News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Optical Coriolis force guides light along Trojan beams
Optical Coriolis force guides light along Trojan beams
Trojan beams, which are optical counterparts of Trojan asteroids that maintain stable orbits alongside planets, have been successfully showcased in experiments, opening up possibilities for transporting light in unconventional settings.
- Tomáš Tyc
- & Tomáš Čižmár
-
Article |
 Guiding Trojan light beams via Lagrange points
Guiding Trojan light beams via Lagrange points
Twisted structures are shown to confine and guide light without total internal reflection, using an effect analogous to the stable Lagrange points in celestial mechanics.
- Haokun Luo
- , Yunxuan Wei
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
-
Article
| Open Access Heating and cooling are fundamentally asymmetric and evolve along distinct pathways
Heating and cooling are fundamentally asymmetric and evolve along distinct pathways
Heating and cooling are shown to happen along distinct thermodynamic pathways, which makes the former faster than the latter. This finding calls for a rethink of the fundamentals of thermalization processes at the microscale and of devices like Brownian heat engines.
- M. Ibáñez
- , C. Dieball
- & R. A. Rica
-
Article |
 Size-dependent transition from steady contraction to waves in actomyosin networks with turnover
Size-dependent transition from steady contraction to waves in actomyosin networks with turnover
The behaviour of actomyosin networks with turnover emerges from the interplay between advection and percolation. The contraction pattern is shown to be size-dependent with continuous contraction in small droplets and periodic waves in larger systems.
- Ashwini Krishna
- , Mariya Savinov
- & Kinneret Keren
-
Matters Arising |
Reply to: Gauge non-invariance due to material truncation in ultrastrong-coupling quantum electrodynamics
- Omar Di Stefano
- , Alessio Settineri
- & Franco Nori
-
Matters Arising |
 Gauge non-invariance due to material truncation in ultrastrong-coupling quantum electrodynamics
Gauge non-invariance due to material truncation in ultrastrong-coupling quantum electrodynamics
- Adam Stokes
- & Ahsan Nazir
-
Comment |
 The tangled state of quantum hypothesis testing
The tangled state of quantum hypothesis testing
Quantum hypothesis testing—the task of distinguishing quantum states—enjoys surprisingly deep connections with the theory of entanglement. Recent findings have reopened the biggest questions in hypothesis testing and reversible entanglement manipulation.
- Mario Berta
- , Fernando G. S. L. Brandão
- & Marco Tomamichel
-
News & Views |
Graph theory captures hard-core exclusion
Physical networks, composed of nodes and links that occupy a spatial volume, are hard to study with conventional techniques. A meta-graph approach that elucidates the impact of physicality on network structure has now been introduced.
- Zoltán Toroczkai
-
Editorial |
Lost and found in translation
Many advances in biological physics result from multidisciplinary collaborations. We celebrate the physics of life with a collection of articles that offer insight into successful interactions between researchers from different fields.
-
News & Views |
 A long lifetime floating on neon
A long lifetime floating on neon
Electrons trapped above the surface of solid neon can be used to create qubits using spatial states with different charge distributions. These charge qubits combine direct electric field control with long coherence times.
- Atsushi Noguchi
-
World View |
 Strategies for multidisciplinary research
Strategies for multidisciplinary research
Invest in fostering a culture of collaboration to help break down barriers between disciplines.
- Teresa Sanchis
-
Comment |
 Life through the fluid dynamics lens
Life through the fluid dynamics lens
Fluid flows play a key part in living systems. Cross-disciplinary engagement between fluid physics and biology greatly benefits both fields.
- Kirsty Y. Wan
-
World View |
 The biological control of living systems calls for new laws of statistical mechanics
The biological control of living systems calls for new laws of statistical mechanics
Multidisciplinary residential programmes and workshops help advance all the fields involved.
- Tanniemola Liverpool
- & Tomohiro Sasamoto
-
News & Views |
 Stronger pairs with resonant excitation
Stronger pairs with resonant excitation
Understanding the mechanism underlying light-induced superconductivity could help manifest it at higher temperatures. Experiments now show that the excitation of a specific phonon leads to a resonant enhancement of this effect in K3C60.
- Jingdi Zhang
-
-
World View |
 How to bridge the gap between theory and experiments in biological physics
How to bridge the gap between theory and experiments in biological physics
Creating a common culture and language for successful collaboration across disciplines benefits both researchers and scientific discovery.
- Xavier Trepat
- & Ricard Alert
-
Article |
 Polygonal patterns of Faraday water waves analogous to collective excitations in Bose–Einstein condensates
Polygonal patterns of Faraday water waves analogous to collective excitations in Bose–Einstein condensates
Faraday waves are standing waves on the surface of a vibrating liquid. Large-wavelength polygonal Faraday waves are now observed in concave water containers, the dynamics of which bear resemblance to Faraday waves seen in Bose–Einstein condensates.
- Xinyun Liu
- & Xinlong Wang
-
Matters Arising |
Clarification of braiding statistics in Fabry–Perot interferometry
- Nicholas Read
- & Sankar Das Sarma
-
News & Views |
 When excitons crystallize
When excitons crystallize
Semiconducting dipolar excitons — bound states of electrons and holes — in artificial moiré lattices constitute a promising condensed matter system to explore the phase diagram of strongly interacting bosonic particles.
