Featured
-
-
Article |
 Selective visible-light photocatalysis of acetylene to ethylene using a cobalt molecular catalyst and water as a proton source
Selective visible-light photocatalysis of acetylene to ethylene using a cobalt molecular catalyst and water as a proton source
The acetylene contaminant present in ethylene feeds used to produce polymers is typically removed by thermal hydrogenation. Now, it has been shown that the conversion of acetylene to ethylene at room temperature can be achieved in a visible-light-driven process using an earth-abundant metal (cobalt) catalyst and a water proton source.
- Francesca Arcudi
- , Luka Ðorđević
- & Emily A. Weiss
-
In Your Element |
 The fruit fly of photophysics
The fruit fly of photophysics
The tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) cation, or ‘rubipy’ to its friends, has had a significant influence on our understanding of the photophysics of transition metal complexes, and has also helped revolutionize organic photochemistry, explains Daniela M. Arias-Rotondo.
- Daniela M. Arias-Rotondo
-
Article |
 Chiral control of spin-crossover dynamics in Fe(II) complexes
Chiral control of spin-crossover dynamics in Fe(II) complexes
Despite much research, the high-spin-state relaxation mechanism of Fe(II) spin-crossover complexes is unresolved. Using ultrafast circular dichroism spectroscopy it has now been revealed that the spin relaxation is driven by a torsional twisting mode, which breaks the chiral symmetry of a prototypical Fe(II) compound. Stereocontrolling the configuration of the complex can thus be used to slow down the spin relaxation.
- Malte Oppermann
- , Francesco Zinna
- & Majed Chergui
-
News & Views |
 Fixing photocatalysts
Fixing photocatalysts
Molecular photocatalysts for generating solar fuels such as hydrogen degrade over time, ceasing to function as intended. Now the mechanism by which a ruthenium–platinum-based hydrogen-evolving photocatalyst breaks down has been identified, leading to the development of a repair strategy that uses singlet oxygen to regenerate an inactivated bridging ligand.
- Claudia Turro
-
Article |
 Accelerating symmetry-breaking charge separation in a perylenediimide trimer through a vibronically coherent dimer intermediate
Accelerating symmetry-breaking charge separation in a perylenediimide trimer through a vibronically coherent dimer intermediate
Molecular π-stacked chromophores are promising photonic materials, but much of our understanding is limited to covalent dimers. Now it has been shown that, in a slip-stacked perylenediimide trimer, coherent vibronic coupling to high-frequency modes facilitates ultrafast state mixing between the Frenkel exciton and charge-transfer states, which then collapses by solvent fluctuations and low-frequency vibronic coupling, resulting in ultrafast symmetry-breaking charge separation.
- Chenjian Lin
- , Taeyeon Kim
- & Michael R. Wasielewski
-
Article |
 Photogearing as a concept for translation of precise motions at the nanoscale
Photogearing as a concept for translation of precise motions at the nanoscale
In a similar fashion to its macroscopic counterpart, molecular gearing is a correlated motion of intermeshed molecular fragments against one another. Now it has been shown that photogearing can be used to actively fuel molecular gearing motions with light and concomitantly shift the axis of rotation.
- Aaron Gerwien
- , Frederik Gnannt
- & Henry Dube
-
Article |
 Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion pairing is ubiquitous in low-dielectric-constant solvents, but whether it influences the reactivity of common cationic photoredox catalysts has been unclear. However, it has now been shown that ion pairing is responsible for a 4-fold modulation in reactivity in a prototypical Ir(III) complex and is explained by excited-state ion-pair reorganization.
- J. D. Earley
- , A. Zieleniewska
- & G. Rumbles
-
Article |
 Halogen-bond-assisted radical activation of glycosyl donors enables mild and stereoconvergent 1,2-cis-glycosylation
Halogen-bond-assisted radical activation of glycosyl donors enables mild and stereoconvergent 1,2-cis-glycosylation
Most chemical glycosylation methods operate by acid-promoted, ionic activation of donors. Now, by exploiting the formation of a halogen-bond complex, the activation of glycosyl donors was achieved via a visible light-promoted radical cascade process, resulting in a general, simple and mild way to build challenging 1,2-cis-glycosidic bonds.
