Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Penning-trap measurement of the Q value of electron capture in 163Ho for the determination of the electron neutrino mass
Penning-trap measurement of the Q value of electron capture in 163Ho for the determination of the electron neutrino mass
Electron capture in 163Ho can be used to determine the electron neutrino mass. The Q value of this process is crucial for the evaluation of the systematic uncertainty in such a measurement, and a 50-fold improvement is now reported.
- Christoph Schweiger
- , Martin Braß
- & Klaus Blaum
-
News & Views |
 Pathway to cool hot molecules
Pathway to cool hot molecules
A promising pathway towards the laser cooling of a molecule containing a radioactive atom has been identified. The unique structure of such a molecule means that it can act as a magnifying lens to probe fundamental physics.
- Steven Hoekstra
-
Article |
 Precision spectroscopy and laser-cooling scheme of a radium-containing molecule
Precision spectroscopy and laser-cooling scheme of a radium-containing molecule
Measurements of the rovibronic structure of radium monofluoride molecules allow the identification of a laser cooling scheme. This will enable precise tests of fundamental physics, such as searches for parity or time-reversal symmetry violation.
- S. M. Udrescu
- , S. G. Wilkins
- & C. Zülch
-
Article
| Open Access Mass measurements show slowdown of rapid proton capture process at waiting-point nucleus 64Ge
Mass measurements show slowdown of rapid proton capture process at waiting-point nucleus 64Ge
Rapid proton capture nucleosynthesis stalls at waiting-point nuclides, including 64Ge. Precision mass measurements in the vicinity of this nuclide influence state-of-the-art calculations of X-ray bursts from accreting neutron stars.
- X. Zhou
- , M. Wang
- & S. Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Modified in medium
Modified in medium
The strong interaction is modified in the presence of nuclear matter. An experiment has now quantified with high precision and accuracy the reduction of the order parameter of the system’s chiral symmetry, which is partially restored.
- Sean Freeman
-
Article |
 Chiral symmetry restoration at high matter density observed in pionic atoms
Chiral symmetry restoration at high matter density observed in pionic atoms
In quantum chromodynamics, the condensation of quark–antiquark pairs breaks the chiral symmetry of vacuum. Experiments with pionic tin atoms demonstrate that the symmetry is partially restored at high densities.
- Takahiro Nishi
- , Kenta Itahashi
- & Koichi Yoshida
-
News & Views |
 A route to greener Big Science
A route to greener Big Science
By recovering energy from a relativistically accelerated electron beam in a multiturn configuration, a reduction of radiofrequency power has been demonstrated. This is a milestone toward more efficient and better performing accelerators.
- Peter Williams
-
Article |
 Realization of a multi-turn energy recovery accelerator
Realization of a multi-turn energy recovery accelerator
By combining energy recovery technology and a multi-turn accelerating scheme in a linear accelerator, high-power beams can be achieved with considerably reduced energy consumption.
- Felix Schliessmann
- , Michaela Arnold
- & Simon Weih
-
News & Views |
 The study of the journey of cosmic antimatter
The study of the journey of cosmic antimatter
A potential observation of low-energy antihelium-3 nuclei would have profound impacts on our understanding of the Galaxy. Experiments at particle colliders help us understand how cosmic antimatter travels over long distances before reaching Earth.
- Aihong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of anti-3He nuclei absorption in matter and impact on their propagation in the Galaxy
Measurement of anti-3He nuclei absorption in matter and impact on their propagation in the Galaxy
Measurements of the inelastic cross section of anti-3He allow the estimation of the transparency of the Milky Way to the propagation of these light antinuclei produced in either cosmic-ray collisions or annihilation of dark-matter particles.
- S. Acharya
- , D. Adamová
- & N. Zurlo
-
Research Briefing |
 Testing the theory of the strong force by measuring proton spin polarizabilities
Testing the theory of the strong force by measuring proton spin polarizabilities
Measurements of a transversely polarized target were used to probe the spin structure of the proton in the low-energy region where the interactions between the quarks cannot be ignored. These results provide a benchmark for testing our understanding of the strong force.
