Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible temperature regulation of electrical and thermal conductivity using liquid–solid phase transitions
Reversible temperature regulation of electrical and thermal conductivity using liquid–solid phase transitions
Temperature-controlled regulation of thermal conductivity is difficult to achieve because thermal properties do not change significantly through solid-state phase transitions. Here temperature control of thermal conductivities is demonstrated using liquid–solid phase transitions in a nanoparticle suspension.
- Ruiting Zheng
- , Jinwei Gao
- & Gang Chen
-
Article |
 Observation of atomic speckle and Hanbury Brown–Twiss correlations in guided matter waves
Observation of atomic speckle and Hanbury Brown–Twiss correlations in guided matter waves
Speckle patterns are a manifestation of decoherence and can result from two-particle interference. Here, the authors image atomic speckle for guided matter waves and link this to atom bunching in the second-order correlation function, suggesting potential use in squeezed-atom interferometry applications.
- R.G. Dall
- , S.S. Hodgman
- & A.G. Truscott
-
Article |
 Size and mechanics effects in surface-induced melting of nanoparticles
Size and mechanics effects in surface-induced melting of nanoparticles
Melting-related phenomena are of fundamental and applied interest, but the melting theory is poorly understood. Levitas and Samani develop an advanced phase-field theory of melting coupled to mechanics that resolves existing contradictions and reveals the features of melting phenomena.
- Valery I Levitas
- & Kamran Samani
-
Article |
 Plasmonic beaming and active control over fluorescent emission
Plasmonic beaming and active control over fluorescent emission
Nanometallic optical antennas can concentrate light into a deep-subwavelength volume for sensor and photovoltaic applications. Junet al. demonstrate an optical antenna design that achieves a high level of control over fluorescent emission for a wide range of nanoscale optical spectroscopy applications.
- Young Chul Jun
- , Kevin C.Y. Huang
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Fractal fronts of diffusion in microgravity
Fractal fronts of diffusion in microgravity
Theory and simulations predict scale-invariant concentration fluctuations during diffusion in liquids, but on Earth, large-scale fluctuations are damped by gravity. Microgravity experiments by Vailatiet al. reveal the scale-invariant nature of diffusion, associated with fractal fronts and long-ranged correlations.
- Alberto Vailati
- , Roberto Cerbino
- & Marzio Giglio
-
Article |
 A monolithically integrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera
A monolithically integrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera
Infrared cameras are used for night vision and in medical diagnostics, but currently only present monochrome images. Krishnaet al. demonstrate a monolithically intergrated plasmonic infrared quantum dot camera as a step towards coloured infrared imaging.
- Sang Jun Lee
- , Zahyun Ku
- & Sam Kyu Noh
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-engineered electron–hole exchange interaction controls exciton dynamics in core–shell semiconductor nanocrystals
Nano-engineered electron–hole exchange interaction controls exciton dynamics in core–shell semiconductor nanocrystals
Electron–hole exchange interaction is an intrinsic property of semiconductors, which affects their fine structure. Brovelliet al. demonstrate a nanoengineering-based approach that provides control over the exchange interaction energy at nearly constant emission energy, which cannot be carried out using core-only nanocrystals.
- S. Brovelli
- , R.D. Schaller
- & V.I. Klimov
-
Article
| Open Access Patterns and flow in frictional fluid dynamics
Patterns and flow in frictional fluid dynamics
Pattern-forming processes in simple fluids and suspensions are well understood, but displacement morphologies in frictional fluids and granular mixtures have not been studied extensively. Sandneset al. consider the effects of Coulomb friction and compressibility on the fluid dynamics of granular mixtures.
- B. Sandnes
- , E.G. Flekkøy
- & H. See
-
Article
| Open Access The Meissner effect in a strongly underdoped cuprate above its critical temperature
The Meissner effect in a strongly underdoped cuprate above its critical temperature
In the pseudogap state of cuprates, although diamagnetic signals have been detected, a Meissner effect has never been observed. Morenzoni and colleagues probe the local diamagnetic response in the normal state of an underdoped layer showing that a 'barrier' layer exhibits a Meissner effect.
- Elvezio Morenzoni
- , Bastian M. Wojek
- & Ivan Božović
-
Article |
 Molecular dynamics of single-particle impacts predicts phase diagrams for large scale pattern formation
Molecular dynamics of single-particle impacts predicts phase diagrams for large scale pattern formation
Energetic particle irradiation can lead to surface smoothing, pattern formation or degradation of the structural integrity of nuclear reactor components. Here, molecular dynamics simulations are used to study the mechanisms that determine the transitions between these disparate processes.