- Chen Zhang
- , Hao Zuo
- & Dawen Niu
-
Article |
 Quantum–classical simulations of rhodopsin reveal excited-state population splitting and its effects on quantum efficiency
Quantum–classical simulations of rhodopsin reveal excited-state population splitting and its effects on quantum efficiency
Rhodopsin activation is driven by an ultrafast double-bond isomerization, but questions remain about the origin of its sensitivity. Now, quantum–classical simulations show that, 15 fs after light absorption, a degeneracy between the reactive excited state and a neighbouring state causes the splitting of the rhodopsin population into subpopulations, which propagate with different velocities, leading to distinct contributions to the quantum efficiency.
- Xuchun Yang
- , Madushanka Manathunga
- & Massimo Olivucci
-
Article |
 Active repair of a dinuclear photocatalyst for visible-light-driven hydrogen production
Active repair of a dinuclear photocatalyst for visible-light-driven hydrogen production
Molecular catalysts for artificial photosynthesis can break down during operation and stop working, whereas biological photosynthesis uses an enzymatic repair strategy to maintain function. Now, the degradation pathway of a hydrogen-evolving RuPt photocatalyst has been identified, enabling the development of an active repair strategy involving the use of 1O2 to reoxidize the deactivated bridging ligand.
- Michael G. Pfeffer
- , Carolin Müller
- & Sven Rau
-
Article |
 Decarboxylative cross-nucleophile coupling via ligand-to-metal charge transfer photoexcitation of Cu(ii) carboxylates
Decarboxylative cross-nucleophile coupling via ligand-to-metal charge transfer photoexcitation of Cu(ii) carboxylates
Direct coupling methods, which do not require substrate prefunctionalization, are highly desirable for the construction of complex molecular scaffolds. Now, a photochemical method has been developed for the direct decarboxylative coupling of carboxylic acids with diverse nitrogen, oxygen and carbon nucleophiles, taking advantage of the photochemistry of copper(II) carboxylate complexes assembled in situ.
- Qi Yukki Li
- , Samuel N. Gockel
- & Tehshik P. Yoon
-
Article |
 Visible light-driven conjunctive olefination
Visible light-driven conjunctive olefination
A conjunctive olefination between aldehydes and carboxylic acids has been developed by merging photoredox catalysis with the Wittig reaction. The process uses a readily available phosphonium salt to join together complex molecular fragments with high functional group tolerance and minimal use of protecting groups, enabling access to coupling products with user-defined geometries.
- Dario Filippini
- & Mattia Silvi
-
Article |
 Prebiotic photoredox synthesis from carbon dioxide and sulfite
Prebiotic photoredox synthesis from carbon dioxide and sulfite
Carbon dioxide is a substantial component of many planetary atmospheres, but reduction of carbon dioxide requires conditions and substrates that are rare on planetary surfaces. Now, the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic species with biological relevance has been photochemically coupled to the oxidation of sulfite, suggesting that prebiotic carbon fixation could take place on the surfaces of rocky planets.
- Ziwei Liu
- , Long-Fei Wu
- & John D. Sutherland
-
News & Views |
 Made with manganese
Made with manganese
Transition metal complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) luminescence and photoactivity typically rely on precious metals such as ruthenium or iridium. Now, two complexes of the Earth-abundant 3d manganese have displayed room-temperature MLCT luminescence in solution and a unique excited-state reactivity.