-
Article |
 Proton spin structure and generalized polarizabilities in the strong quantum chromodynamics regime
Proton spin structure and generalized polarizabilities in the strong quantum chromodynamics regime
Measurements of the proton’s generalized spin polarizabilities provide discriminating power between effective descriptions of the strong interaction at low energy.
- D. Ruth
- , R. Zielinski
- & X. Zheng
-
News & Views |
 A historic match for nuclei and neutron stars
A historic match for nuclei and neutron stars
Bayesian history matching is a statistical tool used to calibrate complex numerical models. Now, it has been applied to first-principles simulations of several nuclei, including 208Pb, whose properties are linked to the interior of neutron stars.
- Arnau Rios
-
Article
| Open Access Ab initio predictions link the neutron skin of 208Pb to nuclear forces
Ab initio predictions link the neutron skin of 208Pb to nuclear forces
Predictions of the properties of 208Pb from first principles augmented by statistical learning techniques reproduce those seen in experiments but rule out very thick neutron skins.
- Baishan Hu
- , Weiguang Jiang
- & Ian Vernon
-
Editorial |
 Accelerate to the next level
Accelerate to the next level
The merits of conventional particle accelerators range from fundamental science to applications like radiotherapy. Plasma-based accelerators are getting up to speed and may overtake conventional ones in the near future.
-
-
News & Views |
 Still too small to be measured
Still too small to be measured
Although the mass of the electron antineutrino is still eluding direct measurement, the KATRIN experiment with its huge spectrometer has pushed the sensitivity below a billionth of the proton mass.
- Angelo Nucciotti
-
Article
| Open Access Direct neutrino-mass measurement with sub-electronvolt sensitivity
Direct neutrino-mass measurement with sub-electronvolt sensitivity
In its second measurement campaign, the Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino experiment achieved a sub-electronvolt sensitivity on the effective electron anti-neutrino mass.
- M. Aker
- , A. Beglarian
- & G. Zeller
-
-
-
News & Views |
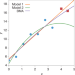 No need to decide
No need to decide
To test the validity of theoretical models, the predictions they make must be compared with experimental data. Instead of choosing one model out of many to describe mass measurements of zirconium, Bayesian statistics allows the averaging of a variety of models.
- Alessandro Pastore
-
Article |
 Precision mass measurement of lightweight self-conjugate nucleus 80Zr
Precision mass measurement of lightweight self-conjugate nucleus 80Zr
High-precision mass measurements of exotic zirconium nuclei are reported, and reveal a double-shell closure for the deformed nucleus 80Zr, which is more strongly bound than previously thought.
- A. Hamaker
- , E. Leistenschneider
- & I. T. Yandow
-
-
News & Views |
 News on the neutron structure
News on the neutron structure
Precise measurements of the annihilation of an electron–positron pair into a neutron–antineutron pair allow us to take a look inside the neutron to better understand its complex structure.
- Galina Pakhlova
-
Letter |
 Oscillating features in the electromagnetic structure of the neutron
Oscillating features in the electromagnetic structure of the neutron
Form factors encode the structure of nucleons. Measurements from electron–positron annihilation at BESIII reveal an oscillating behaviour of the neutron electromagnetic form factor, and clarify a long-standing photon–nucleon interaction puzzle.
- M. Ablikim
- , M. N. Achasov
- & J. H. Zou
-
Comment |
 Young African universities take the lead
Young African universities take the lead
Having long played the role of collaborators with other, more renowned, institutions, historically disadvantaged South African universities are now challenging the status quo — and emerging as leaders.
- José Nicolás Orce
- & Sifiso Ntshangase
-
News & Views |
 Close to the edge
Close to the edge
The tin isotope 100Sn is key to understanding nuclear stability, but little is known about its properties. Precision measurements of closely related indium isotopes have now pinned down its mass.