- Scott A. Norris
- , Juha Samela
- & Michael J. Aziz
-
Article
| Open Access Gapless spin liquid of an organic triangular compound evidenced by thermodynamic measurements
Gapless spin liquid of an organic triangular compound evidenced by thermodynamic measurements
Frustrated magnetic systems can form an exotic quantum spin-liquid ground state, in which strongly correlated spins fluctuate in the spin lattices. Here, the low-temperature electronic state of a charge-transfer compound is found to form a gapless spin liquid.
- Satoshi Yamashita
- , Takashi Yamamoto
- & Reizo Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic vortex core reversal by excitation of spin waves
Magnetic vortex core reversal by excitation of spin waves
Micron and submicron-sized magnetic platelets in a vortex configuration may be useful in micromagnetics and spintronics applications. Kammereret al. show that a fast unidirectional vortex core reversal process occurs when azimuthal spin wave modes are excited at GHz frequency.
- Matthias Kammerer
- , Markus Weigand
- & Gisela Schuetz
-
Article |
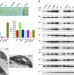 LTD is a protein required for sorting light-harvesting chlorophyll-binding proteins to the chloroplast SRP pathway
LTD is a protein required for sorting light-harvesting chlorophyll-binding proteins to the chloroplast SRP pathway
Chloroplast proteins are synthesized in the cytosol and imported into the chloroplast before being delivered to the thylakoids. The authors report that an ankyrin-repeat protein, LTD, is essential for the routing of chlorophyll-binding proteins to the signal recognition particle pathway.
- Min Ouyang
- , Xiaoyi Li
- & Lixin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access 3D optical Yagi–Uda nanoantenna array
3D optical Yagi–Uda nanoantenna array
Nanoantennas may be important for future photonic circuits; they combine an emitter or detector with free-space propagation of light. Dregelyet al. fabricate an array of 3D optical Yagi–Uda nanoantennas and show that radiofrequency antenna array concepts applied to the optical regime can provide improved directional properties.
- Daniel Dregely
- , Richard Taubert
- & Harald Giessen
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum interference of large organic molecules
Quantum interference of large organic molecules
Observing superposition states of mesoscopic quantum systems is an ongoing challenge. Gerlichet al. report quantum interference of large tailor-made organic compounds, demonstrating delocalization and the quantum wave nature of entire molecules composed of up to 430 atoms.
- Stefan Gerlich
- , Sandra Eibenberger
- & Markus Arndt
-
Article |
 A flow-microreactor approach to protecting-group-free synthesis using organolithium compounds
A flow-microreactor approach to protecting-group-free synthesis using organolithium compounds
Protecting-group-free synthesis has received significant attention, but organolithium species react rapidly with ketones necessitating protection of the ketone carbonyl. Here, a flow-microreactor approach is described that allows protecting-group-free organolithium reactions in the presence of ketones.
- Heejin Kim
- , Aiichiro Nagaki
- & Jun-ichi Yoshida
-
Article |
 Subcellular in vivo time-lapse imaging and optical manipulation of Caenorhabditis elegans in standard multiwell plates
Subcellular in vivo time-lapse imaging and optical manipulation of Caenorhabditis elegans in standard multiwell plates
The nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans is a widely used model organism for visualizing development, ageing and other phenomena, but high-throughput imaging requires immobilization of the animal. Rohde and Yanik report a rapid immobilization and imaging method for the high-throughput screening of C. elegans.
- Christopher B. Rohde
- & Mehmet Fatih Yanik
-
Article |
 Tip-enhanced photovoltaic effects in bismuth ferrite
Tip-enhanced photovoltaic effects in bismuth ferrite
Bismuth ferrite has photoelectric properties that make it an attractive alternative for use in photovoltaic devices. Here, using photoelectric atomic force microscopy, the authors show that photogenerated carriers can be collected by the tip and suggest that this can be used in photoelectric applications.
- Marin Alexe
- & Dietrich Hesse
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a universal stress sensor for graphene and carbon fibres
Development of a universal stress sensor for graphene and carbon fibres
Embedding carbon fibres in polymer matrices provides significant gains in strength and stiffness. Here, the Raman G peak of carbon fibre is studied in relation to applied strain and referenced to graphene; the work could facilitate stress measurements of carbon fibre polymer composites.