- Katja Heinze
-
Article |
 Manganese(i) complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer luminescence and photoreactivity
Manganese(i) complexes with metal-to-ligand charge transfer luminescence and photoreactivity
Manganese(i) is isoelectronic to iron(ii) but has typically been overlooked as a cheap Earth-abundant metal for the development of 3d6 metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) emitters and photosensitizers. Now, using chelating isocyanide ligands, air-stable manganese(i) complexes have been obtained that exhibit MLCT luminescence, as well as energy- and electron-transfer photoreactivity.
- Patrick Herr
- , Christoph Kerzig
- & Oliver S. Wenger
-
Article |
 Switching on prodrugs using radiotherapy
Switching on prodrugs using radiotherapy
Prodrugs offer one route to treat cancer, but they require activation once they have been delivered to the tumour. Now, a simultaneous chemo-radiotherapy strategy has been demonstrated in mice that uses gamma or X-ray irradiation to locally activate an anticancer prodrug.
- Jin Geng
- , Yichuan Zhang
- & Mark Bradley
-
Article |
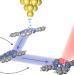 Energy funnelling within multichromophore architectures monitored with subnanometre resolution
Energy funnelling within multichromophore architectures monitored with subnanometre resolution
Energy funnelling within multichromophoric assemblies is key to the conversion of solar energy by plants. Now, energy transport between phthalocyanine-based chromophores has been monitored at the submolecular level using scanning tunnelling microscopy, focusing on the role of ancillary, passive and blocking chromophores in promoting and directing energy transfer between distant donor and acceptor units.
- Shuiyan Cao
- , Anna Rosławska
- & Guillaume Schull
-
Article |
 Catalytic asymmetric C–C cross-couplings enabled by photoexcitation
Catalytic asymmetric C–C cross-couplings enabled by photoexcitation
A chiral (η3-allyl)iridium(iii) complex has previously been used to catalyse enantioselective allylic substitution reactions in the polar domain. Now, it has been shown that the visible-light excitation of this iridium complex unlocks an otherwise inaccessible radical-based pathway to achieve enantioselective alkyl–alkyl cross-coupling reactions between allylic alcohols and radical precursors.
- Giacomo E. M. Crisenza
- , Adriana Faraone
- & Paolo Melchiorre
-
Article |
 A far-red hybrid voltage indicator enabled by bioorthogonal engineering of rhodopsin on live neurons
A far-red hybrid voltage indicator enabled by bioorthogonal engineering of rhodopsin on live neurons
Voltage imaging is a powerful technique for studying electrical signalling in neurons. A palette of bright and sensitive voltage indicators has now been developed via enzyme-mediated ligation and Diels–Alder cycloaddition. Among these, a far-red indicator faithfully reports neuronal action potential dynamics with an excitation spectrum orthogonal to optogenetic actuators and green/red-emitting biosensors.
- Shuzhang Liu
- , Chang Lin
- & Peng Zou
-
Article |
 Asymmetric, visible light-mediated radical sulfinyl-Smiles rearrangement to access all-carbon quaternary stereocentres
Asymmetric, visible light-mediated radical sulfinyl-Smiles rearrangement to access all-carbon quaternary stereocentres
The assembly of a single configuration of an all-carbon quaternary centre within acyclic systems remains a challenge for synthetic chemists. Now, it has been shown that α-all-carbon quaternary centres can be installed in acyclic amides, with excellent levels of absolute stereocontrol, through a radical sulfinyl Truce–Smiles rearrangement.
- Cédric Hervieu
- , Mariia S. Kirillova
- & Cristina Nevado
-
Article |
 Free-triplet generation with improved efficiency in tetracene oligomers through spatially separated triplet pair states
Free-triplet generation with improved efficiency in tetracene oligomers through spatially separated triplet pair states
The overall efficiency of free-triplet generation from intramolecular singlet fission is limited by the efficiency of the dissociation of spatially adjacent triplet pairs. Now, using transient magneto-optical spectroscopy, it has been shown that this limitation can be overcome by promoting a pathway mediated by spatially separated triplet pairs in tetracene trimers and tetramers.
