soliton formation controlled by angle twisting in photonic moiré lattices
Optical soliton formation controlled by angle twisting in photonic moiré lattices
Moiré lattices optically induced in photorefractive nonlinear media are used to explain the formation of optical solitons under different geometrical conditions controlled by the twisting angle between the constitutive sublattices.
- Qidong Fu
- , Peng Wang
- & Fangwei Ye
-
News & Views |
 Disordering a superfluid of light
Disordering a superfluid of light
A phase transition between disordered and quasi-ordered states, known as the Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless transition, has now been revealed in a two-dimensional photonic ‘fluid’. The interplay between phase singularities and coherence may lead to new vortex-based optical applications.
- Matthieu Bellec
- & Claire Michel
-
Letter |
 Thermal decoherence and laser cooling of Kerr microresonator solitons
Thermal decoherence and laser cooling of Kerr microresonator solitons
Observations of decoherence from thermodynamic noise in microresonator soliton frequency combs and laser cooling that reduces soliton thermal decoherence to far below the ambient-temperature limit are described, linking nonlinear photonics and microscopic fluctuations.
- Tara E. Drake
- , Jordan R. Stone
- & Scott B. Papp
-
Article |
 The pure-quartic soliton laser
The pure-quartic soliton laser
By suppressing the second- and third-order intracavity dispersion using an intracavity spectral pulse shaper, a mode-locked laser that emits pure-quartic soliton pulses that arise from the interaction of the fourth-order dispersion and the Kerr nonlinearity is demonstrated.
- Antoine F. J. Runge
- , Darren D. Hudson
- & Andrea Blanco-Redondo
-
Article |
 Photonic microwave generation in the X- and K-band using integrated soliton microcombs
Photonic microwave generation in the X- and K-band using integrated soliton microcombs
Nanophotonic microwave synthesizers in the X-band (10 GHz, for radar) and K-band (20 GHz, for 5G), based on integrated soliton microcombs driven by a low-noise fibre laser, link the fields of microwave photonics and integrated microcombs.
- Junqiu Liu
- , Erwan Lucas
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Letter |
 Resonant excitation and all-optical switching of femtosecond soliton molecules
Resonant excitation and all-optical switching of femtosecond soliton molecules
By driving ultrafast soliton molecules with an all-optical external perturbation and monitoring their response in real time, a form of spectroscopy of soliton molecules akin to optical spectroscopy of chemical bonds is introduced.
- F. Kurtz
- , C. Ropers
- & G. Herink
-
Comment |
 In memory of Mikhail Gorodetsky
In memory of Mikhail Gorodetsky
As a pioneer in the research on ultra-high-quality dielectric microresonators and their applications in nonlinear optics, frequency metrology and laser science, Mikhail Gorodetsky is badly missed.
- Igor Bilenko
- , Vladimir Ilchenko
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
News & Views |
 Striving for extreme solitons
Striving for extreme solitons
Judicious scaling of the waveguide properties of a simple hollow capillary fibre filled with helium allows for powerful pulse temporal compression down to the sub-femtosecond level, further enabling the efficient generation of ultrafast ultraviolet light.
- Benjamin Wetzel
- & Fetah Benabid
-
Article |
 Super-efficient temporal solitons in mutually coupled optical cavities
Super-efficient temporal solitons in mutually coupled optical cavities
Efficient power transfer from the pump to the soliton can be achieved through field coupling between two optical resonators, allowing soliton frequency comb generation with tens-to-hundreds-of-fold improvement in conversion efficiency compared with a traditional single-resonator comb.
- Xiaoxiao Xue
- , Xiaoping Zheng
- & Bingkun Zhou
-
Article |
 High-energy pulse self-compression and ultraviolet generation through soliton dynamics in hollow capillary fibres
High-energy pulse self-compression and ultraviolet generation through soliton dynamics in hollow capillary fibres
Optical soliton dynamics in large-core hollow capillary fibres is demonstrated. The findings enable the scaling of soliton effects by several orders of magnitude to the multi-millijoule energy and terawatt peak power levels, and open up opportunities for new-generation table-top light sources for ultrafast strong-field physics and advanced spectroscopy.
- John C. Travers
- , Teodora F. Grigorova
- & Federico Belli
-
Letter |
 Laser cavity-soliton microcombs
Laser cavity-soliton microcombs
By nesting a Kerr microresonator in a fibre loop with gain, 50-nm-wide bright microcavity-based soliton combs with a mode efficiency of 75% can be induced at average powers more than one order of magnitude lower than the Lugiato–Lefever soliton power threshold, facilitating real-world applications.
- Hualong Bao
- , Andrew Cooper
- & Alessia Pasquazi
-
Letter |
 Temporal solitons in free-space femtosecond enhancement cavities
Temporal solitons in free-space femtosecond enhancement cavities
Temporal dissipative soliton formation in a free-space femtosecond enhancement cavity with a thin Kerr medium is reported. Locking a 350-fs, 1,035-nm pulse train with a repetition rate of 100 MHz to this cavity-soliton state generates a 37-fs sech2-shaped pulse with a peak-power enhancement of 3,200.
- N. Lilienfein
- , C. Hofer
- & I. Pupeza
-
Letter |
 A microphotonic astrocomb
A microphotonic astrocomb
A microphotonic astrocomb is demonstrated via temporal dissipative Kerr solitons in photonic-chip-based silicon nitride microresonators with a precision of 25 cm s–1 (radial velocity equivalent), useful for Earth-like planet detection and cosmological research.