- Otakar Frank
- , Georgia Tsoukleri
- & Costas Galiotis
-
Article
| Open Access Whispering gallery microresonators for second harmonic light generation from a low number of small molecules
Whispering gallery microresonators for second harmonic light generation from a low number of small molecules
Small molecules can be detected by second harmonic light generation, but sensitive detection usually requires a large number of molecules and a high-power laser source. Here, relatively low numbers of molecules are detected using Q spherical microresonators and low average power.
- J.L. Dominguez-Juarez
- , G. Kozyreff
- & Jordi Martorell
-
Article |
 The lifetime of the deviations from bulk behaviour in polymers confined at the nanoscale
The lifetime of the deviations from bulk behaviour in polymers confined at the nanoscale
Monitoring the impact of annealing on nanometre-thick polymer layers provides new insight into the changes in the performance of macromolecular materials. Here, the authors present results showing a correlation between the deviations from bulk behaviour and the growth of an irreversibly adsorbed layer.
- Simone Napolitano
- & Michael Wübbenhorst
-
Article |
 Adhesive water networks facilitate binding of protein interfaces
Adhesive water networks facilitate binding of protein interfaces
The formation of hydrophilic protein–protein interactions cannot be explained by charge–charge interactions. Here, molecular simulations reveal that water forms an adhesive hydrogen-bonded network between proteins, stabilizing intermediate states before the bound complex forms.
- Mazen Ahmad
- , Wei Gu
- & Volkhard Helms
-
Article |
 A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
A nanomechanical interface to rapid single-molecule interactions
Single-molecule force spectroscopy is used to study single molecule interactions, but probing short-lived events is difficult. Here, a nanomechanical interface is developed, which allows the study of microsecond timescale interactions.
- Mingdong Dong
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article |
 Quasi-two-dimensional Skyrmion lattices in a chiral nematic liquid crystal
Quasi-two-dimensional Skyrmion lattices in a chiral nematic liquid crystal
Skyrmions are particle-like topological entities in a continuous field that have a role in various condensed matter systems. Here, numerical methods are used to show that a chiral nematic liquid crystal could be used as a model system to facilitate direct structural investigation of Skyrmions.
- Jun-ichi Fukuda
- & Slobodan Žumer
-
Article |
 Electrical injection and detection of spin accumulation in silicon at 500 K with magnetic metal/silicon dioxide contacts
Electrical injection and detection of spin accumulation in silicon at 500 K with magnetic metal/silicon dioxide contacts
Harnessing spin angular momentum could allow the development of electronic devices that are not limited by Moore's law. Here, electrical injection and detection of spin accumulation is achieved at temperatures that are practical for device operation.
- C.H. Li
- , O.M.J. van 't Erve
- & B.T. Jonker
-
Article
| Open Access Near-field examination of perovskite-based superlenses and superlens-enhanced probe-object coupling
Near-field examination of perovskite-based superlenses and superlens-enhanced probe-object coupling
A superlens with a negative index of refraction creates a perfect image because propagating waves focus and evanescent waves reconstruct in the image plane. Here, a perovskite-based superlens is demonstrated for electric evanescent fields, which has potential thermal sensor applications.
- S.C. Kehr
- , Y.M. Liu
- & R. Ramesh
-
Review Article |
 Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings
Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings
Biofouling, or the unwanted growth of biological organisms, is a particular problem in marine environments. This review considers recent advances in the development of environmentally friendly coatings to combat biofouling of submerged surfaces.
- James A. Callow
- & Maureen E. Callow
-
Article |
 Coherent electron–phonon coupling in tailored quantum systems
Coherent electron–phonon coupling in tailored quantum systems
Graphene and InAs nanowires are both promising materials for coherent spin manipulation, but coupling between a quantum system and its environment leads to decoherence. Here, the contribution of electron–phonon coupling to decoherence in graphene and InAs nanowire is studied.
- P. Roulleau
- , S. Baer
- & T. Ihn
-
Article |
 Nanofriction in cold ion traps
Nanofriction in cold ion traps
Cold ion traps have not previously been used to study sliding friction between crystal lattices. Here, Benassiet al. use simulations to show that cold ion traps could be used for detailed investigation of atomic scale friction.
