Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Woven organic crystals
Woven organic crystals
The entanglement of fibrous elements produces flexible structures with enhanced strength and resilience to abrasion. Here, the authors report the weaving of organic crystals into flexible and robust patches with plain, twill, and satin topologies of arbitrary porosity, expanding one-dimensional crystals into flexible, two-dimensional planar structures with potential for future applications in flexible electronics.
- Linfeng Lan
- , Liang Li
- & Hongyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of aligned dipoles and angular chromism of exciplexes in organic molecular heterostructures
Observation of aligned dipoles and angular chromism of exciplexes in organic molecular heterostructures
The directional features of dipole moments of Frenkel excitons and exciplexes are important for optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors study photo- and electro-luminescence emissions of organic heterostructures and observe angular chromism of exciplexes, indicating possible delocalization.
- Sang-hun Lee
- , Taek Joon Kim
- & Jinsoo Joo
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired thermadapt shape-memory polymer with light-induced reversible fluorescence for rewritable 2D/3D-encoding information carriers
Bioinspired thermadapt shape-memory polymer with light-induced reversible fluorescence for rewritable 2D/3D-encoding information carriers
The stimuli responsive color-shifting properties of fluorescent materials have been used for 2D encoding for information encryption applications but possessing a risk of information leakage. Here, the authors develop shape-memory fluorescent films with reversible fluorescence-shifting and thermadapt shape-memory properties for integrating rewritable 2D/3D encoding in one system.
- Jinhui Huang
- , Yue Jiang
- & Shaobing Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Light-responsive polymers with polarization-dependent deformation are promising material to develop tunable devices usually limited by irreversible dynamic control. Here, the authors use controlled polarization of visible light to produce arbitrary deformations into amorphous composites containing azopolymer microdomains to unlock the next level of complex actuation in soft lightdriven robots.
- David Urban
- , Niccolò Marcucci
- & Emiliano Descrovi
-
Article
| Open Access Twistedly hydrophobic basis with suitable aromatic metrics in covalent organic networks govern micropollutant decontamination
Twistedly hydrophobic basis with suitable aromatic metrics in covalent organic networks govern micropollutant decontamination
The synergetic regulation of the electronic structure and interfacial reaction of covalent organic frameworks (COF) for water purification remains a challenge. Here the authors propose that COFs materials possessing molecular interfaces with ordered π skeletons, suitable pore size, and hydrophilic/hydrophobic channels synergically break through the adsorption energy barrier achieving high removal rates for micropollutants.
- Chencheng Qin
- , Yi Yang
- & Hou Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Aromatized liposomes for sustained drug delivery
Aromatized liposomes for sustained drug delivery
The development of liposome-based drug delivery systems has been hindered by the systemic toxicity and limited duration of effect due to insufficient drug loading and leakage of payload. Here the authors address these issues by designing aromatized liposomes that feature increased drug loading and slowed release compared to conventional liposomes.
- Yang Li
- , Tianjiao Ji
- & Daniel S. Kohane
-
Article
| Open Access Light-oriented 3D printing of liquid crystal/photocurable resins and in-situ enhancement of mechanical performance
Light-oriented 3D printing of liquid crystal/photocurable resins and in-situ enhancement of mechanical performance
Complex computerized geometries can be obtained by additive manufacturing. However, the printing of purely three-dimensional polymer shapes possesses inherent poor mechanical stability. Here, the authors overcome this drawback by the light-driven orientation of liquid crystals to guide the alignment of acrylate prepolymers along the direction parallel to UV light vibrations.
- Xiaolu Sun
- , Shaoyun Chen
- & Dongxian Zhuo
-
Article
| Open Access Growing recyclable and healable piezoelectric composites in 3D printed bioinspired structure for protective wearable sensor
Growing recyclable and healable piezoelectric composites in 3D printed bioinspired structure for protective wearable sensor
Smart monitoring devices with integrated mechanical protection and piezoelectric induction are limited. Here, the authors report a strategy to grow piezoelectric Rochelle salt crystals in 3D-printed cuttlebone-inspired structures to produce smart monitoring devices with integrated mechanical protection and electrical sensing capability.
