News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
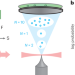 Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Photoemission experiments demonstrate that the photon number statistics of the exciting light can be imprinted on the emitted electrons, allowing the controlled generation of classical or non-classical electron number statistics of free electrons.
- Jonas Heimerl
- , Alexander Mikhaylov
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
News & Views |
 Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Even by shining classical light on a single opening, one can perform a double-slit experiment and discover a surprising variety of quantum mechanical multi-photon correlations — thanks to surface plasmon polaritons and photon-number-resolving detectors.
- Martijn Wubs
-
Article
| Open Access Cavity-mediated long-range interactions in levitated optomechanics
Cavity-mediated long-range interactions in levitated optomechanics
Combining multiparticle levitation with cavity control enables cavity-mediated interaction between levitated nanoparticles, whose strength can be tailored via optical detuning and position of the two particles.
- Jayadev Vijayan
- , Johannes Piotrowski
- & Lukas Novotny
-
Article |
 Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons
Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons
Most applications of surface plasmons are based on their near-field properties. These properties are now shown to be governed by nonclassical scattering between multiparticle plasmonic subsystems.
- Mingyuan Hong
- , Riley B. Dawkins
- & Omar S. Magaña-Loaiza
-
Article |
 Non-classical microwave–optical photon pair generation with a chip-scale transducer
Non-classical microwave–optical photon pair generation with a chip-scale transducer
A transducer that generates microwave–optical photon pairs is demonstrated. This could provide an interface between optical communication networks and superconducting quantum devices that operate at microwave frequencies.
- Srujan Meesala
- , Steven Wood
- & Oskar Painter
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Light passing through complex media is subject to scattering processes that mix together different photonic modes. This complexity can be harnessed to implement quantum operations.
- Suraj Goel
- , Saroch Leedumrongwatthanakun
- & Mehul Malik
-
Article |
 Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Quantum-correlated photons typically characterize strongly nonlinear quantum emitters. A two-photon correlation spectroscopy method now provides a powerful probe of weakly nonlinear many-body quantum systems.
- Lorenzo Scarpelli
- , Cyril Elouard
- & Thomas Volz
-
Article |
 Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for molecular vibronic spectra
Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for molecular vibronic spectra
It has been suggested that Gaussian boson sampling may provide a quantum computational advantage for calculating the vibronic spectra of molecules. Now, an equally efficient classical algorithm has been identified.
- Changhun Oh
- , Youngrong Lim
- & Liang Jiang
-
Article |
 A squeezed mechanical oscillator with millisecond quantum decoherence
A squeezed mechanical oscillator with millisecond quantum decoherence
Achieving low decoherence is challenging in hybrid quantum systems. A superconducting-circuit-based optomechanical platform realizes millisecond-scale quantum state lifetime, which allows tracking of the free evolution of a squeezed mechanical state.
- Amir Youssefi
- , Shingo Kono
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 High-harmonic generation driven by quantum light
High-harmonic generation driven by quantum light
High-harmonic generation is a source of high-frequency radiation and is typically driven by strong, but classical, laser fields. A theoretical study now shows that using quantum light states as the driver extends the spectrum of outgoing radiation in a controllable manner.
- Alexey Gorlach
- , Matan Even Tzur
- & Ido Kaminer
-
-
Article |
 A non-equilibrium superradiant phase transition in free space
A non-equilibrium superradiant phase transition in free space
Some driven systems sustain non-equilibrium phases in which phase transitions occur without symmetry breaking. The use of a laser-cooled atomic cloud confined in a pencil beam now allows the demonstration of such a system.
- Giovanni Ferioli
- , Antoine Glicenstein
- & Antoine Browaeys
-
Article |
 Spectral engineering of cavity-protected polaritons in an atomic ensemble
Spectral engineering of cavity-protected polaritons in an atomic ensemble
Engineering the frequency spectrum of systems of multiple quantum emitters is the key for many quantum technologies. A cavity quantum electrodynamics experiment now demonstrates the real-time frequency modulation of cavity-protected polaritons.