- A. Benassi
- , A. Vanossi
- & E. Tosatti
-
Article |
 Secure device-independent quantum key distribution with causally independent measurement devices
Secure device-independent quantum key distribution with causally independent measurement devices
Device-independent quantum key distribution aims to distribute cryptographic keys without requiring assumptions about the quantum devices in the protocol. Here, a general security proof is reported for a class of quantum key distribution protocols, which could aid the development of highly secure encryption.
- Lluís Masanes
- , Stefano Pironio
- & Antonio Acín
-
Article
| Open Access A new method to position and functionalize metal-organic framework crystals
A new method to position and functionalize metal-organic framework crystals
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have potential catalysis, filtration and sensing applications, but device fabrication will require controlled MOF growth. Here, α-hopeite microparticles are used to achieve spatial control of MOF nucleation, and accelerate MOF growth.
- Paolo Falcaro
- , Anita J. Hill
- & Dario Buso
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon-tunnelling dissipation in mechanical resonators
Phonon-tunnelling dissipation in mechanical resonators
The performance of micromechanical and nanomechanical resonators is often hampered by mechanical damping. In this study, the authors demonstrate a numerical solver for the prediction of support-induced losses in these structures and verify experimentally the fidelity of this method.
- Garrett D. Cole
- , Ignacio Wilson-Rae
- & Markus Aspelmeyer
-
Article |
 Electrically controllable spontaneous magnetism in nanoscale mixed phase multiferroics
Electrically controllable spontaneous magnetism in nanoscale mixed phase multiferroics
Complex oxide interfaces are important for electronic and spintronic applications. In this study, the authors show the emergence of spontaneous magnetism at one such interface between two phases of BiFeO3due to strain effects and piezoelectric coupling.
- Q. He
- , Y. -H. Chu
- & R. Ramesh
-
Article
| Open Access Multimode quantum interference of photons in multiport integrated devices
Multimode quantum interference of photons in multiport integrated devices
Multimode interference devices could allow the implementation of multiport circuits for quantum technologies. Here, quantum interference is demonstrated in 2×2 and 4×4 multimode interference devices, and a technique is reported to characterize such devices.
- Alberto Peruzzo
- , Anthony Laing
- & Jeremy L. O'Brien
-
Article
| Open Access A fast and low-power microelectromechanical system-based non-volatile memory device
A fast and low-power microelectromechanical system-based non-volatile memory device
New memory devices are being developed to overcome the limitations of conventional silicon-based flash memory. Here, a non-volatile memory design is reported that uses a micromechanical cantilever to charge and discharge a floating gate, which controls charge transport through a carbon nanotube field-effect transistor.
- Sang Wook Lee
- , Seung Joo Park
- & Yung Woo Park
-
Article
| Open Access First direct observation of the Van Hove singularity in the tunnelling spectra of cuprates
First direct observation of the Van Hove singularity in the tunnelling spectra of cuprates
In two-dimensional lattices the electronic levels are unevenly spaced and the density of states exhibits a divergence known as the Van Hove singularity. In this study, the Van Hove singularity is observed for the first time in a cuprate using scanning tunnelling microscopy.
- A. Piriou
- , N. Jenkins
- & Ø. Fischer
-
Article |
 Organocatalytic enantioselective β-functionalization of aldehydes by oxidation of enamines and their application in cascade reactions
Organocatalytic enantioselective β-functionalization of aldehydes by oxidation of enamines and their application in cascade reactions
The transformation of iminium ions to enamines has been used extensively in organocatalysis, but conversion of enamines to iminium species has not been exploited. In this study, oxidative enamine catalysis allows the conversion of enamines to iminium ions and the direct asymmetric β-functionalization of simple aldehydes.
- Shi-Lei Zhang
- , He-Xin Xie
- & Wei Wang
-
Article |
 Identification of active atomic defects in a monolayered tungsten disulphide nanoribbon
Identification of active atomic defects in a monolayered tungsten disulphide nanoribbon
The physical and chemical properties of low-dimensional materials, such as nanoribbons, are affected by edge structures and atomic defects. Here, single-atom defects in a monolayered tungsten disulphide nanoribbon are discriminated and the motions of atomic defects are visualized.
- Zheng Liu
- , Kazu Suenaga
- & Sumio Iijima
-
Article |
 Optical virtual imaging at 50 nm lateral resolution with a white-light nanoscope
Optical virtual imaging at 50 nm lateral resolution with a white-light nanoscope
Lenses are restricted by diffraction to imaging features roughly the size of visible wavelengths. Wanget al. develop a white-light nanoscope that uses optically transparent spherical silica lenses to virtually image, in the far-field, features down to 50 nm resolution.