- Qingqing He
- , Yushun Zeng
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-protection soft fluidic robots with rapid large-area self-healing capabilities
Self-protection soft fluidic robots with rapid large-area self-healing capabilities
The soft fluidic robots designed so far are lacking intelligent self-protection and present poor fluidic power source. Here, the authors report soft fluidic robots that integrate soft electrohydrodynamic pumps, healing electrofluids, actuators and E-skins endowing them with self-sensing, self-judgment, and self-heating behaviours for rapid self-healing.
- Wei Tang
- , Yiding Zhong
- & Jun Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Counteranion-mediated efficient iodine capture in a hexacationic imidazolium organic cage enabled by multiple non-covalent interactions
Counteranion-mediated efficient iodine capture in a hexacationic imidazolium organic cage enabled by multiple non-covalent interactions
The development of efficient adsorbents to capture iodine originating from radioactive wastes is of importance. Here, the authors synthesize hexacationic imidazolium organic cages and study the crucial role of the counter anions for iodine capture and the iodine binding modes at the molecular level on the solid state.
- Jian Yang
- , Shao-Jun Hu
- & Qing-Fu Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent Deborah number-dependent transition from homogeneity to heterogeneity
Divergent Deborah number-dependent transition from homogeneity to heterogeneity
Due to the complexity of living systems, it is challenging to identify the factors influencing the formation of native heterogeneous structures. Here, the authors employ flexible polymer networks with embedded stiff cellulose nanocrystals to simulate heterogeneous core-sheath structures interrelated with the divergence of Deborah number.
- Dan Xu
- , Yang Yang
- & Kai Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Grinding-induced supramolecular charge-transfer assemblies with switchable vapochromism toward haloalkane isomers
Grinding-induced supramolecular charge-transfer assemblies with switchable vapochromism toward haloalkane isomers
The use of macrocycles to develop charge-transfer complexes in the solid state was recently demonstrated. Here, the authors develop an on-off type vapochromic system toward positional bromoalkane isomers by the reassembly and disassembly of charge-transfer complexes between a pillar[5]arene and electron-deficient aromatic guests in the solid state.
- Jia-Rui Wu
- , Gengxin Wu
- & Ying-Wei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Heterostructure particles enable omnidispersible in water and oil towards organic dye recycle
Heterostructure particles enable omnidispersible in water and oil towards organic dye recycle
Dispersion of colloidal particles in water or oil is desired for industrial and environmental applications but it often strongly depends on indispensable assistance of chemical surfactants or introduction of nanoprotrusions onto the particle surface. Here, the authors demonstrate the omnidispersity of hydrophilic-hydrophobic heterostructure particles, synthesized by a surface heterogeneous nanostructuring strategy.
- Yongyang Song
- , Jiajia Zhou
- & Shutao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Smart dynamic hybrid membranes with self-cleaning capability
Smart dynamic hybrid membranes with self-cleaning capability
The performance of membrane desalination of seawater is hampered by fouling. Here the authors develop smart gating hybrid membranes by surface coating with polymer-embedded thermosalient crystals. These membranes enhance pure water flux by over 40% in saltwater desalination by osmotic distillation.
- Elvira Pantuso
- , Ejaz Ahmed
- & Gianluca Di Profio
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral recognition of neutral guests by chiral naphthotubes with a bis-thiourea endo-functionalized cavity
Chiral recognition of neutral guests by chiral naphthotubes with a bis-thiourea endo-functionalized cavity
Chiral receptors with an endo-functionalized cavity for chiral recognition are of interest in the field of molecular recognition. Here, the authors develop chiral naphthotubes containing a bis-thiourea endo-functionalized cavity to effectively recognize neutral chiral molecules with high enantioselectivity.
- Song-Meng Wang
- , Yan-Fang Wang
- & Liu-Pan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Cold-programmed shape-morphing structures based on grayscale digital light processing 4D printing
Cold-programmed shape-morphing structures based on grayscale digital light processing 4D printing
The 3D/4D printing of shape memory polymers to create shape-morphing structures typically goes through a hot programming step possessing limited reconfigurability. Here the authors introduce a cold-programmed grayscale digital light processing-based 3D printing to encode different configurations during the 3D printing of shape-morphing structures.