- Mohamed Baghdad
- , Pierre-Antoine Bourdel
- & Romain Long
-
Article |
 Experimental super-Heisenberg quantum metrology with indefinite gate order
Experimental super-Heisenberg quantum metrology with indefinite gate order
Normally, quantum operations are thought of as being applied in a particular order, but it is possible to create superpositions of different orders. An experiment now demonstrates this indefinite causal order may give an advantage for quantum sensing.
- Peng Yin
- , Xiaobin Zhao
- & Guang-Can Guo
-
Article |
 Simultaneous cavity cooling of all six degrees of freedom of a levitated nanoparticle
Simultaneous cavity cooling of all six degrees of freedom of a levitated nanoparticle
Optically trapped and levitated nanoparticles can be used to study macroscopic quantum effects, but fully controlling their motion is difficult. Now, all six roto-translational degrees of freedom have been cooled, although not to the quantum ground state.
- A. Pontin
- , H. Fu
- & P. F. Barker
-
Research Briefing |
 Observing the dynamics of photon bound states using a single quantum dot
Observing the dynamics of photon bound states using a single quantum dot
Photon bound states are quantum states of light that emerge in systems with ultrahigh optical non-linearities. A single artificial atom was used to study the dynamics of these states, revealing that the number of photons within the pulse determines the time delay after the pulse scatters off the atom.
-
Article
| Open Access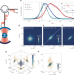 Photon bound state dynamics from a single artificial atom
Photon bound state dynamics from a single artificial atom
Measurements on a single artificial atom—a quantum dot—coupled to an optical cavity show scattering dynamics that depend on the number of photons involved in the light–matter interaction, which is a signature of stimulated emission.
- Natasha Tomm
- , Sahand Mahmoodian
- & Richard J. Warburton
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous ground-state cooling of two mechanical modes of a levitated nanoparticle
Simultaneous ground-state cooling of two mechanical modes of a levitated nanoparticle
A levitated nanoparticle in an optical cavity has been cooled to its motional ground state in two degrees of freedom at the same time. Control of the cavity properties also enabled the observation of the transition from 1D to 2D ground-state cooling.
- Johannes Piotrowski
- , Dominik Windey
- & Lukas Novotny
-
Article |
 Scalable and programmable phononic network with trapped ions
Scalable and programmable phononic network with trapped ions
The scalability of quantum information processing applications is generally hindered by loss and inefficient preparation and detection. A minimal loss network based on phonons has now been realized with trapped ions.
- Wentao Chen
- , Yao Lu
- & Kihwan Kim
-
Article |
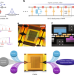 Broadband squeezed microwaves and amplification with a Josephson travelling-wave parametric amplifier
Broadband squeezed microwaves and amplification with a Josephson travelling-wave parametric amplifier
Parametric amplifiers are a key component in the operation and readout of superconducting quantum circuits. An improved travelling-wave amplifier design enables broadband squeezing and high-performance operation.
- Jack Y. Qiu
- , Arne Grimsmo
- & William D. Oliver
-
News & Views |
 Quantum correlated atoms in intense laser fields
Quantum correlated atoms in intense laser fields
Strongly laser-driven quantum correlated many-body systems lead to the generation of light with exotic quantum features — the quantumness of a many-body system is imprinted on the state of the emitted light.
- Paraskevas Tzallas
-
Article |
 Light emission from strongly driven many-body systems
Light emission from strongly driven many-body systems
Strongly driven light sources have become useful in many ways but are limited to classical emission. A quantum-optical theory now shows how non-classical states of light can be achieved from strongly-driven many-body systems, for example, non-coherent and correlated high-harmonic generation.
- Andrea Pizzi
- , Alexey Gorlach
- & Ido Kaminer
-
Article |
 Coherent backscattering of entangled photon pairs
Coherent backscattering of entangled photon pairs
Dynamic and disordered media destroy the correlations that underlie many quantum measurement protocols and applications. However, coherently backscattered photons can remain partially correlated due to interference between scattering trajectories.
- Mamoon Safadi
- , Ohad Lib
- & Yaron Bromberg
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear multi-frequency phonon lasers with active levitated optomechanics
Nonlinear multi-frequency phonon lasers with active levitated optomechanics
Sufficient optical gain provided by Yb3+ doping allows phonon lasing from a levitated optomechanical system at the microscale, which exhibits strong mechanical amplitudes and nonlinear mechanical harmonics above the lasing threshold.