- Nadine Leisgang
-
-
-
Comment |
 Soviet influences on Kenneth Wilson’s renormalization group work
Soviet influences on Kenneth Wilson’s renormalization group work
Kenneth Wilson worked on the renormalization group during the Cold War, when communication between scientists in the Soviet Union and in the West was restricted. Nevertheless, Soviet physicists had a strong influence on Wilson’s work.
- P. Chandra
-
Comment |
 The renormalization group for non-equilibrium systems
The renormalization group for non-equilibrium systems
Historically, most renormalization group studies have been performed for equilibrium systems. Here, I give a personal reflection on the unexpected outcome of studying non-equilibrium flocking using renormalization methods.
- Yuhai Tu
-
News & Views |
 Electron spin finds a fresh excitation
Electron spin finds a fresh excitation
The Kondo effect — the screening of an impurity spin by conduction electrons — is a fundamental many-body effect. However, recent experiments combined with simulations have caused a long-standing model system for the single-atom Kondo effect to fail.
- Jörg Kröger
- & Takashi Uchihashi
-
-
Comment |
 Consequences of the renormalization group for perturbative quantum chromodynamics
Consequences of the renormalization group for perturbative quantum chromodynamics
The renormalization group is a key ingredient in methods of improving perturbative computations in particle physics. Here I briefly discuss its role in perturbative quantum chromodynamics and particularly the running of its coupling constant.
- Diogo Boito
-
Comment |
 Supersymmetric renormalization group flow
Supersymmetric renormalization group flow
Supersymmetric quantum field theories have special properties that make them easier to study. This Comment discusses how the constraints that supersymmetry places on renormalization group flows have been used to study strongly coupled field theories.
- Jaewon Song
-
Comment |
 The microscopic structure of quantum space-time and matter from a renormalization group perspective
The microscopic structure of quantum space-time and matter from a renormalization group perspective
The correct microscopic theory of quantum gravity may be an interacting, scale-invariant, ‘asymptotically safe’ model. This Comment discusses the renormalization group’s role in defining asymptotic safety and understanding its consequences.
- Astrid Eichhorn
-
Comment |
Rigorous renormalization group
The renormalization group evolved from ad hoc procedures to cope with divergences in perturbative calculations. This Comment summarizes efforts to develop a mathematically rigorous approach to renormalization group calculations.
- Antti Kupiainen
-
Comment |
 Fifty years of Wilsonian renormalization and counting
Fifty years of Wilsonian renormalization and counting
Renormalization began as a tool to eliminate divergences in quantum electrodynamics, but it is now the basis of our understanding of physics at different energy scales. Here, I review its evolution with an eye towards physics beyond the Wilsonian paradigm.
- Philip W. Phillips
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Time-resolved measurements show that coupling between electrons and phonons in lead halide perovskites can mediate attractive interactions between excitons, although the interaction strength depends on the specific material.
- Nuri Yazdani
- , Maryna I. Bodnarchuk
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Modulated Kondo screening along magnetic mirror twin boundaries in monolayer MoS2
Modulated Kondo screening along magnetic mirror twin boundaries in monolayer MoS2
Interactions between a localized magnetic moment and electrons in a metal can produce an emergent resonance that affects the metal’s properties. A realization of this Kondo effect in MoS2 provides an opportunity to study it in microscopic detail.
- Camiel van Efferen
- , Jeison Fischer
- & Wouter Jolie
-
News & Views |
 Rearranged under stress
Rearranged under stress
Permanent deformation in solids results from atoms not aligning with the external stress causing the deformation. Detecting such non-affine atomic rearrangements and connecting them to measurable mechanical effects is now shown to be feasible by means of high-energy X-ray diffraction.
- Saswati Ganguly
-
Research Briefing |
 A proximate model material for triangular lattice quantum spin liquids
A proximate model material for triangular lattice quantum spin liquids
Neutron spectroscopy, entanglement analysis, and simulations provide evidence that KYbSe2 closely approximates a 2D quantum spin liquid. Although KYbSe2 displays magnetic ordering at low temperatures, its magnetic dynamics are dominated by fractionalized excitations that exhibit anomalously large quantum entanglement, indicating that on finite timescales KYbSe2 exhibits quantum spin liquid physics.
-
Comment |
 Dependency of ERC-funded research on US collaborations
Dependency of ERC-funded research on US collaborations
Annually, the European Research Council (ERC) and the National Science Foundation (NSF) allocate resources to promote research excellence in Europe and the USA. We observe that European Union (EU)-based researchers rely strongly on United States (US) collaborations to secure top EU funding, while the reverse is much less common.
- Sandeep Chowdhary
- , Nicolò Defenu
- & Federico Battiston
-
Article |
 Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice
Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice
Interactions between excitons and correlated electrons can lead to the formation of interesting states. Now, evidence suggests that these interactions can give rise to a Mott insulator of excitons.