- Zengbo Wang
- , Wei Guo
- & Minghui Hong
-
Article |
 Imaging oxygen defects and their motion at a manganite surface
Imaging oxygen defects and their motion at a manganite surface
Oxygen diffusion processes are critical for the catalytic action of manganites but a full understanding of these processes is elusive. The authors perform atomic resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy imaging of layered manganites and show oxygen and defect dynamics on these surfaces.
- B. Bryant
- , Ch. Renner
- & G. Aeppli
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity-induced optical anomaly in an iron arsenide
Superconductivity-induced optical anomaly in an iron arsenide
Electronic excitations with energies near the superconducting energy gap are strongly affected by superconducting transitions. The authors show, with a comprehensive optical investigation, that excitations with energies up to two orders of magnitude greater are also affected by the transition.
- A. Charnukha
- , P. Popovich
- & A. V. Boris
-
Article
| Open Access Observation and electric current control of a local spin in a single-molecule magnet
Observation and electric current control of a local spin in a single-molecule magnet
In molecular spintronics, the spin state of a molecule may be switched by changing the molecular structure. Here, the spin of a single-molecule magnet is switched by applying an electric current using a scanning tunnelling microscope, which may aid in information coding at the single-molecule level.
- Tadahiro Komeda
- , Hironari Isshiki
- & Masahiro Yamashita
-
Article |
 Heisenberg-limited sensitivity with decoherence-enhanced measurements
Heisenberg-limited sensitivity with decoherence-enhanced measurements
Quantum-enhanced measurements use quantum mechanical effects to enhance measurement sensitivity of classical quantities; but the required quantum states are generally highly entangled and difficult to produce. In this study, the use of entangled states is avoided allowing Heisenberg-limited measurements.
- Daniel Braun
- & John Martin
-
Article |
 Porous organic molecular solids by dynamic covalent scrambling
Porous organic molecular solids by dynamic covalent scrambling
The construction of porous solids from discrete organic molecules usually involves the formation of regular porous crystals. In this study, a covalent scrambling reaction gives molecules with a range of shapes that do not pack effectively — manipulation of the reagent ratio allows fine control of porosity.
- Shan Jiang
- , James T. A. Jones
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 Metallosupramolecular self-assembly of a universal 3-ravel
Metallosupramolecular self-assembly of a universal 3-ravel
There has been recent progress in the synthesis of complex intertwined supramolecular topologies. In this study, Liet al.report the self-assembly of an intertwined structure based on a universal 3-ravel.
- Feng Li
- , Jack K. Clegg
- & George V. Meehan
-
Article |
 Chemical processes in the deep interior of Uranus
Chemical processes in the deep interior of Uranus
The unusual magnetic fields of Uranus and Neptune are important considerations when developing hydrodynamic models of the planetary interiors. In this study, molecular dynamics simulations are used to study how chemical processes could create the interior structures predicted from the planets' magnetic fields.
- Ricky Chau
- , Sebastien Hamel
- & William J. Nellis
-
Article
| Open Access Transport spectroscopy of non-equilibrium many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots
Transport spectroscopy of non-equilibrium many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots
All-electrical quantum state manipulation is highly desirable for quantum information technologies. In this study, the authors demonstrate the preparation and detection of excited many-particle spin states in self-assembled quantum dots at 4 K, using only electrical means.
- B. Marquardt
- , M. Geller
- & A. Lorke
-
Article |
 Rationally tuned micropores within enantiopure metal-organic frameworks for highly selective separation of acetylene and ethylene
Rationally tuned micropores within enantiopure metal-organic frameworks for highly selective separation of acetylene and ethylene
Separation of acetylene and ethylene is an important industrial challenge, which may be aided by selectively adsorbant materials. In this study, a metal-organic framework material is reported, which allows highly selective separation of acetylene and ethylene.
- Sheng-Chang Xiang
- , Zhangjing Zhang
- & Banglin Chen
-
Article |
 Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Water-soluble peptides with stable α-helical conformations are desirable for a range of applications, but incorporating charged residues to improve solubility usually leads to reduced helical stability. Here, polypeptides produced from amino acids with elongated charged side chains are found to be water soluble and exhibit very high helical stability.
- Hua Lu
- , Jing Wang
- & Jianjun Cheng

 Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures
Synthesis of hexagonal close-packed gold nanostructures