- Tengfang Kuang
- , Ran Huang
- & Guangzong Xiao
-
Letter |
 Floquet engineering of strongly driven excitons in monolayer tungsten disulfide
Floquet engineering of strongly driven excitons in monolayer tungsten disulfide
The interaction of strong laser fields with tungsten disulfide leads to light-dressed Floquet replica of excitonic states, which manifest as new features in the transient absorption spectrum.
- Yuki Kobayashi
- , Christian Heide
- & Shambhu Ghimire
-
Article |
 On-demand directional microwave photon emission using waveguide quantum electrodynamics
On-demand directional microwave photon emission using waveguide quantum electrodynamics
Light could be used to carry quantum information in networks, but this requires methods to prepare and control individual photons. A superconducting circuit can controllably emit photons in either direction along a microwave waveguide.
- Bharath Kannan
- , Aziza Almanakly
- & William D. Oliver
-
News & Views |
 Not commuting around Hilbert space
Not commuting around Hilbert space
A clever experiment with a photonic circuit has realized three-dimensional non-Abelian quantum behaviour — introducing an experimental testbed for field and gauge theories.
- Andrew G. White
-
Editorial |
 Time for a different Nobel prediction
Time for a different Nobel prediction
The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded “for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science”, a long-anticipated topic for the prize.
-
Perspective |
 Quantum light in complex media and its applications
Quantum light in complex media and its applications
It is not immediately obvious whether photons retain the information they carry when they traverse a disordered or multimodal medium. This Perspective discusses the extent to which the quantum properties of light can be preserved and controlled.
- Ohad Lib
- & Yaron Bromberg
-
News & Views |
 Quantum underpinnings of an all-photonic switch
Quantum underpinnings of an all-photonic switch
All-optical devices hold promise as a platform for ultralow-power, sub-nanosecond photonic classical and quantum information processing. Measurements of the dynamics of a single photon switch unveil the quantum correlations at the root of its operation.
- Victoria A. Norman
- & Marina Radulaski
-
Letter |
 Dynamical photon–photon interaction mediated by a quantum emitter
Dynamical photon–photon interaction mediated by a quantum emitter
Efficient interactions between two photons is a challenging requirement for quantum information processing. A quantum dot coupled to a waveguide produces strong interactions that can induce photon correlations and reshape two-photon wavepackets.
- Hanna Le Jeannic
- , Alexey Tiranov
- & Peter Lodahl
-
News & Views |
 Good vibrations for quantum computing
Good vibrations for quantum computing
Quantum computing operations are realized using acoustic devices, paving the way for a new type of quantum processor.
- Amy Navarathna
- & Warwick P. Bowen
-
Article |
 Coherent control of a multi-qubit dark state in waveguide quantum electrodynamics
Coherent control of a multi-qubit dark state in waveguide quantum electrodynamics
Dark states of quantum systems do not absorb or emit light, removing a major source of decoherence. Four superconducting qubits in a waveguide can be combined to make a coherently controlled dark-state qubit with a long lifetime.
- Maximilian Zanner
- , Tuure Orell
- & Gerhard Kirchmair
-
Article |
 Topological dissipation in a time-multiplexed photonic resonator network
Topological dissipation in a time-multiplexed photonic resonator network
Topological phenomena have mostly been studied in conservative systems. Experiments on optical resonator networks now show that topologically non-trivial characteristics can also emerge in dissipation.
- Christian Leefmans
- , Avik Dutt
- & Alireza Marandi
-
Article |
 Error correction of a logical grid state qubit by dissipative pumping
Error correction of a logical grid state qubit by dissipative pumping
Physical systems with continuous degrees of freedom can be used to implement quantum error correction codes. An autonomous correction protocol has now been used to extend the lifetime of a qubit encoded in the motion of a trapped ion.