- Liang Yue
- , Xiaohao Sun
- & H. Jerry Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Nonporous amorphous superadsorbents for highly effective and selective adsorption of iodine in water
Nonporous amorphous superadsorbents for highly effective and selective adsorption of iodine in water
Porous or crystalline materials are generally employed as adsorbents for environmental remediation. Here the authors employ nonporous and amorphous covalent organic superphane cages for aqueous iodine adsorption achieving good selectivity, high adsorption capability and fast kinetics.
- Wei Zhou
- , Aimin Li
- & Qing He
-
Article
| Open Access Stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with tunable thermal and rheological properties
Stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with tunable thermal and rheological properties
Enriching the toolbox of polymers, the design and construction of novel polymers with desired properties and functions remains an attractive topic in polymer chemistry. Here the authors demonstrate rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with rotaxane-branched dendrons attached onto the polymer chains as polymers with attractive dynamic properties.
- Yu Zhu
- , Hanqiu Jiang
- & Hai-Bo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamically controlled multiphase separation of heterogeneous liquid crystal colloids
Thermodynamically controlled multiphase separation of heterogeneous liquid crystal colloids
Phase separation is driven by the component activity, elasticity, or composition of a homogeneous mixture. Here the authors, develop heterogeneous colloidal suspensions exhibiting both liquid-liquid phase separation of polymers and liquid crystal phase separation of nanoparticles controlled by the trade-off between thermodynamics and kinetics.
- Han Tao
- , Carlo Rigoni
- & Guang Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis, structural analysis, and properties of highly twisted alkenes 13,13’-bis(dibenzo[a,i]fluorenylidene) and its derivatives
Synthesis, structural analysis, and properties of highly twisted alkenes 13,13’-bis(dibenzo[a,i]fluorenylidene) and its derivatives
The rotation of a carbon double bond in an alkene can be efficiently accelerated by creating the high strain ground state and stabilizing the transition state of the process. Here, the authors report the synthesis, structures, and properties of several highly twisted alkenes.
- Hao-Wen Kang
- , Yu-Chiao Liu
- & Yao-Ting Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Direct visual observation of pedal motion-dependent flexibility of single covalent organic frameworks
Direct visual observation of pedal motion-dependent flexibility of single covalent organic frameworks
To correlate the microstructure of flexible covalent organic frameworks with their flexibility is challenging. Here, the authors visually track the deformation behaviors of single covalent organic framework particles with dark-field microscopy discovering that their flexibility is dictated by the pedal motion around rigid imine bonds.
- Hongbin Chi
- , Yang Liu
- & Yi He
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric control of olefin isomerization kinetics via remote metal binding and its mechanochemical analysis
Allosteric control of olefin isomerization kinetics via remote metal binding and its mechanochemical analysis
The mechanisms by which changes in local geometries of receptor sites lower activation reaction barriers in electronically uncoupled, remote reaction moieties remain relatively unexplored. Here, the authors demonstrate allosteric acceleration in the thermal isomerization of an alkene triggered by the binding of a metal ion to a remote receptor site.
- Yichen Yu
- , Robert T. O’Neill
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven predictions of complex organic mixture permeation in polymer membranes
Data-driven predictions of complex organic mixture permeation in polymer membranes
Membranes can be used for energy efficient organic liquid mixture separations. Here the authors use machine learning and transport simulations to predict the separation of complex mixtures such as crude oils by any linear polymer membrane.
- Young Joo Lee
- , Lihua Chen
- & Ryan P. Lively
-
Article
| Open Access Effector-dependent structural transformation of a crystalline framework with allosteric effects on molecular recognition ability
Effector-dependent structural transformation of a crystalline framework with allosteric effects on molecular recognition ability
Porous crystals with molecular recognition sites in the inner pores are promising for achieving functional control, where the local binding of effectors triggers a distortion which propagates throughout the structure. Here the authors report that the structure of a porous molecular crystal can be allosterically controlled by local adsorption of effectors within low-symmetry nanochannels with multiple molecular recognition sites.
- Ryunosuke Hayashi
- , Shohei Tashiro
- & Mitsuhiko Shionoya
-
Article
| Open Access A photochemical method to evidence directional molecular motions
A photochemical method to evidence directional molecular motions
Light driven synthetic molecular motors represent crucial building blocks for advanced molecular machines and their applications but the development of very fast motors remains challenging. Here the authors restrict fast molecular motor rotations and force them to proceed in two separate rotation-photoequilibria enabling them to elucidate the directionality of the motion.
