Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Tailor-made genetic codes
Tailor-made genetic codes
Expanding the range of amino acids polymerizable by ribosomes could enable new functionalities to be added to polypeptides. Now, the genetic code has been reprogrammed using a reconstituted in vitro translation system to enable synthesis of unnatural peptides with unmatched flexibility.
- Michael C. Jewett
- & Vincent Noireaux
-
Article |
 Phosphorylation-mediated RNA/peptide complex coacervation as a model for intracellular liquid organelles
Phosphorylation-mediated RNA/peptide complex coacervation as a model for intracellular liquid organelles
Intracellular bodies called liquid organelles are rich in nucleic acids and proteins, and are thought to occur by liquid–liquid phase coexistence. Now, enzymatic control over the phosphorylation state of a simple cationic peptide, thereby altering its electrostatic interaction with RNA, has been shown to drive formation and dissolution of droplets that mimic these intracellular liquid bodies.
- William M. Aumiller Jr
- & Christine D. Keating
-
News & Views |
 Biomimetic and built to order
Biomimetic and built to order
Synthetic oligomers could potentially expand beyond the functions offered by proteins and nucleic acids. However, this requires precise methods for controlling their folding and self-assembly. Now, it is shown that two drastically different supramolecular architectures can be fabricated from closely related sequences using a single biomimetic scaffold.
- W. Seth Horne
-
Article |
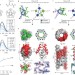 Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation
Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation
The self-assembly of short amphiphilic α-helicomimetic foldamers bearing proteinaceous side-chains can be controlled by manipulating the side-chain sequence. This enables the foldamers to be programmed to form either discrete helical bundles containing isolated cavities, or pH-responsive water-filled channels with controllable pore diameters.
- Gavin W. Collie
- , Karolina Pulka-Ziach
- & Gilles Guichard
-
-
News & Views |
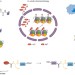 Chromatin chemistry goes cellular
Chromatin chemistry goes cellular
Analysing post-translational modifications of histone proteins as they occur within chromatin is challenging due to their large number and chemical diversity. A major step forward has now been achieved by using split intein chemistry to engineer functionalized histones within cells.
- Wolfgang Fischle
- , Dirk Schwarzer
- & Henning D. Mootz
-
Article |
 Structure and biosynthesis of a macrocyclic peptide containing an unprecedented lysine-to-tryptophan crosslink
Structure and biosynthesis of a macrocyclic peptide containing an unprecedented lysine-to-tryptophan crosslink
Structural elucidation of a peptide natural product has revealed an unprecedented post-translational modification involving formation of a carbon–carbon bond between the side-chains of lysine and tryptophan. This motif defines a new family of cyclic peptides. Biochemical studies reveal that this C-C bond is generated by a radical SAM enzyme, and delineate its catalytic mechanism.
- Kelsey R. Schramma
- , Leah B. Bushin
- & Mohammad R. Seyedsayamdost
-
Article |
 A protein-targeting strategy used to develop a selective inhibitor of the E17K point mutation in the PH domain of Akt1
A protein-targeting strategy used to develop a selective inhibitor of the E17K point mutation in the PH domain of Akt1
It is difficult to develop a selective ligand for point mutations in proteins that are not found in easily addressable locations. Now, an all-chemical, epitope-targeting strategy has been reported, and was used to discover an inhibitory peptide with selectivity for the E17K point mutation in the PH Domain of the Akt1 oncoprotein.
- Kaycie M. Deyle
- , Blake Farrow
- & James R. Heath
-
News & Views |
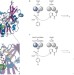 Getting a handle on peptides
Getting a handle on peptides
Enhancing the structural diversity of peptide natural products relies on synthetic modifications that are typically not chemo- or regioselective. A nonribosomal peptide synthetase has now been engineered to incorporate a non-natural amino acid containing a reactive bio-orthogonal handle.
- Jaclyn M. Winter
- & Yi Tang
-
News & Views |
 Bicycling into cells
Bicycling into cells
Bicyclic peptides that are cell-permeable and can inhibit an intracellular target have been developed. These peptides consist of two rings: one enables the peptide to pass through the membrane, the other can inhibit the target.
- Rob M. J. Liskamp
-
Article |
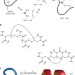 Dithiol amino acids can structurally shape and enhance the ligand-binding properties of polypeptides
Dithiol amino acids can structurally shape and enhance the ligand-binding properties of polypeptides
Disulfide bonds formed between two cysteine residues are important in the folding and stability of proteins. Now, unnatural amino acids with side-chains that contain two thiol groups are described. Incorporation of these dithiol amino acids into a serine protease inhibitor and a nicotinic acetyl choline receptor antagonist is shown to increase their inhibitory activity.
- Shiyu Chen
- , Ranganath Gopalakrishnan
- & Christian Heinis
-
Article |
 Asymmetric triplex metallohelices with high and selective activity against cancer cells
Asymmetric triplex metallohelices with high and selective activity against cancer cells
Water-soluble metallohelices containing an antiparallel head-to-head-to-tail arrangement of strands are reported. This amphipathic functional topology is akin to that of host-defence peptides. The metallohelices show high and selective toxicity to a cancer cell line, causing dramatic changes in the cell cycle without DNA damage. In contrast, there is no significant toxicity to MRSA and Escherichia coli.
- Alan D. Faulkner
- , Rebecca A. Kaner
- & Peter Scott
-
News & Views |
 Catalytic amyloid fibrils
Catalytic amyloid fibrils
Amyloid fibrils are formed from polypeptide chains assembled into an organized fibrillar structure. Now, it has been shown that such fibrillar structures can also bind metal ions and catalyse chemical reactions.
- Tobias Aumüller
- & Marcus Fändrich
-
Article |
 End-to-end conformational communication through a synthetic purinergic receptor by ligand-induced helicity switching
End-to-end conformational communication through a synthetic purinergic receptor by ligand-induced helicity switching
Biological receptors communicate information through ligand-induced conformational changes. A synthetic receptor with a boron-containing binding site that can selectively and reversibly complex a ligand (such as a purine nucleoside) is shown to function in a similar fashion. The resulting conformational change is relayed through the receptor, communicating structural information about the ligand to a spectroscopic reporter more than 2 nm away.
- Robert A. Brown
- , Vincent Diemer
- & Jonathan Clayden
-
-
News & Views |
 Spectroscopy meets theory
Spectroscopy meets theory
Combined spectroscopic measurements and theoretical calculations bring to light an ultrafast excited-state deactivation process in peptides that may contribute to the ultraviolet photostability of proteins.
- Wolfgang Domcke
- & Andrzej L. Sobolewski
-
Review Article |
 Contemporary strategies for peptide macrocyclization
Contemporary strategies for peptide macrocyclization
Peptide macrocycles have a number of important applications. Among other things, the reduced conformational freedom of the cyclic structure enables strong binding to the extended contact regions of protein–protein complexes. Here, emerging methods directed towards the synthesis of these valuable molecules are reviewed.
- Christopher J. White
- & Andrei K. Yudin
-
Research Highlights |
 Peptides make the difference
Peptides make the difference
Microporous crystals formed by hydrogen-bonded dipeptides show different permeabilities for argon, nitrogen and oxygen.
- Anne Pichon

 Expanding the chemical toolbox for the synthesis of large and uniquely modified proteins
Expanding the chemical toolbox for the synthesis of large and uniquely modified proteins A SAGE design
A SAGE design