- Ewelina Obrzud
- , Monica Rainer
- & Tobias Herr
-
Letter |
 Searching for exoplanets using a microresonator astrocomb
Searching for exoplanets using a microresonator astrocomb
A soliton microcomb as an astronomical spectrograph calibrator is presented. It can ultimately have a footprint of a few cubic centimetres, and reduced weight and power consumption, attractive for precision radial velocity measurement.
- Myoung-Gyun Suh
- , Xu Yi
- & Kerry Vahala
-
-
-
News & Views |
 And then there were three
And then there were three
Spatial multiplexing enables the simultaneous generation of several low-noise frequency combs in a single microresonator, promising to enhance a host of applications such as multidimensional coherent spectroscopy.
- Miro Erkintalo
-
Article |
 Narrow-linewidth lasing and soliton Kerr microcombs with ordinary laser diodes
Narrow-linewidth lasing and soliton Kerr microcombs with ordinary laser diodes
A broadband multi-frequency Fabry–Pérot laser diode, when coupled to a high-Q microresonator, can be efficiently transformed to an ~100 mW narrow-linewidth single-frequency light source, and subsequently, to a coherent soliton Kerr comb oscillator.
- N. G. Pavlov
- , S. Koptyaev
- & M. L. Gorodetsky
-
Article |
 Spatial multiplexing of soliton microcombs
Spatial multiplexing of soliton microcombs
Up to three distinct frequency combs are simultaneously generated from an optical microresonator and a continuous-wave laser, enabling the deployment of dual- and triple-comb-based methods to applications unachievable by current technologies.
- E. Lucas
- , G. Lihachev
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 Mid-infrared frequency comb via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides
Mid-infrared frequency comb via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides
The direct generation of mid-infrared optical frequency combs in the region 2.5–4.0 μm from a 1.55-μm conventional and compact erbium-fibre-based femtosecond laser is demonstrated via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides.
- Hairun Guo
- , Clemens Herkommer
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
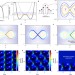 Fibre multi-wave mixing combs reveal the broken symmetry of Fermi–Pasta–Ulam recurrence
Fibre multi-wave mixing combs reveal the broken symmetry of Fermi–Pasta–Ulam recurrence
The Fermi–Pasta–Ulam recurrence process—the recovery of the initial state of a nonlinear system after a certain time—is observed for the first time in a low-loss optical fibre by building a multi-channel, vector optical-time-domain reflectometer.
- Arnaud Mussot
- , Corentin Naveau
- & Stefano Trillo
-
Article |
 Real-time full-field characterization of transient dissipative soliton dynamics in a mode-locked laser
Real-time full-field characterization of transient dissipative soliton dynamics in a mode-locked laser
The simultaneous use of dispersive Fourier transform and time-lens measurements allows complete characterization of the unstable spectral and temporal evolution of ultrashort dissipative solitons, providing further insight into ultrafast transient dynamics in optics.
- P. Ryczkowski
- , M. Närhi
- & J. M. Dudley
-
News & Views |
 Cavity solitons come of age
Cavity solitons come of age
The generation and manipulation of cavity solitons in microresonators is creating new opportunities for Kerr combs to aid applications such as optical communications and spectroscopy.
- Andrew M. Weiner
-
Article |
 Temporal solitons in microresonators driven by optical pulses
Temporal solitons in microresonators driven by optical pulses
By driving a high-Q fibre-based Fabry–Pérot microresonator with periodic, picosecond optical pulses, deterministic generation of stable femtosecond dissipative cavity solitons has been experimentally realized.
- Ewelina Obrzud
- , Steve Lecomte
- & Tobias Herr
-
Letter |
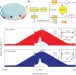 Counter-propagating solitons in microresonators
Counter-propagating solitons in microresonators
Counter-propagating solitons are generated in microresonator systems, producing dual-soliton frequency-comb streams with different repetition rates but high relative coherence useful for spectroscopy and laser ranging systems.
- Qi-Fan Yang
- , Xu Yi
- & Kerry Vahala
-
Review Article |
 Time stretch and its applications
Time stretch and its applications
Photonic time-stretch techniques and their applications are reviewed. The approach enables the observation of signals that are otherwise too short or rapid for conventional measurement.
- Ata Mahjoubfar
- , Dmitry V. Churkin
- & Bahram Jalali
-
-
Article |
 Polarization domain walls in optical fibres as topological bits for data transmission
Polarization domain walls in optical fibres as topological bits for data transmission
Localized polarization knots formed in conventional optical fibres are shown to be able to act as topological bits of information for optical data communication.
- M. Gilles
- , P.-Y. Bony
- & J. Fatome
-
Letter |
 All-optical bit storage in a fibre laser by optomechanically bound states of solitons
All-optical bit storage in a fibre laser by optomechanically bound states of solitons
Optomechanically coupled modes in a fibre laser cavity make it possible to generate and robustly store gigahertz-rate soliton sequences.
- M. Pang
- , W. He
- & P. St. J. Russell

 Parametrically driven pure-Kerr temporal solitons in a chip-integrated microcavity
Parametrically driven pure-Kerr temporal solitons in a chip-integrated microcavity Realizing 3D topological solitons
Realizing 3D topological solitons