- Benjamin Lukas Regen-Pregizer
- , Ani Ozcelik
- & Henry Dube
-
Article
| Open Access Twisting, untwisting, and retwisting of elastic Co-based nanohelices
Twisting, untwisting, and retwisting of elastic Co-based nanohelices
The reversible transformation of a nanohelix is one of the most exquisite and important phenomenon in nature but nanomaterials usually fail to twist into helical crystals or untwist. Here, the authors report a reciprocal effect between molecular geometry and crystal structure which triggers a twisting-untwisting-retwisting cycle for tri-cobalt salicylate hydroxide hexahydrate.
- Wei Du
- , Feng Gao
- & Qingyi Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of propenone-linked covalent organic frameworks via Claisen-Schmidt reaction for photocatalytic removal of uranium
Synthesis of propenone-linked covalent organic frameworks via Claisen-Schmidt reaction for photocatalytic removal of uranium
The synthesis of sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks is limited to a few reactions and monomers due to the poor irreversibility of carbon double bonds. Here the authors synthesize propenone-linked covalent organic frameworks for the removal of radionuclide uranium from mine wastewater samples.
- Cheng-Peng Niu
- , Cheng-Rong Zhang
- & Jian-Ding Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry-breaking dynamics in a tautomeric 3D covalent organic framework
Symmetry-breaking dynamics in a tautomeric 3D covalent organic framework
Controlling the ketoenamine-enolimine tautomerism and correlating their structure to photoelectronic properties remains challenging in organic solids. Here, the authors show tautomerization in a crystalline dynamic 3D covalent organic framework (dynaCOF) through host-guest interactions leading to reversible framework deformation accompanied by chromic effects which can be used in chemosensing.
- Yangyang Xu
- , Tu Sun
- & Yue-Biao Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The host–guest inclusion driven by host-stabilized charge transfer for construction of sequentially red-shifted mechanochromic system
The host–guest inclusion driven by host-stabilized charge transfer for construction of sequentially red-shifted mechanochromic system
The understanding of the structure-property relationship of mechanochromic luminescent molecules remains challenging. Here, the authors elucidate the effect of host-guest interactions on the mechanochromic properties of organic molecules.
- Dongdong Sun
- , Yong Wu
- & Simin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating the proximity effect of heterocycle-containing AIEgens
Regulating the proximity effect of heterocycle-containing AIEgens
Proximity effect (PE) can impact the behaviour of heterocyclic luminogens, but is rarely used to manipulate the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) related properties. Here, the authors systematically illustrate the impacts of PE and AIE on luminescent behaviors.
- Jianyu Zhang
- , Yujie Tu
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric transformation of achiral gold nanoclusters with negative nonlinear dependence between chiroptical activity and enantiomeric excess
Asymmetric transformation of achiral gold nanoclusters with negative nonlinear dependence between chiroptical activity and enantiomeric excess
Atomically precise metal nanoclusters provide an ideal platform for studying chirality at the nanoscale. Here, the authors use a phosphoramidite ligand as a chiral inducer to asymmetrically transform achiral into chiral gold nanoclusters with negative nonlinear CD-ee dependence.
- Chang Liu
- , Yan Zhao
- & Man-Bo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Collective photothermal bending of flexible organic crystals modified with MXene-polymer multilayers as optical waveguide arrays
Collective photothermal bending of flexible organic crystals modified with MXene-polymer multilayers as optical waveguide arrays
Organic crystals represent potential alternatives to silicon dioxide due to their high flexibility and controllable properties. Here, the authors prepared a hybrid organic crystal material that responds mechanically to infrared light.
- Xuesong Yang
- , Linfeng Lan
- & Hongyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Trichalcogenasupersumanenes and its concave-convex supramolecular assembly with fullerenes
Trichalcogenasupersumanenes and its concave-convex supramolecular assembly with fullerenes
Synthesis of buckybowls has remained challenging due to the inherent high strain induced by the curvature. Herein, the authors report the synthesis of two bowl-shaped polycyclic aromatics with three chalcogen atoms and three methylene groups embedded at the bay regions of hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene and demonstrate guest host complexation with trithiasupersumanene.