- Zhiwei Wang
- , Heyuan Liu
- & Min Xiao
-
News & Views |
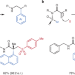 An asymmetric smile
An asymmetric smile
The formation of all-carbon quaternary centres is a challenging problem in organic chemistry, with far-reaching implications for functional molecule discovery. Now an inventive solution has been developed, using sulfinamides as traceless linkers for an asymmetric radical Truce–Smiles rearrangement.
- David M. Whalley
- & Michael F. Greaney
-
Article |
 Direct observation of coherent femtosecond solvent reorganization coupled to intramolecular electron transfer
Direct observation of coherent femtosecond solvent reorganization coupled to intramolecular electron transfer
Solvent plays a critical role in electron-transfer reactions, but short-range solvation dynamics are challenging to observe. Now, femtosecond X-ray solution scattering has been used to directly monitor the reorganization of water upon ultrafast intramolecular electron transfer in a bimetallic complex. Coherent motions of the first-shell water molecules are observed, arising from changes in solute–solvent hydrogen bonding.
- Elisa Biasin
- , Zachary W. Fox
- & Munira Khalil
-
Article |
 The photochemical reaction of phenol becomes ultrafast at the air–water interface
The photochemical reaction of phenol becomes ultrafast at the air–water interface
Reactions at the interface between water and other phases play important roles in various chemical settings. Now, ultrafast phase-sensitive interface-selective vibrational spectroscopy has revealed that the photoionization of phenol can occur four orders of magnitude faster at the water surface than in the bulk aqueous phase.
- Ryoji Kusaka
- , Satoshi Nihonyanagi
- & Tahei Tahara
-
Article |
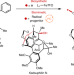 Mimicking oxidative radical cyclizations of lignan biosynthesis using redox-neutral photocatalysis
Mimicking oxidative radical cyclizations of lignan biosynthesis using redox-neutral photocatalysis
Many biosynthetic cyclizations are catalysed by iron oxygenases and appear to involve long-lived radical species. Now, mimicking these biosynthetic transformations, the total synthesis of highly oxidized lignan natural products has been reported using redox-neutral photocatalysis to enable late-stage radical cyclizations that install challenging 5- and 11-membered rings.
- Zheng Huang
- & Jean-Philip Lumb
-
Article |
 Charge transfer driven by ultrafast spin transition in a CoFe Prussian blue analogue
Charge transfer driven by ultrafast spin transition in a CoFe Prussian blue analogue
Cyanide-bridged CoFe coordination networks exhibit photomagnetism because of coupled charge-transfer and spin transition. Now, femtosecond X-ray and optical absorption spectroscopies have enabled the electronic and structural dynamics of this light-induced process to be disentangled and show that it is the spin transition on the cobalt atom, occurring within ~50 fs, that induces the Fe-to-Co charge-transfer within ~200 fs.
- Marco Cammarata
- , Serhane Zerdane
- & Eric Collet
-
Article |
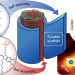 Frenkel excitons in heat-stressed supramolecular nanocomposites enabled by tunable cage-like scaffolding
Frenkel excitons in heat-stressed supramolecular nanocomposites enabled by tunable cage-like scaffolding
Nature successfully uses supramolecular assemblies for efficient and robust solar energy harvesting; however, mimicking such material systems for applications in optoelectronic devices has been hampered by stability issues such as the fragility of the supramolecular structures used and the delicate nature of Frenkel excitons. Now, enabled by tunable cage-like scaffolds, stable supramolecular light-harvesting nanotubes have been composed that are robust even under heat stress.
- Kara Ng
- , Megan Webster
- & Dorthe M. Eisele
-
Matters Arising |
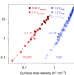 Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
- Camilo A. Mesa
- , Reshma R. Rao
- & James R. Durrant
-
News & Views |
 A light touch for complex products
A light touch for complex products
The [2+2] photocycloaddition of two double-bond moieties is arguably the most efficient way to form a four-membered ring, but this route is rarely used to construct azetidine rings. Now, the development of an isoxazoline carboxylate cycloaddition partner offers a general approach to synthesize diverse azetidine products.