- Brennan de Neeve
- , Thanh-Long Nguyen
- & Jonathan P. Home
-
Review Article |
 Optomechanics for quantum technologies
Optomechanics for quantum technologies
Interaction with light can be used to precisely control motional states. This Review surveys recent progress in the preparation of non-classical mechanical states and in the application of optomechanical platforms to specific tasks in quantum technology.
- Shabir Barzanjeh
- , André Xuereb
- & Eva M. Weig
-
News & Views |
 Mix and match
Mix and match
It has long been assumed that the quantum statistics of light are preserved when photons interact with plasmons. An analysis of the scattering process shows that this is not always the case, as light can mix and match different plasmonic pathways.
- Mark Tame
-
News & Views |
 Spins strain to see the light
Spins strain to see the light
Integrating quantum technology with existing telecom infrastructure is hampered by a mismatch in operating frequencies. An optomechanical resonator now offers a strain-mediated spin–photon interface for long-distance quantum networks.
- Lilian Childress
- & Jack Sankey
-
Article |
 Witnessing quantum correlations in a nuclear ensemble via an electron spin qubit
Witnessing quantum correlations in a nuclear ensemble via an electron spin qubit
Atoms in a semiconductor can have non-zero nuclear spins, creating a large ensemble with many quantum degrees of freedom. An electron spin coupled to the nuclei of a semiconductor quantum dot can witness the creation of entanglement within the ensemble.
- Dorian A. Gangloff
- , Leon Zaporski
- & Mete Atatüre
-
News & Views |
 A light imprint
A light imprint
In a study on high-harmonic generation from a dense atomic xenon gas, the strong-field light–matter interaction is shown to leave a quantum mechanical imprint on the incident light that escapes the semiclassical picture of strong-field physics.
- Thomas Fennel
-
Letter |
 Generation of optical Schrödinger cat states in intense laser–matter interactions
Generation of optical Schrödinger cat states in intense laser–matter interactions
Schrödinger cat states are observed in intense laser–atom interactions. These are a superposition of the initial state of the laser and the coherent state that results from the interaction between the light and atoms.
- M. Lewenstein
- , M. F. Ciappina
- & P. Tzallas
-
Letter |
 Vectorial polaritons in the quantum motion of a levitated nanosphere
Vectorial polaritons in the quantum motion of a levitated nanosphere
A levitated nanosphere that is strongly coupled to an optical cavity mode forms an optomechanical system with three degrees of freedom, which supports hybrid light–mechanical states of a vectorial nature.
- A. Ranfagni
- , P. Vezio
- & F. Marin
-
Article |
 Deterministic multi-mode gates on a scalable photonic quantum computing platform
Deterministic multi-mode gates on a scalable photonic quantum computing platform
Measurement-based quantum computing performs quantum gates on entangled states without difficult multi-qubit coherent dynamics. A set of gates sufficient for universal quantum computing has now been implemented on a programmable optical platform.
- Mikkel V. Larsen
- , Xueshi Guo
- & Ulrik L. Andersen
-
-
Article |
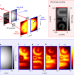 Polarization entanglement-enabled quantum holography
Polarization entanglement-enabled quantum holography
By exploiting polarization entanglement between photons, quantum holography can circumvent the need for first-order coherence that is vital to classical holography.
- Hugo Defienne
- , Bienvenu Ndagano
- & Daniele Faccio
-
-
-
News & Views |
 An odd couple
An odd couple
An atomic spin oscillator coupled to a mechanical membrane resonator forms an effective negative-mass oscillator. Entanglement in this hybrid quantum system is created by a backaction-evading position measurement, despite the macroscopic separation.
- Brian D’Urso
- & James Millen
-
Article |
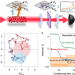 Entanglement between distant macroscopic mechanical and spin systems
Entanglement between distant macroscopic mechanical and spin systems
Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen entanglement between a millimetre-size mechanical membrane oscillator and a collective atomic spin oscillator formed by an ensemble of caesium atoms is achieved, although the two systems are spatially separated by one metre.
- Rodrigo A. Thomas
- , Michał Parniak
- & Eugene S. Polzik

 Electrons bunch up in quantum light
Electrons bunch up in quantum light Tweezers on repeat
Tweezers on repeat Detect, don’t destroy
Detect, don’t destroy Bigger is better
Bigger is better