- Nunzio Itaco
-
Letter
| Open Access Mass measurements of 99–101In challenge ab initio nuclear theory of the nuclide 100Sn
Mass measurements of 99–101In challenge ab initio nuclear theory of the nuclide 100Sn
Accurate mass measurements of the indium isotopes adjacent to the doubly magic 100Sn provide critical benchmarks for ab initio theory, which withstands the challenge.
- M. Mougeot
- , D. Atanasov
- & K. Zuber
-
News & Views |
 Nucleon spins surprise
Nucleon spins surprise
Recent measurements of observables related to proton and neutron spin properties at low energies are in disagreement with the available theoretical predictions, and continue to challenge nuclear experimentalists and theorists alike.
- Mohammad W. Ahmed
-
Letter |
 Measurement of the generalized spin polarizabilities of the neutron in the low-Q2 region
Measurement of the generalized spin polarizabilities of the neutron in the low-Q2 region
Measurements of observables sensitive to the neutron’s spin precession are extended to a regime that probes distances of the size of the nucleon. They are found to disagree with predictions from chiral effective field theory.
- Vincent Sulkosky
- , Chao Peng
- & Lingyan Zhu
-
Article |
 Measurement of the proton spin structure at long distances
Measurement of the proton spin structure at long distances
Measurements of the proton’s spin structure in experiments scattering a polarized electron beam off polarized protons in regions of low momentum transfer squared test predictions from chiral effective field theory of the strong interaction.
- X. Zheng
- , A. Deur
- & Z. W. Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Knock-out interpretability
Knock-out interpretability
A detailed analysis of a nucleon-knockout experiment has put forward a methodological roadmap for overcoming ambiguities in the interpretation of the data — promising access to the nuclear wave functions in unstable nuclei.
- Jan Ryckebusch
-
Letter |
 Unperturbed inverse kinematics nucleon knockout measurements with a carbon beam
Unperturbed inverse kinematics nucleon knockout measurements with a carbon beam
Initial- and final-state interactions distort the kinematics in particle knockout scattering experiments, complicating their interpretation. These effects are suppressed by detecting 11B nuclei in quasi-free scattering of 12C ions from hydrogen.
- M. Patsyuk
- , J. Kahlbow
- & M. Zuev
-
News & Views |
 The case of the exotic isotopes
The case of the exotic isotopes
With increasing neutron number, the size of a nucleus grows, subject to subtle effects that act as fingerprints of its internal structure. A fresh look at potassium calls for theory to decipher the details.
- Gianluca Colò
-
Letter
| Open Access Charge radii of exotic potassium isotopes challenge nuclear theory and the magic character of N = 32
Charge radii of exotic potassium isotopes challenge nuclear theory and the magic character of N = 32
The charge radii of potassium isotopes up to 52K are measured, and show no sign of magicity at 32 neutrons as previously suggested in calcium. The observations are interpreted with coupled cluster and density functional theory calculations.
- Á. Koszorús
- , X. F. Yang
- & S. G. Wilkins
-
News & Views |
 Contact between nucleons
Contact between nucleons
The contact formalism describes short-range correlations, which play a crucial role in nuclear systems. Initially introduced for ultracold atoms, its generalization to the nuclear case was now validated by ab initio calculations.
- Michael Urban
-
Letter |
 Many-body factorization and position–momentum equivalence of nuclear short-range correlations
Many-body factorization and position–momentum equivalence of nuclear short-range correlations
Effects of nucleon–nucleon correlations are studied with the generalized contact formalism and ab initio quantum Monte Carlo calculations. For nuclei from deuteron to 40Ca, the many-body nuclear wave function is shown to factorize at short distances.
- R. Cruz-Torres
- , D. Lonardoni
- & O. Hen
-
Article |
 Underground test of gravity-related wave function collapse
Underground test of gravity-related wave function collapse
The radiation emission rate from gravity-related wave function collapse is calculated and the results of a dedicated experiment at the Gran Sasso laboratory are reported, ruling out the natural parameter-free version of the Diósi–Penrose model.