- Susannah Coote
-
Article |
 Synthesis of azetidines via visible-light-mediated intermolecular [2+2] photocycloadditions
Synthesis of azetidines via visible-light-mediated intermolecular [2+2] photocycloadditions
Although azetidines represent highly desirable building blocks in drug discovery, methods for their efficient and straightforward synthesis remain underdeveloped. Now, it has been shown that highly functionalized azetidines can be prepared via an intermolecular [2+2] photocycloaddition reaction between cyclic oximes and alkenes, in a process enabled by a visible-light-mediated triplet energy transfer.
- Marc R. Becker
- , Emily R. Wearing
- & Corinna S. Schindler
-
News & Views |
 The future iron age
The future iron age
Recent research has shown that vibronic coherences are one of the primary drivers for ultrafast light-induced processes. Now, ultrafast spectroscopy has been used to uncover vibronic coherences in the excited-state dynamics of an iron complex, leading to its redesign and the drastic prolonging of its excited-state lifetime.
- Julia A. Weinstein
-
Article |
 Tracking the ultraviolet-induced photochemistry of thiophenone during and after ultrafast ring opening
Tracking the ultraviolet-induced photochemistry of thiophenone during and after ultrafast ring opening
Photoinduced isomerization reactions, including ring-opening reactions, lie at the heart of many chemical processes in nature. The pathway and dynamics of the ring opening of a model heterocycle have now been investigated by femtosecond photoelectron spectroscopy combined with ab initio theory, enabling the visualization of rich dynamics in both the ground and excited electronic states.
- Shashank Pathak
- , Lea M. Ibele
- & Daniel Rolles
-
News & Views |
 Photoswitching to the core
Photoswitching to the core
The potential applications of smart photoswitchable porous materials are currently limited by incomplete switching. Now, efficient bulk switching has been achieved by embedding a photoisomerizable overcrowded alkene in a highly porous aromatic framework, creating a material capable of photomodulated gas uptake.
- Jet-Sing M. Lee
- & Hiroshi Sato
-
Article |
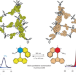 Modulation of porosity in a solid material enabled by bulk photoisomerization of an overcrowded alkene
Modulation of porosity in a solid material enabled by bulk photoisomerization of an overcrowded alkene
Despite numerous potential applications, the development of light-responsive solid materials based on molecular photoswitches is impeded by the low efficiency of photoisomerization in the solid environment. Now a robust, solid porous material made from tetraphenylmethane and a photoswitchable overcrowded alkene exhibits nearly quantitative photoisomerization in the bulk and in photomodulation of gas uptake.
- Fabio Castiglioni
- , Wojciech Danowski
- & Ben L. Feringa
-
News & Views |
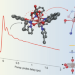 Ultrafast control of anisotropy
Ultrafast control of anisotropy
Single-molecule magnets are able to store information through their magnetic anisotropy, making them very promising systems for memory applications. Now, femtosecond-laser-initiated molecular dynamics that modulate magnetic anisotropy have been observed, paving the way for operation on ultrafast timescales.
- Eric Collet
-
Article |
 Enantioselective photoinduced cyclodimerization of a prochiral anthracene derivative adsorbed on helical metal nanostructures
Enantioselective photoinduced cyclodimerization of a prochiral anthracene derivative adsorbed on helical metal nanostructures
The photoinduced dimerization of a prochiral anthracenecarboxylic acid occurs in an enantioselective fashion when the molecules are adsorbed on helical metal nanostructures. This enantiopreference arises mostly from the helicity of the silver and copper substrates—prepared using shear forces during the deposition process—and may also be influenced by chiroplasmonic effects.