- Zhen Lian
- , Yuze Meng
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article |
 Proximate spin liquid and fractionalization in the triangular antiferromagnet KYbSe2
Proximate spin liquid and fractionalization in the triangular antiferromagnet KYbSe2
A detailed analysis of inelastic neutron scattering data, including the evaluation of entanglement witnesses used in quantum information theory, supports the proposal that the triangular-lattice antiferromagnet KYbSe2 is close to a spin-liquid phase.
- A. O. Scheie
- , E. A. Ghioldi
- & D. A. Tennant
-
Article |
 Impact of physicality on network structure
Impact of physicality on network structure
Physical networks are systems composed of physical entities, which conventional graph-based approaches fail to capture. Theoretical work now introduces a meta-graph technique to uncover the impact of physicality on the structure of networks.
- Márton Pósfai
- , Balázs Szegedy
- & Albert-László Barabási
-
News & Views |
 Anti-laser shows how to make waves behave
Anti-laser shows how to make waves behave
A decade ago, the anti-laser made waves as a new type of perfect absorber that functions as a one-way trap door for light. Experiments have now demonstrated the control of light without absorbing it.
- A. Douglas Stone
-
Article |
 Geometric description of clustering in directed networks
Geometric description of clustering in directed networks
Network geometry is an emerging framework used to describe several topological and organizational features of complex networks. Now this approach has been extended to directed networks, which contain both symmetric and asymmetric interactions.
- Antoine Allard
- , M. Ángeles Serrano
- & Marián Boguñá
-
Article |
 Laser ablation and fluid flows reveal the mechanism behind spindle and centrosome positioning
Laser ablation and fluid flows reveal the mechanism behind spindle and centrosome positioning
Cell division is governed by the positioning of a cytoskeletal structure called the spindle. Two methods, one based on laser ablation and the other on fluid flow assessments, are now shown to be useful tools for studying spindle positioning.
- Hai-Yin Wu
- , Gökberk Kabacaoğlu
- & Daniel J. Needleman
-
Article |
 Coherent control of chaotic optical microcavity with reflectionless scattering modes
Coherent control of chaotic optical microcavity with reflectionless scattering modes
Non-Hermitian physics enables dynamic control of optical behaviour in real time, such as reflectionless scattering modes, which have now been demonstrated in a chaotic photonic microcavity.
- Xuefeng Jiang
- , Shixiong Yin
- & Andrea Alù
-
News & Views |
 Phonon slowdown
Phonon slowdown
A detailed understanding of phonon transport is crucial for engineering the thermal properties of materials. A particular doping strategy is now shown to lead to good thermoelectric performance with low thermal conductivity.
- Zhilun Lu
-
Research Briefing |
 Mediated quasiparticle interactions observed in ultracold mixtures
Mediated quasiparticle interactions observed in ultracold mixtures
Landau’s theory of Fermi liquids predicts that impurities embedded in a Fermi sea of atoms form quasiparticles called polarons that interact with one another via the surrounding medium. Such mediated polaron–polaron interactions have been directly observed and are shown to depend on the quantum statistics of the impurities.
-
Article |
 Electron charge qubit with 0.1 millisecond coherence time
Electron charge qubit with 0.1 millisecond coherence time
Individual electrons trapped on the surface of solid neon can operate as charge qubits with very long coherence times.
- Xianjing Zhou
- , Xinhao Li
- & Dafei Jin
-
Article |
 Born effective charges and vibrational spectra in superconducting and bad conducting metals
Born effective charges and vibrational spectra in superconducting and bad conducting metals
A computational method capable of capturing the effects of electronic interactions and scattering can help interpret the vibrational reflectance measurements in superconducting and bad metals.
- Guglielmo Marchese
- , Francesco Macheda
- & Francesco Mauri
-
Article
| Open Access Mediated interactions between Fermi polarons and the role of impurity quantum statistics
Mediated interactions between Fermi polarons and the role of impurity quantum statistics
Polarons are quasi-particles formed by impurities together with induced excitations in a surrounding medium. Now, mediated interactions between polarons have been detected using atomic impurities embedded in a Fermi gas of ultracold atoms.
- Cosetta Baroni
- , Bo Huang
- & Georg M. Bruun
-
Article |
 Evidence for spinarons in Co adatoms
Evidence for spinarons in Co adatoms
Despite the theoretical prediction of spinaron quasiparticles in artificial nanostructures, experimental evidence has not yet been seen. Now it has been observed in a hybrid system comprising Co atoms on a Cu(111) surface.
- Felix Friedrich
- , Artem Odobesko
- & Matthias Bode
-
News & Views |
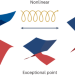 Topological phase transitions have never been faster
Topological phase transitions have never been faster
A nonlinear optical approach has now enabled picosecond control of a complex band structure, driving a non-Hermitian topological phase transition across an exceptional-point singularity.
- Jiangbin Gong
- & Ching Hua Lee

 Molecular motors make waves and sculpt patterns
Molecular motors make waves and sculpt patterns On the wings of a butterfly
On the wings of a butterfly The gravity of quantum thermalization
The gravity of quantum thermalization Gravity is attractive
Gravity is attractive Radiation for cooler cities
Radiation for cooler cities