- Yixun Sun
- , Xin Wang
- & Junfa Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Enantioselective synthesis of chiral quinohelicenes through sequential organocatalyzed Povarov reaction and oxidative aromatization
Enantioselective synthesis of chiral quinohelicenes through sequential organocatalyzed Povarov reaction and oxidative aromatization
Heterohelicenes are of increasing importance in materials science but organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of these molecules remains challenging. Here, the authors synthesize enantioenriched 1-(3-indol)-quino[n]helicenes through chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed Povarov reaction followed by oxidative aromatization and explore the photochemical and electrochemical properties of these compounds.
- Chengwen Li
- , Ying-Bo Shao
- & Xin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Pore partition in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks
Pore partition in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks
The development of ultramicroporous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) remains a daunting challenge. Here, the authors report a pore partition strategy, which allows for the segmentation of mesopores of COFs into multiple uniform ultramicroporous domains.
- Xiaoyi Xu
- , Xinyu Wu
- & Ning Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A porous metal-organic cage liquid for sustainable CO2 conversion reactions
A porous metal-organic cage liquid for sustainable CO2 conversion reactions
Preparation of porous liquids are fluids with the permanent porosity still requires complicated and tedious use of porous hosts and bulky liquids. Here, the authors develop a facile method to produce a porous metal-organic cage liquid by self-assembly of long polyethylene glycolimidazolium chain functional linkers, calixarene molecules and Zn ions.
- Chang He
- , Yu-Huang Zou
- & Yuan-Biao Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Reversibly growing crosslinked polymers with programmable sizes and properties
Reversibly growing crosslinked polymers with programmable sizes and properties
Growth constitutes a powerful method to post-modulate materials’ structures and functions without compromising their mechanical performance for sustainable use, but the process is irreversible. To address this issue, the authors here report a growing-degrowing strategy that enables thermosetting materials to either absorb or release components for continuously changing their sizes, shapes, compositions, and a set of properties simultaneously.
- Xiaozhuang Zhou
- , Yijun Zheng
- & Jiaxi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient-conditions spinning of functional soft fibers via engineering molecular chain networks and phase separation
Ambient-conditions spinning of functional soft fibers via engineering molecular chain networks and phase separation
Producing functional soft fibers via existing spinning methods is environmentally and economically costly due to the complexity of spinning equipment, involvement of copious solvents, intensive consumption of energy. Here, the authors report a nonsolvent vapor-induced phase separation spinning approach under ambient conditions, which resembles the native spider silk fibrillation’.
- Songlin Zhang
- , Mengjuan Zhou
- & Swee Ching Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-controlled magnetism in 2D molecular layers
Pressure-controlled magnetism in 2D molecular layers
Long-range magnetic ordering of two-dimensional crystals can be sensitive to interlayer coupling, enabling the effective control of interlayer magnetism. Here, the authors report the pressure-controlled interlayer magnetic coupling of chromiumpyrazine coordinated magnets.
- Yulong Huang
- , Arjun K. Pathak
- & Shenqiang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanosensitive non-equilibrium supramolecular polymerization in closed chemical systems
Mechanosensitive non-equilibrium supramolecular polymerization in closed chemical systems
Chemical fuel-driven supramolecular systems have been developed showing out of-equilibrium functions such as transient gelation and oscillations but these systems suffer from undesired waste accumulation and they function only in open systems. Here, the authors we report non-equilibrium supramolecular polymerizations in a closed system, which is built by viologens and pyranine in the presence of hydrazine hydrate.
- Xianhua Lang
- , Yingjie Huang
- & Hui Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic polymerization of enantiomeric L−3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into films with enhanced rigidity and stability
Enzymatic polymerization of enantiomeric L−3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine into films with enhanced rigidity and stability
L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine plays an important role in living system. Here, the authors investigated the effect of the molecular chirality of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine on the improved structural and thermal stability of self-assembled films by tyrosinase-induced oxidative polymerization.
- Yuhe Shen
- , Rongxin Su
- & Wei Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-triggered full-color circularly polarized luminescence based on photonic capsules for multilevel information encryption
Photo-triggered full-color circularly polarized luminescence based on photonic capsules for multilevel information encryption
Phototunable full-color circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) features large storage density which is important for the field of information encryption and decryption. Here, the authors present a device-friendly solid film with color-tunability by employing Förster resonance energy transfer among a chiral donor and achiral molecular switches in a liquid crystal photonic capsules.