- Xueqin Wei
- , Junjun Liu
- & Zhifeng Huang
-
Article |
 The merger of decatungstate and copper catalysis to enable aliphatic C(sp3)–H trifluoromethylation
The merger of decatungstate and copper catalysis to enable aliphatic C(sp3)–H trifluoromethylation
Despite the importance of trifluoromethylated compounds, direct catalytic methods for the conversion of C(sp3)–H bonds into the corresponding C(sp3)–CF3 analogues have remained elusive. This transformation has now been achieved by the merger of copper catalysis with decatungstate photocatalysis, enabling the C(sp3)–H trifluoromethylation of abundant feedstocks, natural products and pharmaceuticals.
- Patrick J. Sarver
- , Vlad Bacauanu
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Article |
 Delayed fluorescence from a zirconium(iv) photosensitizer with ligand-to-metal charge-transfer excited states
Delayed fluorescence from a zirconium(iv) photosensitizer with ligand-to-metal charge-transfer excited states
Understanding the photophysical properties of transition-metal complexes is paramount to advances in photocatalysis, solar energy conversion and light-emitting diodes. Now, long-lived emission via thermally activated delayed fluorescence has been demonstrated from an air- and water-stable zirconium complex featuring excited states with significant ligand-to-metal charge transfer character.
- Yu Zhang
- , Tia S. Lee
- & Carsten Milsmann
-
Article |
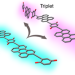 Spatial separation of triplet excitons drives endothermic singlet fission
Spatial separation of triplet excitons drives endothermic singlet fission
Generating high-energy triplet excitons from singlet fission without excess energy loss is a critical goal for potential applications. Now it is shown that molecular chromophores that are connected covalently can harbour multiple long-lived and high-energy triplets—created from one photon—only if more than two chromophoric units are present and they have sufficient flexibility to isolate the excitations upon torsional motion.
- Nadezhda V. Korovina
- , Christopher H. Chang
- & Justin C. Johnson
-
Article |
 Single-chromophore single-molecule photocatalyst for the production of dihydrogen using low-energy light
Single-chromophore single-molecule photocatalyst for the production of dihydrogen using low-energy light
Homogeneous photocatalysts for the conversion and storage of solar energy typically feature separate sensitizer–catalyst assemblies, whereas previous examples of single-chromophore single-molecule photocatalysts are inefficient and do not use significant portions of the visible spectrum. Now a dirhodium single-chromophore single-molecule catalyst has been developed that generates hydrogen using low-energy light through a previously unobserved mechanism.
- T. J. Whittemore
- , C. Xue
- & C. Turro
-
Article |
 Impact of non-equilibrium molecular packings on singlet fission in microcrystals observed using 2D white-light microscopy
Impact of non-equilibrium molecular packings on singlet fission in microcrystals observed using 2D white-light microscopy
Intermolecular coupling plays a critical role in singlet fission. Now, high-resolution 2D white-light spectroscopy has been used to map the presence of non-equilibrium molecular packing in single TIPS-pentacene microcrystals and characterize its effect on the dynamics of singlet fission.
- Andrew C. Jones
- , Nicholas M. Kearns
- & Martin T. Zanni
-
Article |
 Photoredox catalysis with aryl sulfonium salts enables site-selective late-stage fluorination
Photoredox catalysis with aryl sulfonium salts enables site-selective late-stage fluorination
Despite the potential of fluorinated compounds in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, the formation of C–F bonds remains challenging. It has now been shown that aryl sulfonium salts, which can be made by site-selective C–H functionalization, have advantageous photoredox reactivity compared to conventional (pseudo)halides and can be used for late-stage C–H fluorination.