- Sandro Donadi
- , Kristian Piscicchia
- & Angelo Bassi
-
Letter
| Open Access Evidence for quark-matter cores in massive neutron stars
Evidence for quark-matter cores in massive neutron stars
The cores of neutron stars could be made of hadronic matter or quark matter. By combining first-principles calculations with observational data, evidence for the presence of quark matter in neutron star cores is found.
- Eemeli Annala
- , Tyler Gorda
- & Aleksi Vuorinen
-
Article |
 Direct measurement of the intrinsic electric dipole moment in pear-shaped thorium-228
Direct measurement of the intrinsic electric dipole moment in pear-shaped thorium-228
The intrinsic dipole moment of 228Th is reported, from which the degree of the nucleus’s octupole deformation is estimated, suggesting that 229Th and 229Pa may be suitable candidates for the search for a permanent atomic electric dipole moment.
- M. M. R. Chishti
- , D. O’Donnell
- & J. F. Smith
-
Letter
| Open Access Measurement and microscopic description of odd–even staggering of charge radii of exotic copper isotopes
Measurement and microscopic description of odd–even staggering of charge radii of exotic copper isotopes
Isotopes with an odd number of neutrons are usually slightly smaller in size than their even-neutron neighbours. In charge radii of short-lived copper isotopes, a reduction of this effect is observed when the neutron number approaches fifty.
- R. P. de Groote
- , J. Billowes
- & X. F. Yang
-
Letter |
 Thermodynamics of hot strong-interaction matter from ultrarelativistic nuclear collisions
Thermodynamics of hot strong-interaction matter from ultrarelativistic nuclear collisions
The quark–gluon plasma, in which quarks and gluons are deconfined, is a transient state created in collisions of heavy nuclei. By defining an effective temperature, this temperature and the system’s entropy density and speed of sound are determined.
- Fernando G. Gardim
- , Giuliano Giacalone
- & Jean-Yves Ollitrault
-
Letter |
 Measurement of the mass difference and the binding energy of the hypertriton and antihypertriton
Measurement of the mass difference and the binding energy of the hypertriton and antihypertriton
The STAR collaboration reports a measurement of the mass difference and binding energy of the hypertriton and its antiparticle. This work constrains the hyperon–nucleon interaction and allows us to test the CPT theorem in a nucleus with strangeness.
- J. Adam
- , L. Adamczyk
- & M. Zyzak
-
-
Article |
 Deeply virtual Compton scattering off the neutron
Deeply virtual Compton scattering off the neutron
The internal structure of the neutron has now been probed by highly energetic photons scattering off it. Combined with previous results for protons, these measurements reveal the contributions of quark flavours to the nucleon structure.
- M. Benali
- , C. Desnault
- & P. Zhu
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Nearly perfect quark–gluon fluid
Nearly perfect quark–gluon fluid
A statistical analysis of data from ultra-relativistic heavy-ion collisions has uncovered the specific viscosities of the quark–gluon plasma — suggesting that the hottest matter in the current Universe behaves like a near-perfect fluid.
- Kari J. Eskola
-
Letter |
 Bayesian estimation of the specific shear and bulk viscosity of quark–gluon plasma
Bayesian estimation of the specific shear and bulk viscosity of quark–gluon plasma
As the quark–gluon plasma is a short-lived state of matter, its properties cannot be measured directly. A Bayesian parameter estimation method now provides a reliable estimation of the temperature-dependent specific shear and bulk viscosities.
- Jonah E. Bernhard
- , J. Scott Moreland
- & Steffen A. Bass

 Mass difference measurements help to determine the neutrino mass
Mass difference measurements help to determine the neutrino mass A slow burn
A slow burn Lead signatures
Lead signatures The case for cold cases
The case for cold cases