- Siyang Lin
- , Yuqi Tang
- & Quan Li
-
Article
| Open Access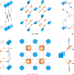 Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with pto and mhq-z topologies based on Tri- and tetratopic linkers
Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with pto and mhq-z topologies based on Tri- and tetratopic linkers
The development of three-dimensional (3D) covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with novel topologies is of both fundamental and practical interest but the construction of highly crystalline 3D COF remains challenging. Here, the authors report highly crystalline 3D COFs with pto and mhq-z topologies by rationally selecting rectangular-planar and trigonal-planar building blocks with appropriate conformational strains.
- Dongyang Zhu
- , Yifan Zhu
- & Rafael Verduzco
-
Article
| Open Access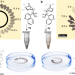 Unidirectional rotation of micromotors on water powered by pH-controlled disassembly of chiral molecular crystals
Unidirectional rotation of micromotors on water powered by pH-controlled disassembly of chiral molecular crystals
‘Molecular motors, fuelled by various physical and chemical means, can perform asymmetric linear and rotary motions that are inherently related to their asymmetric shapes. Here, the authors describe silver-organic micro-complexes of random shapes that exhibit macroscopic unidirectional rotation on water surface through the asymmetric release of cinchonine or cinchonidine chiral molecules.
- Itai Carmeli
- , Celine M. Bounioux
- & Shachar E. Richter
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient selective removal of uremic toxin precursor by olefin-linked covalent organic frameworks for nephropathy treatment
Efficient selective removal of uremic toxin precursor by olefin-linked covalent organic frameworks for nephropathy treatment
Indoxyl sulfate is a key risk factor in the progression of chronic kidney disease, but cannot be removed from the blood by hemodialysis. Here, the authors report the use of a covalent organic framework for the removal of indoxyl sulfate precursor from the intestine.
- Jinxia Wei
- , Rui Li
- & Yao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access [2,2] Paracyclophanes-based double helicates for constructing artificial light-harvesting systems and white LED device
[2,2] Paracyclophanes-based double helicates for constructing artificial light-harvesting systems and white LED device
The construction of efficient artificial lightharvesting (ALH) systems is of vital importance in utilizing solar energy. Here, the authors report the non-covalent syntheses of double helicates by metalcoordination interaction and their applications in ALHSs and white LED device
- Zhe Lian
- , Jing He
- & Hua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access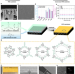 Recovery of homogeneous photocatalysts by covalent organic framework membranes
Recovery of homogeneous photocatalysts by covalent organic framework membranes
Transition metal-based homogenous photocatalysts are important in organic synthesis, but the metals used can be rare and immobilization of the catalysts for recycling is challenging. Here, the authors report the recovery of such catalysts using covalent organic framework membranes with tuneable pore sizes.
- Hao Yang
- , Jinhui Xu
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Switching imidazole reactivity by dynamic control of tautomer state in an allosteric foldamer
Switching imidazole reactivity by dynamic control of tautomer state in an allosteric foldamer
Molecular biology achieves control over complex reaction networks by means of molecular systems that translate a chemical input into an orthogonal chemical output but the application of dynamic foldamers has been limited by the restriction to stereochemical changes that produce spectroscopic signals. Here, the authors present an artificial molecular translation device that converts a chemical input into an unrelated chemical output.
- David P. Tilly
- , Jean-Paul Heeb
- & Jonathan Clayden
-
Article
| Open Access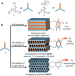 Hierarchical porous photosensitizers with efficient photooxidation
Hierarchical porous photosensitizers with efficient photooxidation
Photosensitizers (PS) with nano- or micro-sized pore provide a great promise in the conversion of light energy into chemical fuel but pore deformation and blocking often decreases the catalytic efficiency. Here, the authors prepare an ordered porous PSs by cross-linking hierarchical porous assemblies of hydrogen donating PSs and functionalized acceptors.
- Yajun Fang
- , Yuntian Yang
- & Zhegang Huang

 In situ observation of a stepwise [2 + 2] photocycloaddition process using fluorescence spectroscopy
In situ observation of a stepwise [2 + 2] photocycloaddition process using fluorescence spectroscopy