- Jiakun Li
- , Junting Chen
- & Tobias Ritter
-
Article |
 Slow charge transfer from pentacene triplet states at the Marcus optimum
Slow charge transfer from pentacene triplet states at the Marcus optimum
Singlet fission produces two low-energy triplet excitons that are difficult to dissociate into free charges. Now, separate optima in charge yield have been observed as a function of driving force for singlet and triplet excitons in pentacene. At optimal driving forces, the triplet-exciton dissociation rate is at least five orders of magnitude smaller than the singlet-exciton dissociation rate.
- Natalie A. Pace
- , Nadezhda V. Korovina
- & Obadiah G. Reid
-
Article |
 Iron(ii) coordination complexes with panchromatic absorption and nanosecond charge-transfer excited state lifetimes
Iron(ii) coordination complexes with panchromatic absorption and nanosecond charge-transfer excited state lifetimes
Replacing rare elements in benchmark photosensitizers with iron would facilitate the large-scale implementation of solar energy conversion, but iron complexes generally do not exhibit sufficiently long-lived photoexcited states. Now, it has been shown that iron(ii) complexes with carefully designed ligands can absorb broadly across the visible light spectrum and have charge-transfer excited states with nanosecond lifetimes.
- Jason D. Braun
- , Issiah B. Lozada
- & David E. Herbert
-
News & Views |
 Beam me up Scotty
Beam me up Scotty
Although transporting a starship crewmember onto the surface of an alien planet is clearly science fiction, quantum state teleportation is not, and has been observed in various systems over the last few decades. Now, electron-spin teleportation has been observed in a carefully designed molecular system, paving the way for such behaviour to be tailored through molecular engineering.
- Malcolm D. E. Forbes
-
Article |
 Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots
Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots
Tuning the selectivity for [2+2] photocycloadditions remains challenging. Now, triplet–triplet energy transfer from CdSe quantum dots enables the homo- and heterocouplings of 4-vinylbenzoic acid derivatives via [2+2] photocycloaddition. Preorganization of substrates on the quantum dots reverses intrinsic stereoelectronic preferences to yield cyclobutane products with unprecedented diastereo- and regioselectivity.
- Yishu Jiang
- , Chen Wang
- & Emily A. Weiss
-
Article |
 Photodriven quantum teleportation of an electron spin state in a covalent donor–acceptor–radical system
Photodriven quantum teleportation of an electron spin state in a covalent donor–acceptor–radical system
Quantum teleportation moves the quantum state of a system between physical locations without losing its coherence, an essential criterion for emerging quantum information applications. Now, electron-spin-state teleportation in covalent organic electron donor–acceptor–stable radical molecules is demonstrated using entangled electron spins produced by photo-induced electron transfer.
- Brandon K. Rugg
- , Matthew D. Krzyaniak
- & Michael R. Wasielewski
-
Article |
 Super-resolution labelling with Action-PAINT
Super-resolution labelling with Action-PAINT
Super-resolution microscopy has enabled optical imaging of individual biomolecules on the nanometre scale. Now, a new method has been developed that allows active manipulation of single-molecule targets on visualization in a sequential manner. This method, called ‘Action-PAINT’, combines real-time super-resolution microscopy (DNA-PAINT) and photoinducible crosslinking chemistry to deliver a single-molecule cargo with <30 nm selectivity.
- Ninning Liu
- , Mingjie Dai
- & Peng Yin
-
Article |
 Ultra-fast intramolecular singlet fission to persistent multiexcitons by molecular design
Ultra-fast intramolecular singlet fission to persistent multiexcitons by molecular design
Although they are synthetically tunable, organic molecules that undergo singlet fission (the generation of two excitons from one photon) have not demonstrated the excited-state properties necessary to improve optoelectronic devices. Now, a general ‘energy cleft’ molecular design scheme has been demonstrated that enables rapid generation and long lifetimes of multiple triplet excitons that are for device applications.
- Andrew B. Pun
- , Amir Asadpoordarvish
- & Matthew Y. Sfeir

 A multi-stage single photochrome system for controlled photoswitching responses
A multi-stage single photochrome system for controlled photoswitching responses